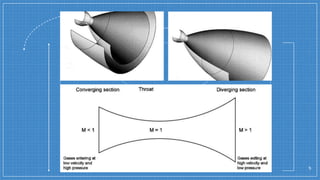
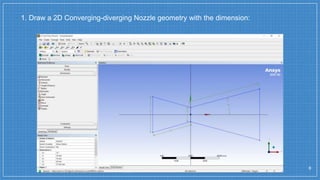
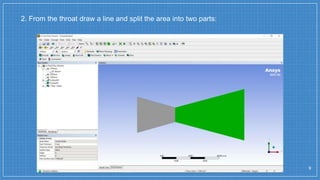
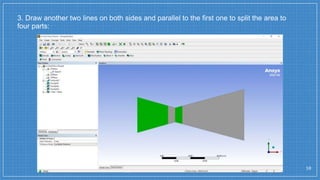
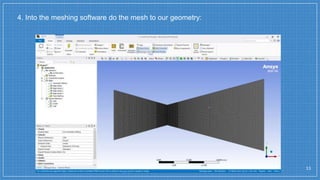
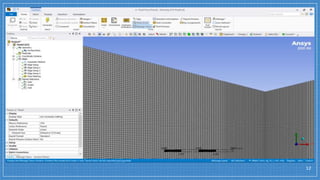
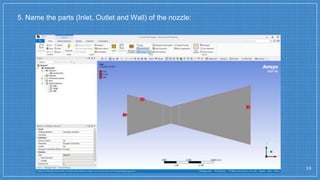
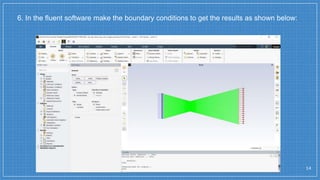
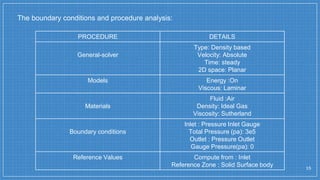
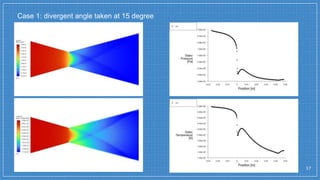
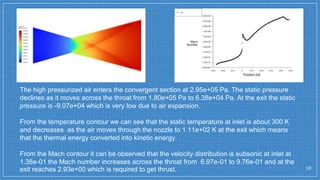
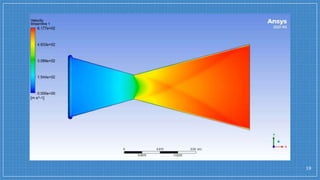
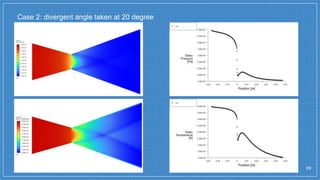
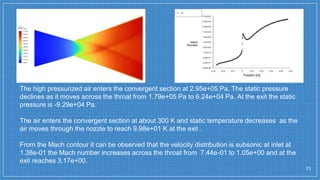
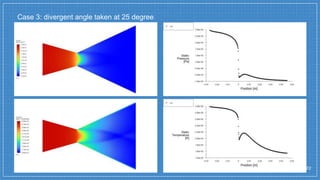
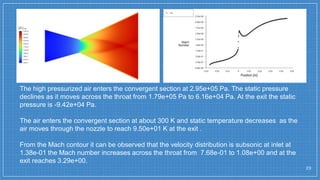
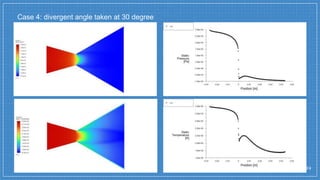
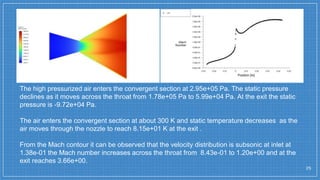
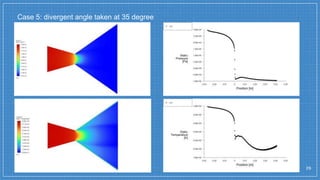
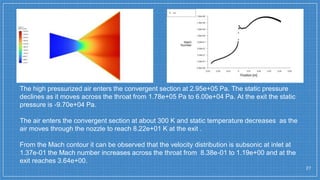
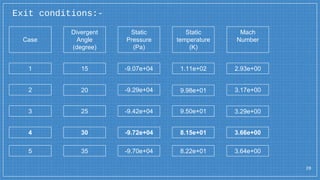
The document summarizes a simulation of a convergent-divergent rocket nozzle using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis. It discusses the aims of analyzing flow parameters like pressure and temperature inside converging-divergent and conical nozzles. It then analyzes 5 cases of converging-divergent nozzles with divergent angles from 15 to 35 degrees. The results show that static pressure decreases and Mach number increases with larger divergent angles, with the optimum angle being 30 degrees where Mach number reaches 3.66.