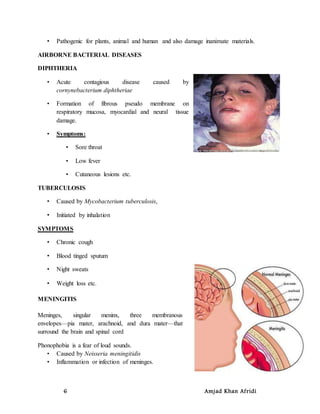
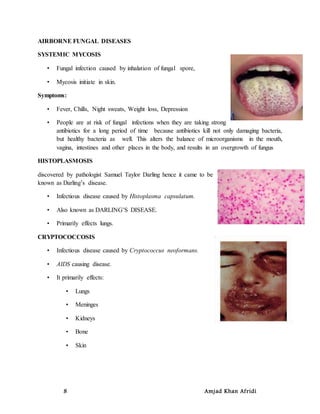
This document discusses aero-microbiology, which is the study of living microbes suspended in air. It covers topics such as the transmission of airborne microorganisms through coughing, sneezing, and being carried by dust particles or droplet nuclei. It also discusses indoor and outdoor aero-microbiology, including the microorganisms present in indoor environments and those that can cause diseases when inhaled, such as bacteria that cause diphtheria, tuberculosis, and meningitis, as well as viruses that cause smallpox, measles, and influenza. Additionally, it covers fungal diseases transmitted through the air, environmental factors affecting airborne microbes, and methods for controlling microorganisms in air