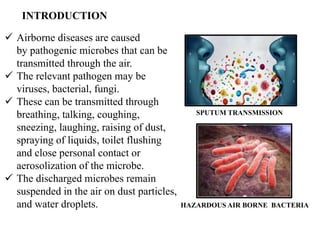
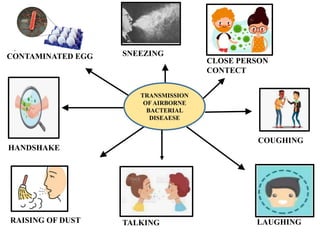
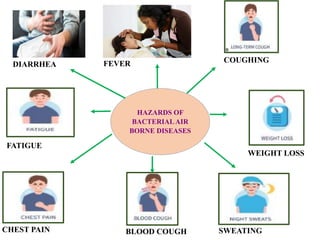
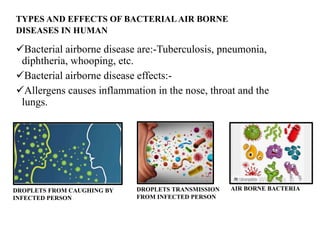
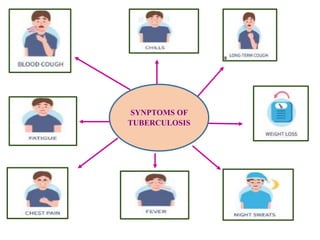
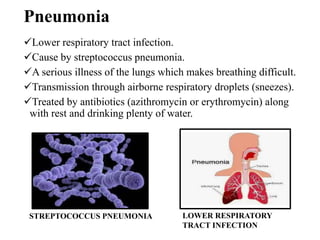
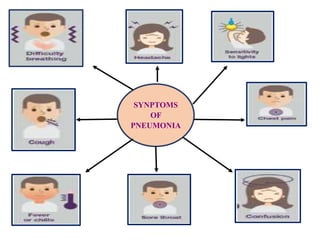
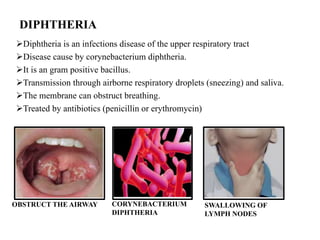
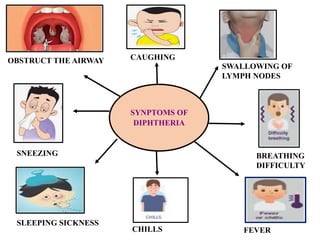
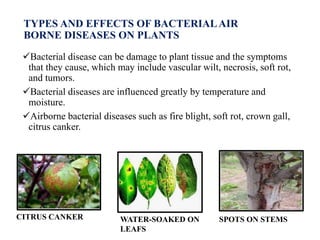
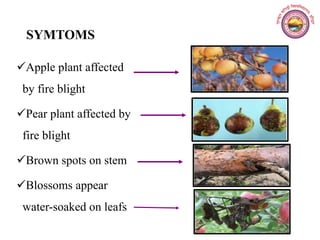
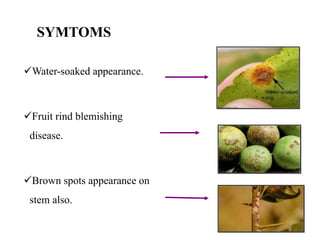
The document discusses airborne bacterial diseases caused by pathogens transmitted through the air, highlighting key diseases such as tuberculosis, pneumonia, and diphtheria along with their symptoms and treatment options. It also covers the types and effects of bacterial airborne diseases on plants like fire blight and citrus canker, along with prevention strategies. Overall, maintaining hygiene and environmental cleanliness is emphasized to control the spread of these diseases.