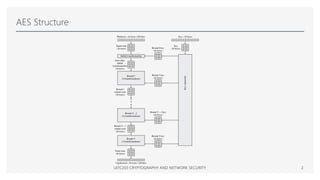
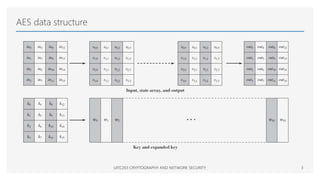
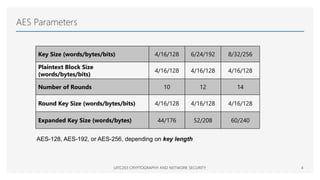
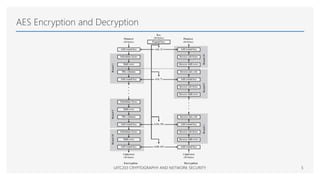
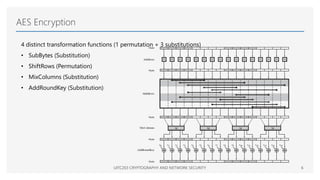
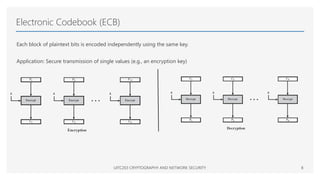
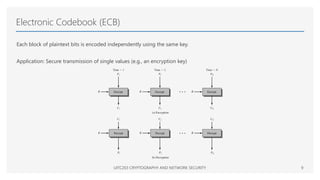
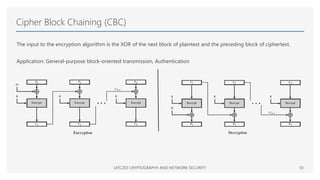
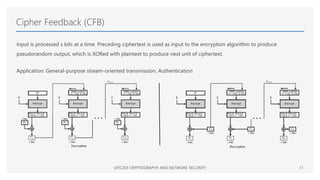
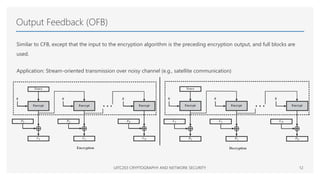
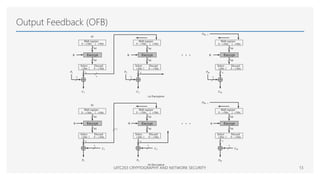
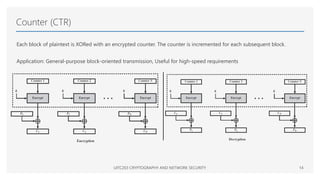
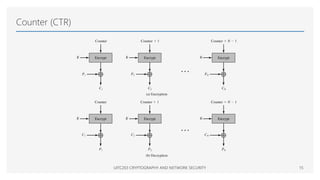
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a symmetric block cipher that can operate with three different key lengths - 128 bits, 192 bits, and 256 bits, known as AES-128, AES-192, and AES-256. The AES algorithm performs encryption and decryption on blocks of 128 bits using rounds of processing that include substitution, permutation, and mixing functions. AES also supports various block cipher modes of operation like Electronic Codebook (ECB), Cipher Block Chaining (CBC), Cipher Feedback (CFB), Output Feedback (OFB), and Counter (CTR) for different applications.