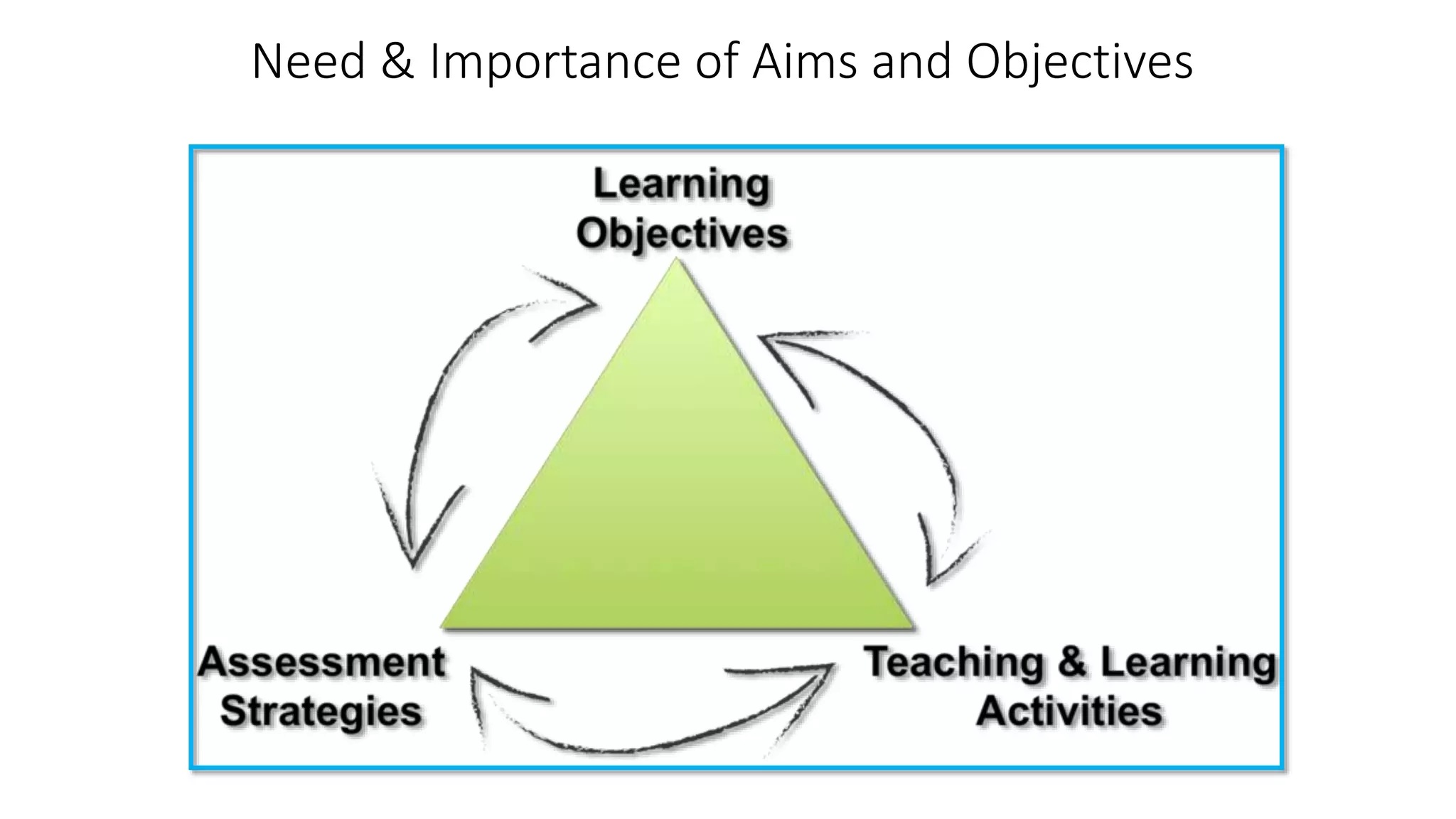
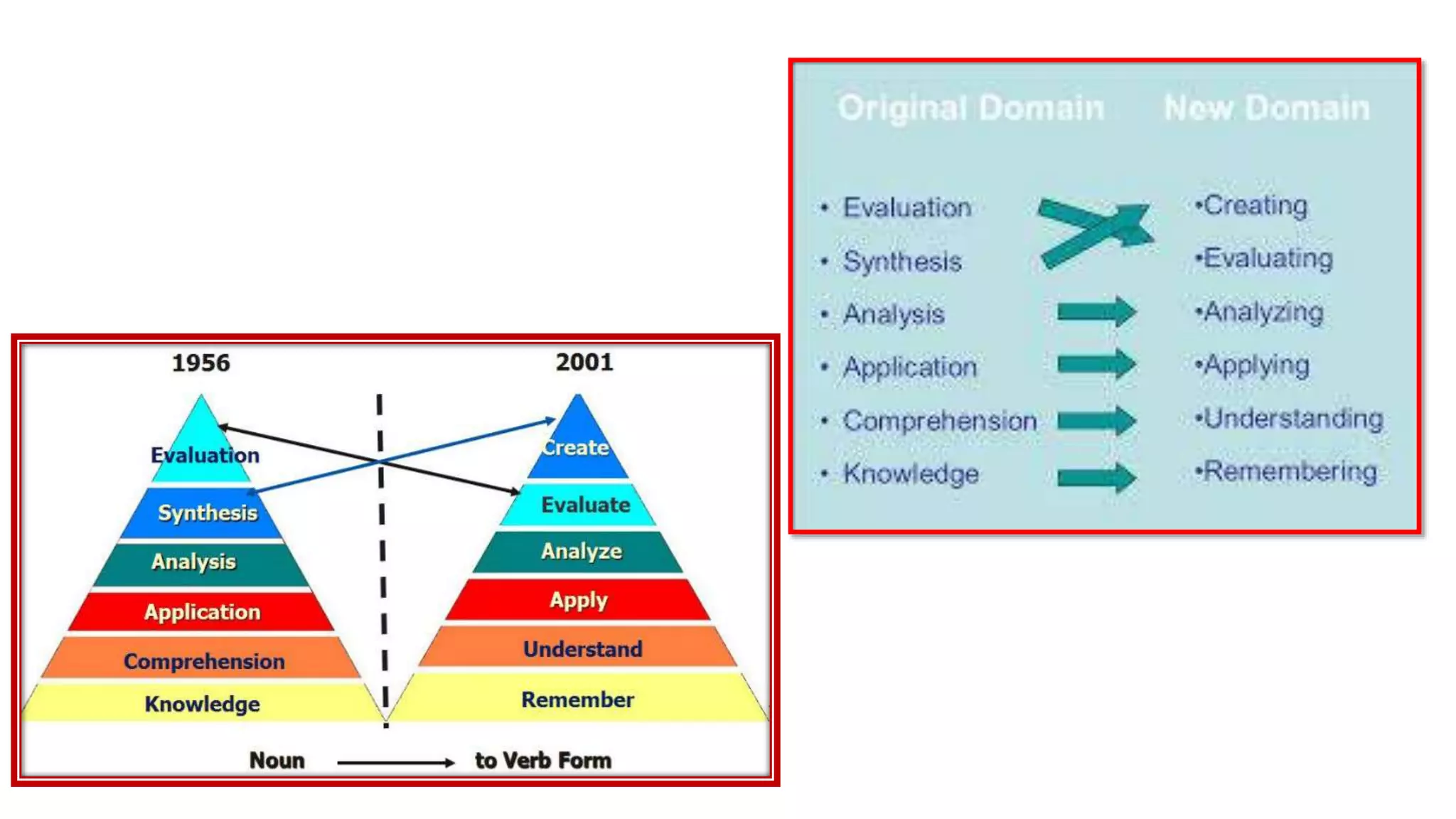
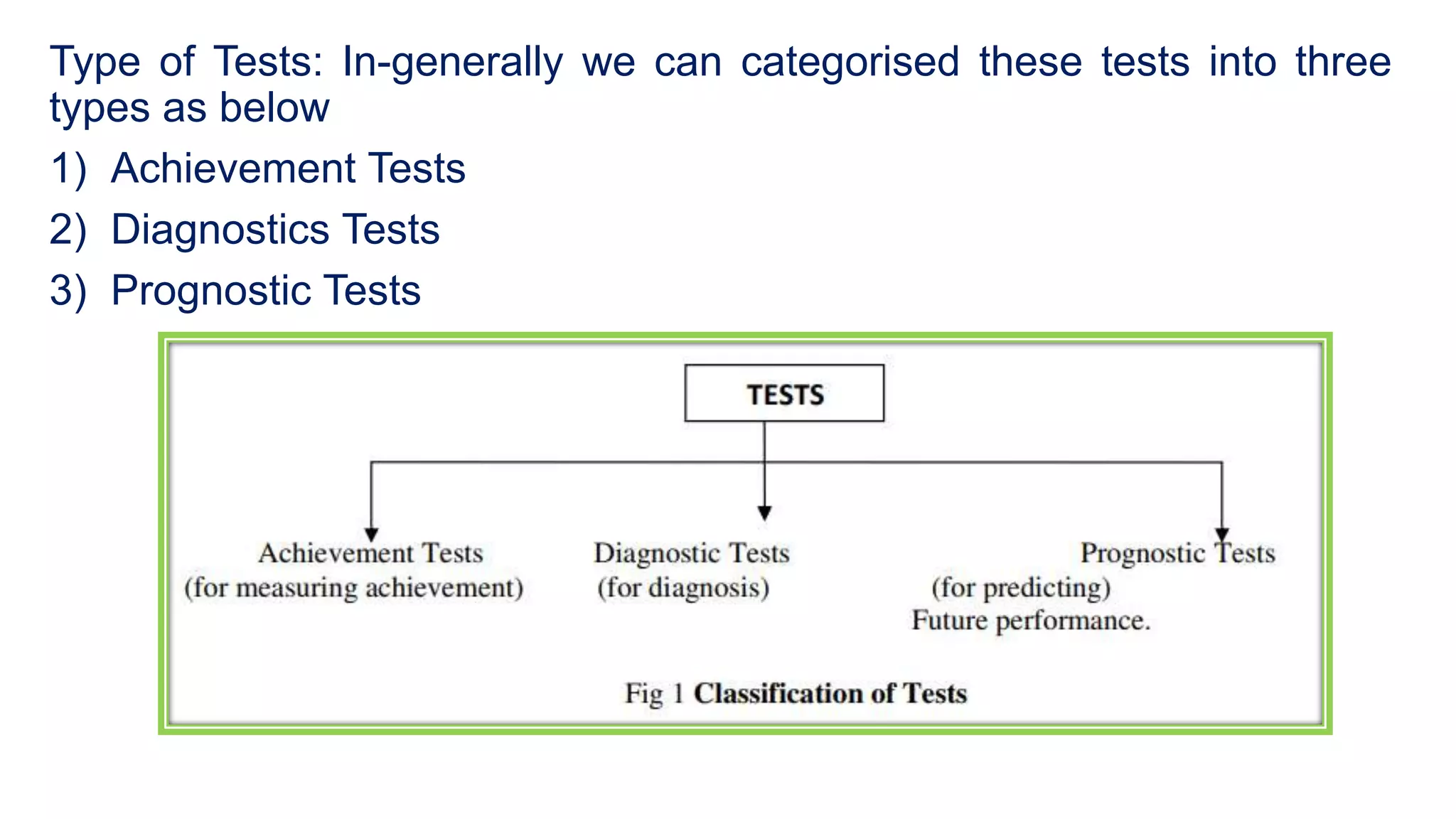
This document discusses the aims and objectives of teaching and learning, including Bloom's Taxonomy. It defines the differences between goals, aims, and objectives, with objectives being more specific and achievable in the short-term compared to aims. It also describes the different domains in Bloom's Taxonomy - cognitive, affective, and psychomotor - and provides examples of learning objectives for each hierarchical level within the domains. Specific methods for writing clear, measurable learning objectives are also outlined.