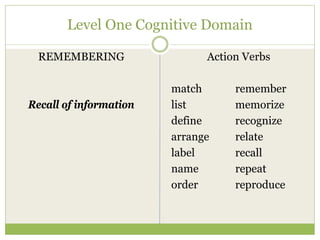
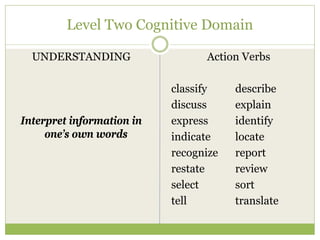
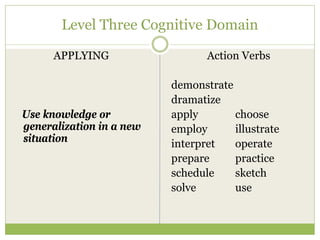
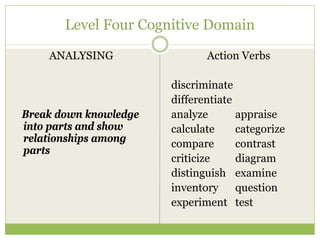
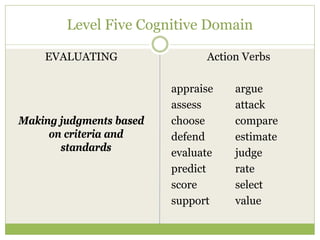
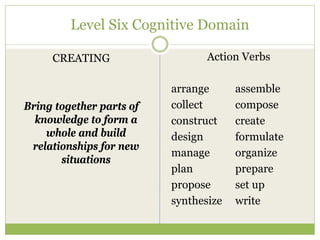
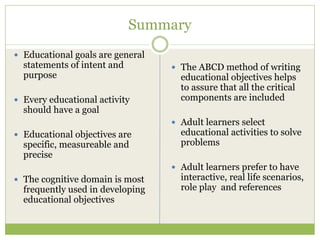
This document discusses educational goals and objectives. It compares goals, which are broad statements of intention, to objectives, which are specific and measurable. The document outlines Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives and how it has influenced curriculum development. It provides examples of writing objectives using the ABCD model, which specifies the Audience, Behavior, Condition, and Degree. Objectives target the cognitive, affective, or psychomotor domains and use action verbs accordingly. Overall, the document provides guidance on developing learner-based instruction through clearly articulated educational goals and objectives.