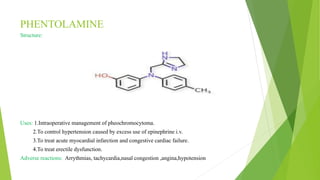
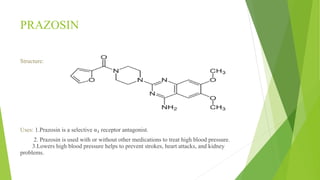
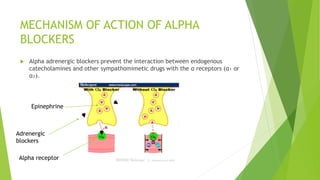
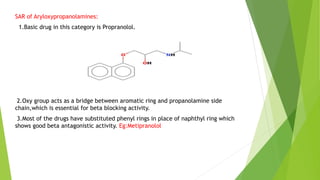
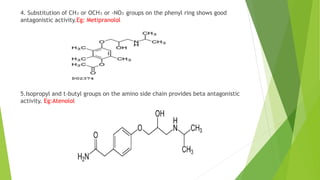
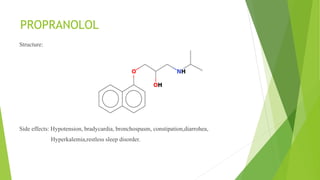
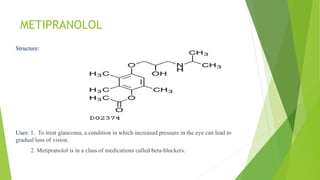
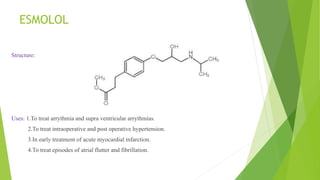
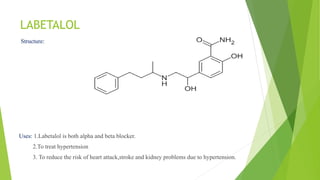
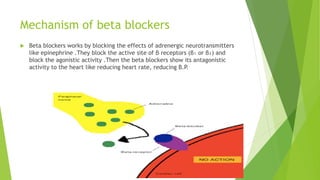
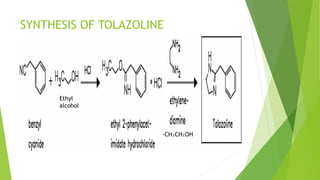
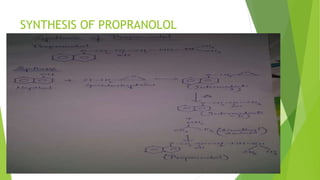
This document discusses adrenergic antagonists, which are drugs that block adrenergic receptors to inhibit the functions of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine. It classifies them as alpha or beta blockers and provides examples of each. Key drugs discussed include tolazoline, phentolamine, phenoxybenzamine, prazosin, dihydroergotamine, methysergide, propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol, betaxolol, esmolol, metaprolol, and carvedilol. Their structures, mechanisms of action, and clinical uses for conditions like hypertension and cardiac issues are summarized. The synthesis of tolazoline and