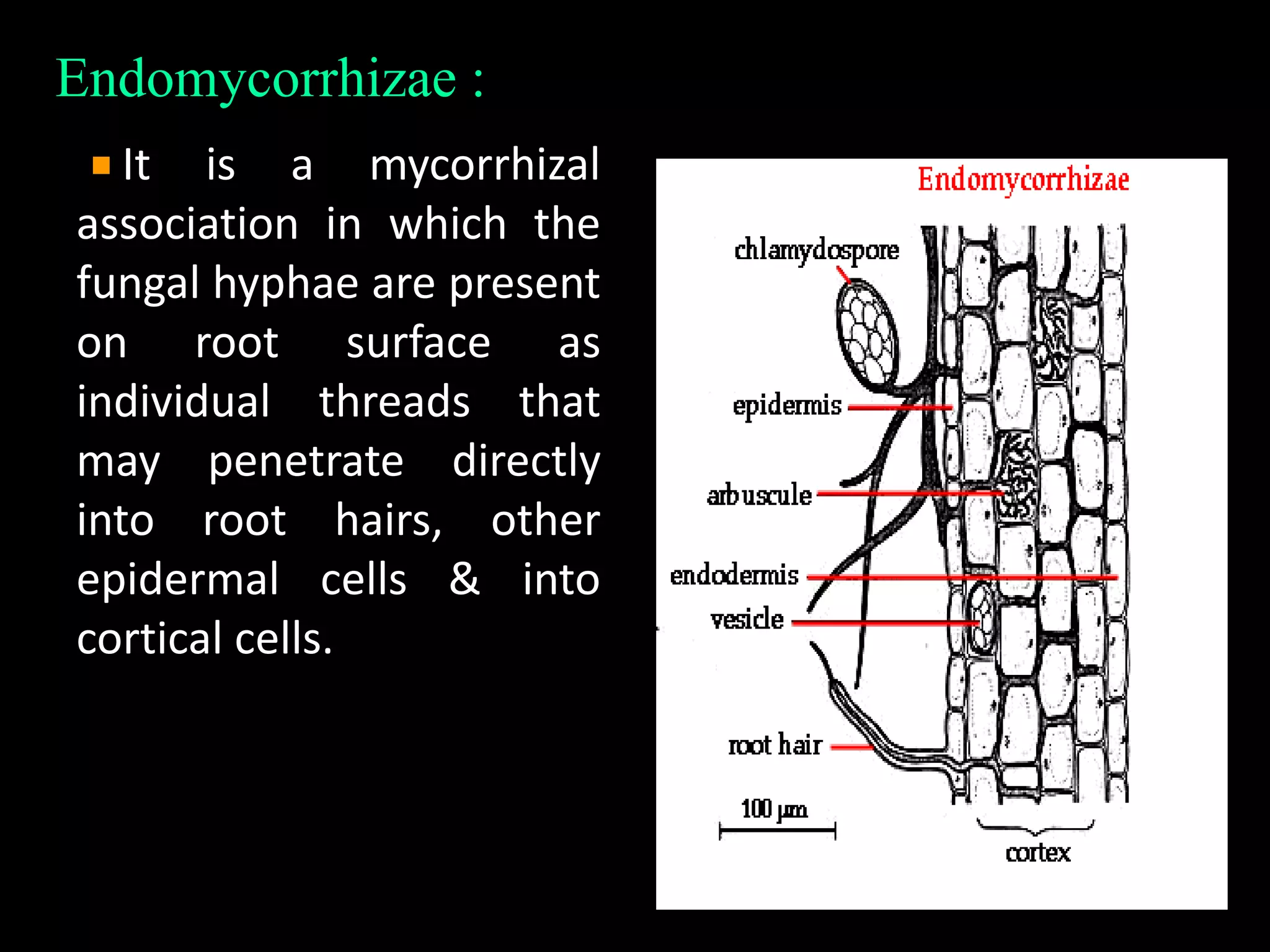
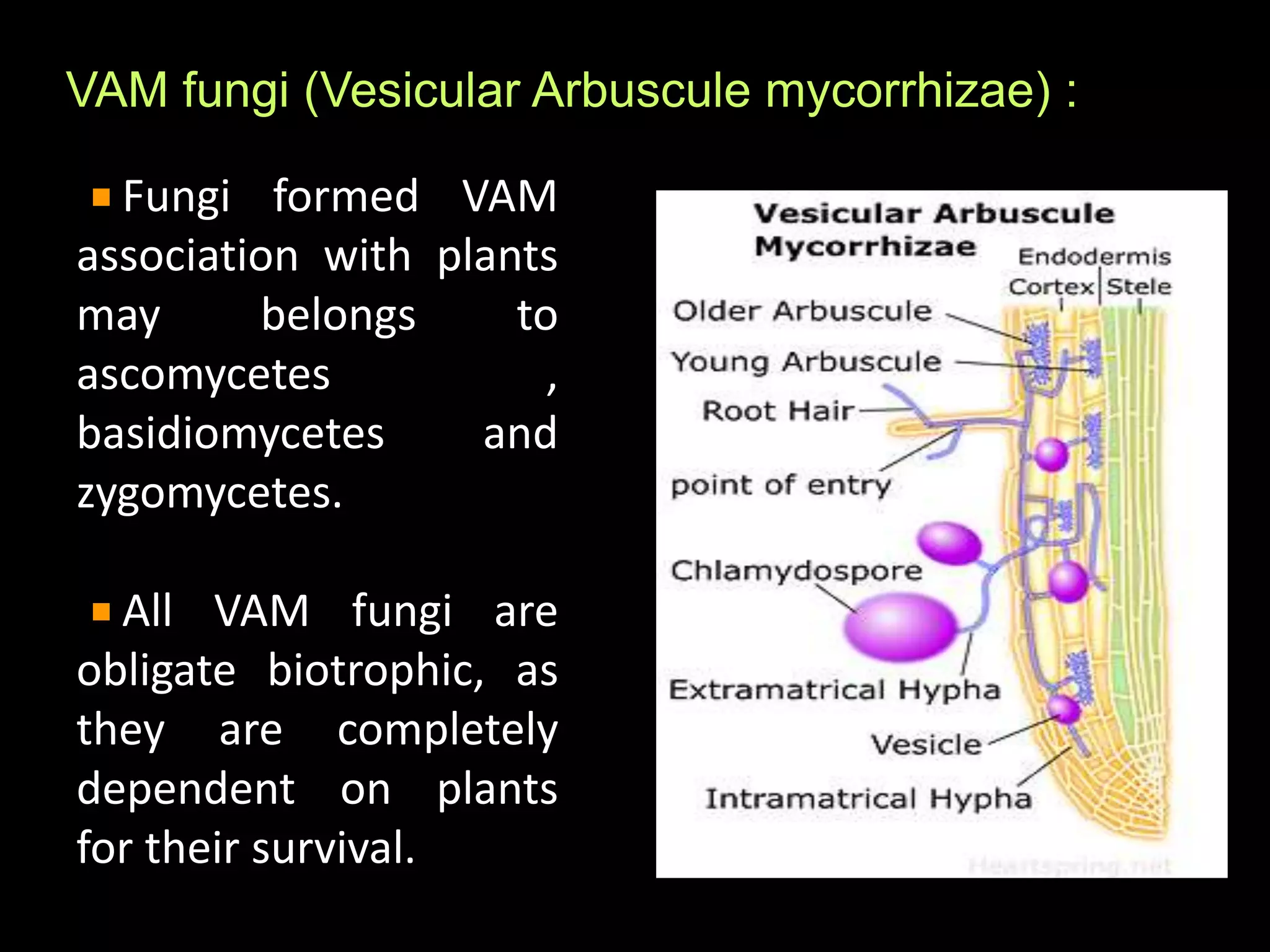
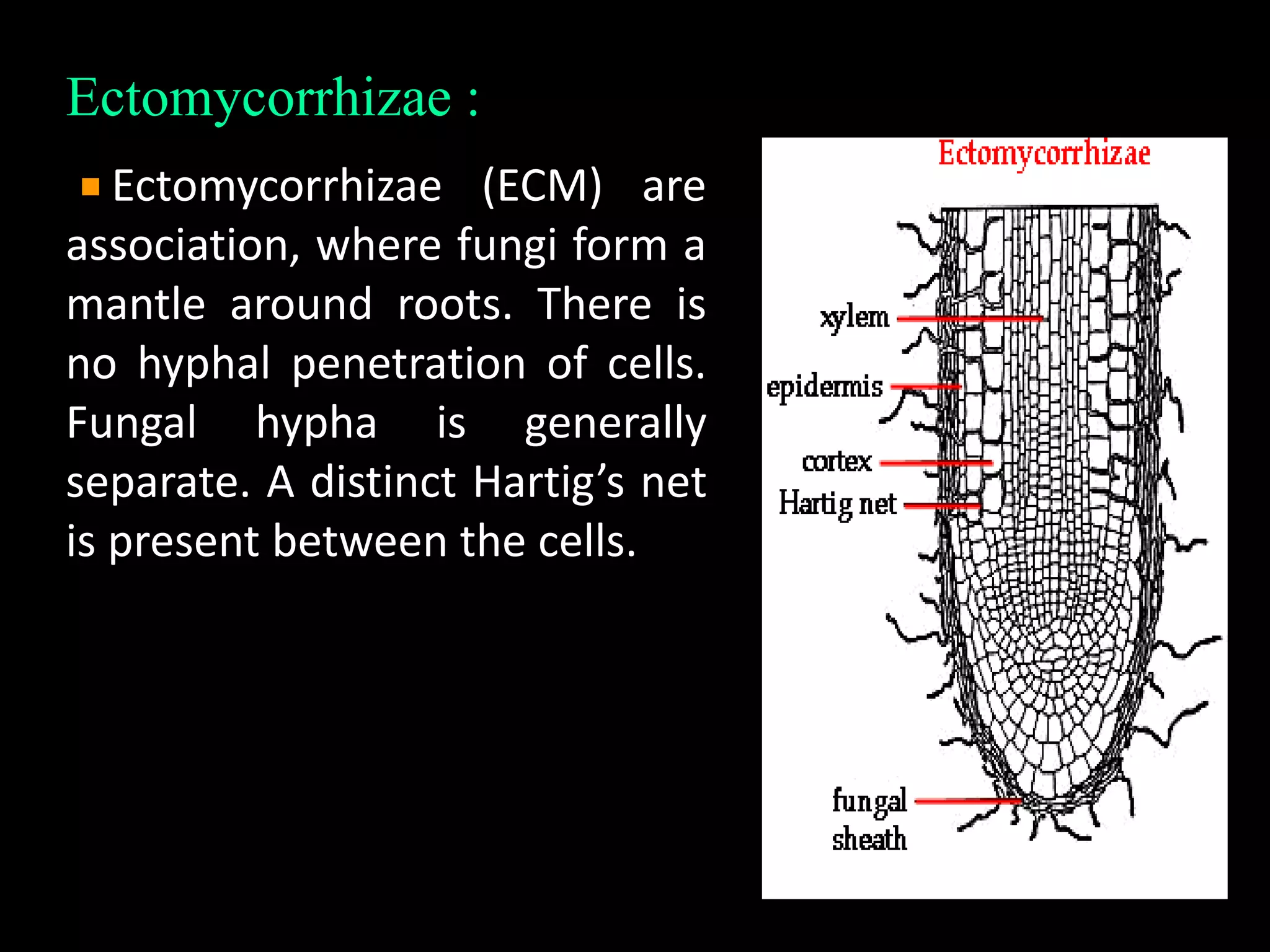
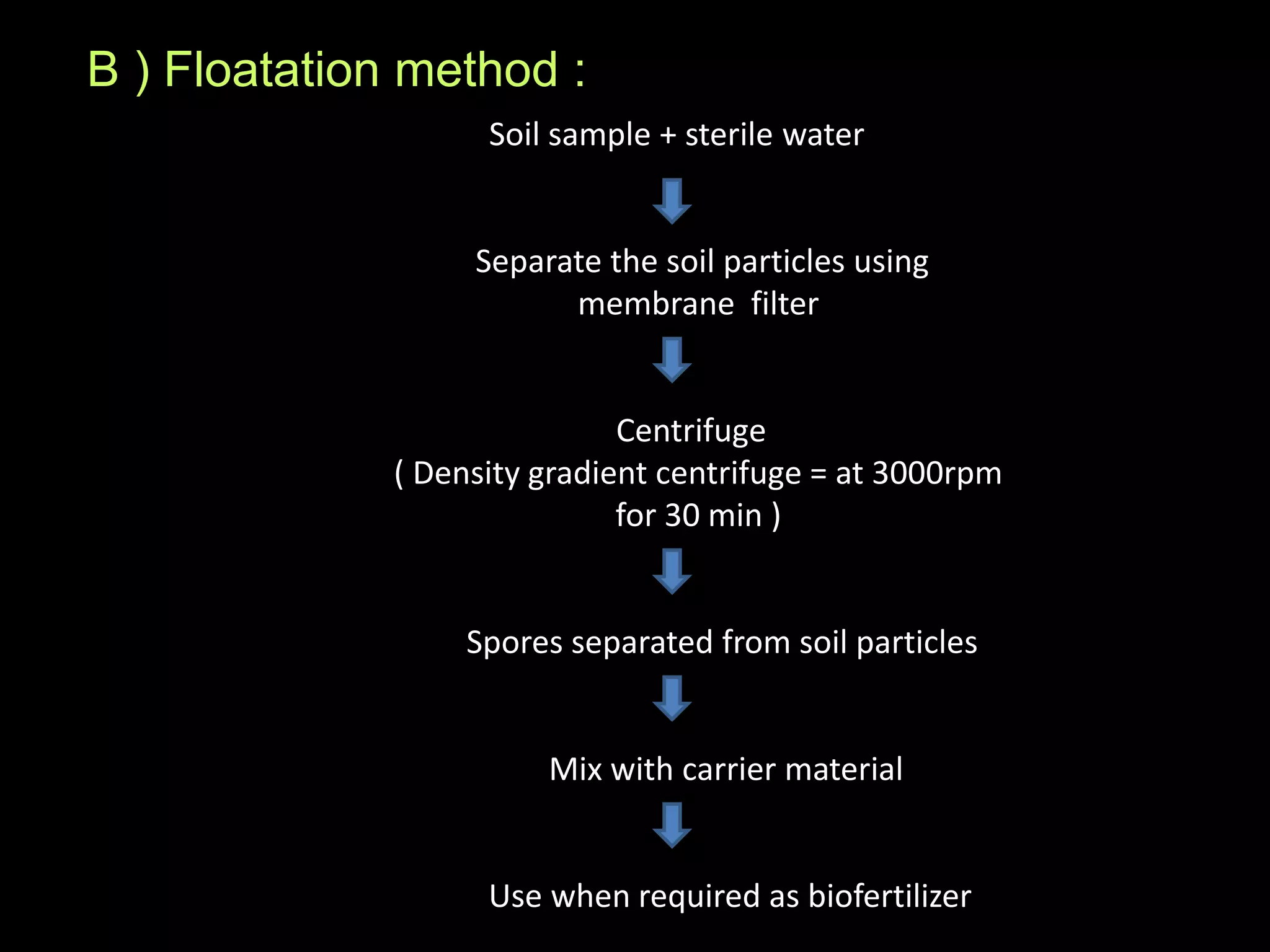
This document discusses mycorrhizae, which are symbiotic associations between fungi and plant roots. It describes the different types of mycorrhizae including endomycorrhizae, ectomycorrhizae, and ectendomycorrhizae. Applications of mycorrhizae include increasing nutrient uptake, plant diversity, and resistance to diseases and drought. The document also discusses methods for isolating and mass producing mycorrhizal fungi for use as biofertilizers to improve soil health and crop yields.