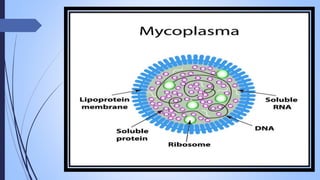
Mycoplasma are small, wall-less bacteria that were first observed in the 18th century and have since been linked to various diseases in both humans and plants. They grow optimally at 35-37 degrees Celsius, are resistant to certain antibiotics, and can reproduce through binary fission. Mycoplasma infections spread via respiratory droplets and can lead to conditions such as pneumonia and infertility in humans, as well as diseases affecting crops.