This document discusses aircraft intake aerodynamics, focusing on subsonic and transonic intake flows. For subsonic intakes, it examines types of intakes, approximate theories of frictional losses, pressure recovery characteristics, plenum chambers, and propeller turbine engines. It finds total pressure loss is from approach and duct losses, corrected for compressibility. For transonic flows, total losses include approach, duct losses corrected for compressibility, and shock losses. The goal of intake design is to provide air to the engine without suffocation while minimizing total pressure losses.













![5.6 Limiting Contraction Ratio
If we combine case (a) and case (b) to find limiting value of contraction ratio (At/Ac), then the forward shock would
have to reach entry plane at same time, when flow at throat reaches Mt=1. If ratio is less than limiting value, than case
(b) would be applied and flow would not be started. Mw ∞ being the subsonic mach number after shock.
( 1)/2( 1)
w 2
w
* 1
( ) M ( )
( 1)M 2wM
t
c
AA
AA
(5.31)
Substituting the value of Mw ∞ from normal shock equation (5.3), we get
1/2 1/( 1)
lim 2 2
1 2 2 1
( )
1 ( 1) 1 ( 1)
t
c
A
A M M
(5.32)
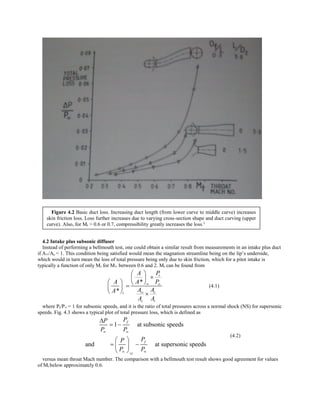
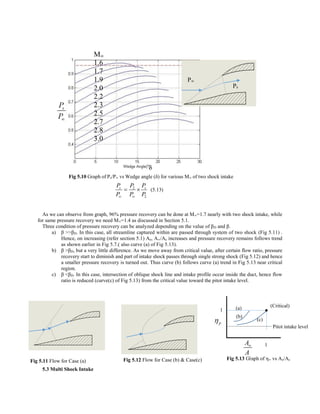
The graph Fig 5.22 of limiting contraction ratio has been drawn with the help of equation (5.32) and of A*/A from
equation (5.31) with matlab code stated in Appendix 5.5. It seems that χ tends to 0.6 as M∞ tends to ∞. Also the
idealized full internal sonic area relation has been plotted in same graph.
Consider Fig 5.19, consider normal shock has been swallowed up and intake has been started, if we reduce the exit
area, then back pressure will increase causing the shock to move forward toward the throat and hence decreasing its
mach number, hence maximum pressure recovery can be done at throat will stable shock.
APPENDICES
Appendix 2.1
function loss()
clear all
close all
clc
u=0:0.01:3;
ICFd=[0.14 0.11 0.08 0.05];
JCFa=[0.010 0.021 0.033 0.054];
axes('FontSize', 18)
hold all
A*/A
------------- ᵡ
Fig 5.22 Limiting Contraction Ratio and A*/A vs M∞](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aircraftintakeaerodynamics-140502134540-phpapp01/85/Aircraft-intake-aerodynamics-21-320.jpg)
![for i=1:4
ploss(:, i) = ICFd(i) + JCFa(i).*u.^3;
plot(u, ploss(:, i), '--')
end
xlabel('mu', 'FontSize', 18)
ylabel('DeltaP/qc', 'FontSize', 18)
title('Loss vs mu', 'FontSize', 20)
legend('0 degree', '30 degrees', '40 degrees', '52 degrees')
end
Appendix 4.1
function lip()
clear all
close all
clc
g = 1.4;
M1 = 0:0.001:0.7;
Minf = [0.115 0.166 0.237 0.330];
t1 = 1+(g-1)*M1.^2/2;
tinf = 1+(g-1)*Minf.^2/2;
l1 = 1-(t1(91:701)/tinf(1)).^((g+1)/(2*g-2))./((1+g*M1(91:701).^2)
.*(tinf(1)./t1(91:701)).^0.5-g*M1(91:701)*Minf(1));
l2 = 1-(t1(181:701)/tinf(2)).^((g+1)/(2*g-2))./((1+g*M1(181:701).^2)
.*(tinf(2)./t1(181:701)).^0.5-g*M1(181:701)*Minf(2));
l3 = 1-(t1(241:701)/tinf(3)).^((g+1)/(2*g-2))./((1+g*M1(241:701).^2)
.*(tinf(3)./t1(241:701)).^0.5-g*M1(241:701)*Minf(3));
l4 = 1-(t1(301:701)/tinf(4)).^((g+1)/(2*g-2))./((1+g*M1(301:701).^2)
.*(tinf(4)./t1(301:701)).^0.5-g*M1(301:701)*Minf(4));
axes('FontSize', 18)
plot(M1(91:701), l1, M1(181:701), l2, M1(241:701), l3, M1(301:701), l4)
xlabel('M_1', 'FontSize', 18)
ylabel('DeltaP/P_i_n_f_i_n_i_t_y', 'FontSize', 18)
title('Loss vs M_1', 'FontSize', 20)
legend('M_i_n_f_i_n_i_t_y=0.115', 'M_i_n_f_i_n_i_t_y=0.166',
'M_i_n_f_i_n_i_t_y=0.237', 'M_i_n_f_i_n_i_t_y=0.330')
end
Appendix 5.1
