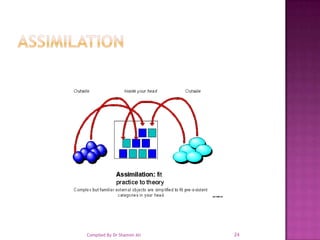
The document discusses cognitive theory as it pertains to language learning, emphasizing the unique qualities of human language that distinguish it from animal communication. It explores key concepts from theorists like Jean Piaget, Wolfgang Kohler, and Edward Tolman, outlining the cognitive processes involved in acquiring language and the impact of prior knowledge and schemas on learning. Additionally, it highlights the importance of teaching strategies that empower learners to manage their own learning processes.