This document provides an overview of how the Australian curriculum can be used as a framework to develop literacy at the Adelaide West Special Education Centre. It discusses key concepts in literacy development including balanced literacy, communication, mastery versus emergent views of literacy. Time recommendations and achievement standards are presented for various learning areas from the Australian curriculum adapted for students with disabilities. The use of individual goal setting and reporting on the general capabilities is also described as part of a balanced literacy approach at the school.




































![History
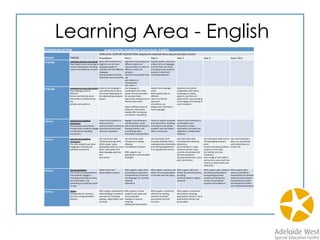
F
What
is
my
history
and
how
do
I
know?(How
stories
of
families
and
their
past
can
be
communicated
through
pictures
books,
artefacts
and
oral
histories.
Y2
Aspects
of
the
past
we
can
see
today.
History
of
local
building,
site
or
part
of
the
local
environment
Y
3
-‐
Who
lived
here
first
and
how
do
we
know?
The
importance
of
place
and
country
to
ATSI
people
who
belong
to
a
local
area
4
What
was
life
like
for
ATSI
people
before
the
arrival
of
Europeans?
Why
did
Europeans
se]le
in
Australia?
Y
7
iden<fy
a
range
of
ques<ons
about
the
past
to
inform
a
historical
inquiry](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agosci2015handout-150512085616-lva1-app6891/85/Literacy-Through-Curriculum-Using-the-Australian-Curriculum-as-a-springboard-for-literacy-45-320.jpg)
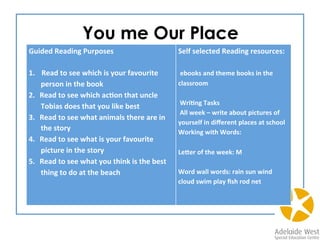
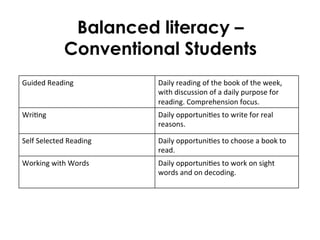
![You me Our Place
Guided
Reading
Purposes
1.
Read
to
see
which
is
your
favourite
person
in
the
book
2. Read
to
see
which
ac<on
that
uncle
Tobias
does
that
you
like
best
3. Read
to
see
what
animals
there
are
in
the
story
4. Read
to
see
what
is
your
favourite
picture
in
the
story
5. Read
to
see
what
you
think
is
the
best
thing
to
do
at
the
beach
Self
selected
Reading
resources:
ebooks
and
theme
books
in
the
classroom
Wri<ng
Tasks
All
week
–
write
about
pictures
of
yourself
in
different
places
at
school
Working
with
Words:
Le]er
of
the
week:
M
Word
wall
words:
rain
sun
wind
cloud
swim
play
fish
rod
net](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agosci2015handout-150512085616-lva1-app6891/85/Literacy-Through-Curriculum-Using-the-Australian-Curriculum-as-a-springboard-for-literacy-46-320.jpg)