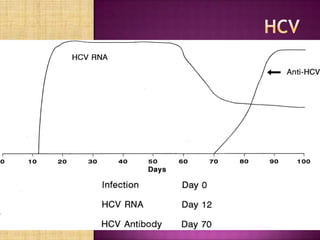
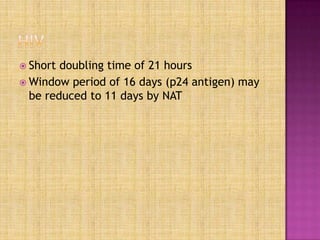
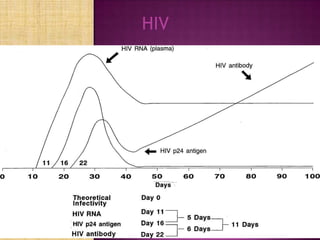
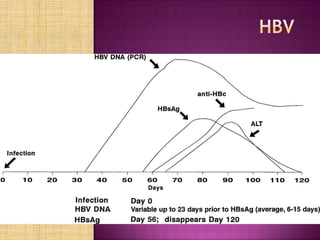
Nucleic acid testing (NAT) involves extracting nucleic acids from blood samples, amplifying any virus or bacteria present, and detecting them. NAT can detect infections during the window period before antibodies form, reducing transfusion-transmitted infection risk. NAT methods approved for donor screening include transcription mediated amplification to detect HIV and HCV RNA. While improving safety, NAT is costly and may still miss some infections. It is used alongside but does not replace serological screening.