function M1_net=normalshock(Pr_net)
%Pr_net=pressure recovery for which system need to be designed
M1=linspace(1,4,100);
r=1.4;
pr=zeros(1,100);%static pressure ratio pr=p2/p1
Pr=zeros(1,100);%stagnation pressure ratio Pr=P2/P1
M2=zeros(1,100);
for i=1:100
pr(i)=1+(2*r/(r+1)*(M1(i)^2-1));
M2(i)=sqrt((1+(r-1)/2*M1(i)^2)/(r*M1(i)^2-(r-1)/2));
Pr(i)=((1+(r-1)/2*M2(i)^2)^(r/(r-1)))*pr(i)/((1+(r-1)/2*M1(i)^2)^(r/(r-
1)));
end
M1_net=1.2; %initial guess
M1_net=fsolve(@(M1)mach1(M1,Pr_net),M1_net);
plot([1 4],[Pr_net Pr_net],'--cyan',[M1_net M1_net],[0 1],'--r')
hold on
plot(M1,M2,M1,Pr)
xlabel('M1')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aircraftintakeaerodynamics-140502134540-phpapp01/85/Aircraft-intake-aerodynamics-22-320.jpg)
![ylabel('M2 & P2/P1')
grid
end
Appendix 5.2
function fun=mach1(M1,Pr)
r=1.4;
fun=Pr-((1+(r-1)/2*(sqrt((1+(r-1)/2*M1^2)/(r*M1^2-(r-1)/2)))^2)^(r/(r-
1)))*(1+(2*r/(r+1)*(M1^2-1)))/((1+(r-1)/2*M1^2)^(r/(r-1)));
end
Appendix 5.3
function Pr=obliqueshock()
n1=100;
th1=linspace(.1,60,n1);
n2=10;
M1=linspace(1.6,3,n2);
th2(1:n1)=th1(1:n1)*3.14/180;
r=1.4;
b1=zeros(n2,n1);
Pr=zeros(n2,n1);
for i=1:n2
m1=M1(i);
for j=1:n1
th=th2(j);
b1(i,j)=fsolve(@(b)betashock(b,m1,th),th);
b=b1(i,j);
m2=sqrt((1+(m1^2*(sin(b)^2)*(r-1)/2))/(sin(b-
th)^2)/(r*m1^2*(sin(b)^2)-(r-1)/2));
pr1=1+(2*r/(r+1)*((m1*sin(b))^2-1)); %p2/p1
Pr1=((1+(r-1)/2*m2^2)^(r/(r-1)))*pr1/((1+(r-1)/2*m1^2)^(r/(r-1)));
%P2/P1
m3=sqrt((1+(r-1)/2*m2^2)/(r*m2^2-(r-1)/2));
pr2=1+(2*r/(r+1)*(m2^2-1)); %p3/p2
Pr2=((1+(r-1)/2*m3^2)^(r/(r-1)))*pr2/((1+(r-1)/2*m2^2)^(r/(r-1)));
%P3/P2
Pr(i,j)=Pr1*Pr2; %P3/P1
end
for i=1:n2
plot(th1(1:1.6*M1(i)*10),Pr(i,1:1.6*M1(i)*10))
hold on
end
plot([0 30],[.96 .96],'--r')
xlabel('Wedge Angle')
ylabel('Ps/P1')
grid
Appendix 5.4
function fun=betashock(b,m1,th)
r=1.4;
fun=tan(th)-2*cot(b)*(m1^2*(sin(b))^2-1)/(m1^2*(r+cos(2*b))+2);
end
Appendix 5.5
function isentropic()
n2=100;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aircraftintakeaerodynamics-140502134540-phpapp01/85/Aircraft-intake-aerodynamics-23-320.jpg)
![M1=linspace(1,5,n2);
M11=linspace(1.5,5,n2);
r=1.4;
v1=zeros(1,n2);
v2=zeros(1,n2);
for i=1:n2
m1=M1(i);
v1(i)=sqrt((r+1)/(r-1))*atan(sqrt((r+1)/(r-1)*(m1^2-1)))-atan(sqrt(m1^2-
1));
m2=1.4;
v2(i)=-sqrt((r+1)/(r-1))*atan(sqrt((r+1)/(r-1)*(m1^2-1)))+atan(sqrt(m1^2-
1))+sqrt((r+1)/(r-1))*atan(sqrt((r+1)/(r-1)*(m2^2-1)))-atan(sqrt(m2^2-1));
end
v1(1,:)=180/3.14*v1(1,:);
v2(1,:)=180/3.14*v2(1,:);
plot(M1,v1,M11,v2)
xlabel('Mach Number(M1)')
ylabel('Turn Angle')
grid
REFERENCES
[1]. J. Seddon & E.L.Goldsmith, Revised 1999, Intake Aerodynamics.
[2] Hongjun Ran & Dimitri Mavris, AIAA 2005, Preliminary Design of a 2D Supersonic Inlet to Maximize
Total Pressure Recovery
[3] C.F. Criggs & E.L. Goldsmith, Ministry of Supply 1959, The Estimation of Shock Pressure Recovery and
External Drag of Conical Centre-Body Intakes at Supersonic Speeds
[4] Mohammad Reza Soltani, Mohammad Farahani, and Javad Sepahi Younsi ,World Academy of Science Vol:2-
2008-04-26,Performance Improvement of a Supersonic External Compression Inlet by Heat Source Addition
[5] Jerry M. Seitzmann, Georgia Tech, School of Aerospace Engineering 2000, Supersonic Flow Turning
[6] MSY Ebaid and KJM Al-Khishali, IMeche 2013, The effect of multiple conical shock waves at the engine intake
on the performance of a single-mode ramjet](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aircraftintakeaerodynamics-140502134540-phpapp01/85/Aircraft-intake-aerodynamics-24-320.jpg)