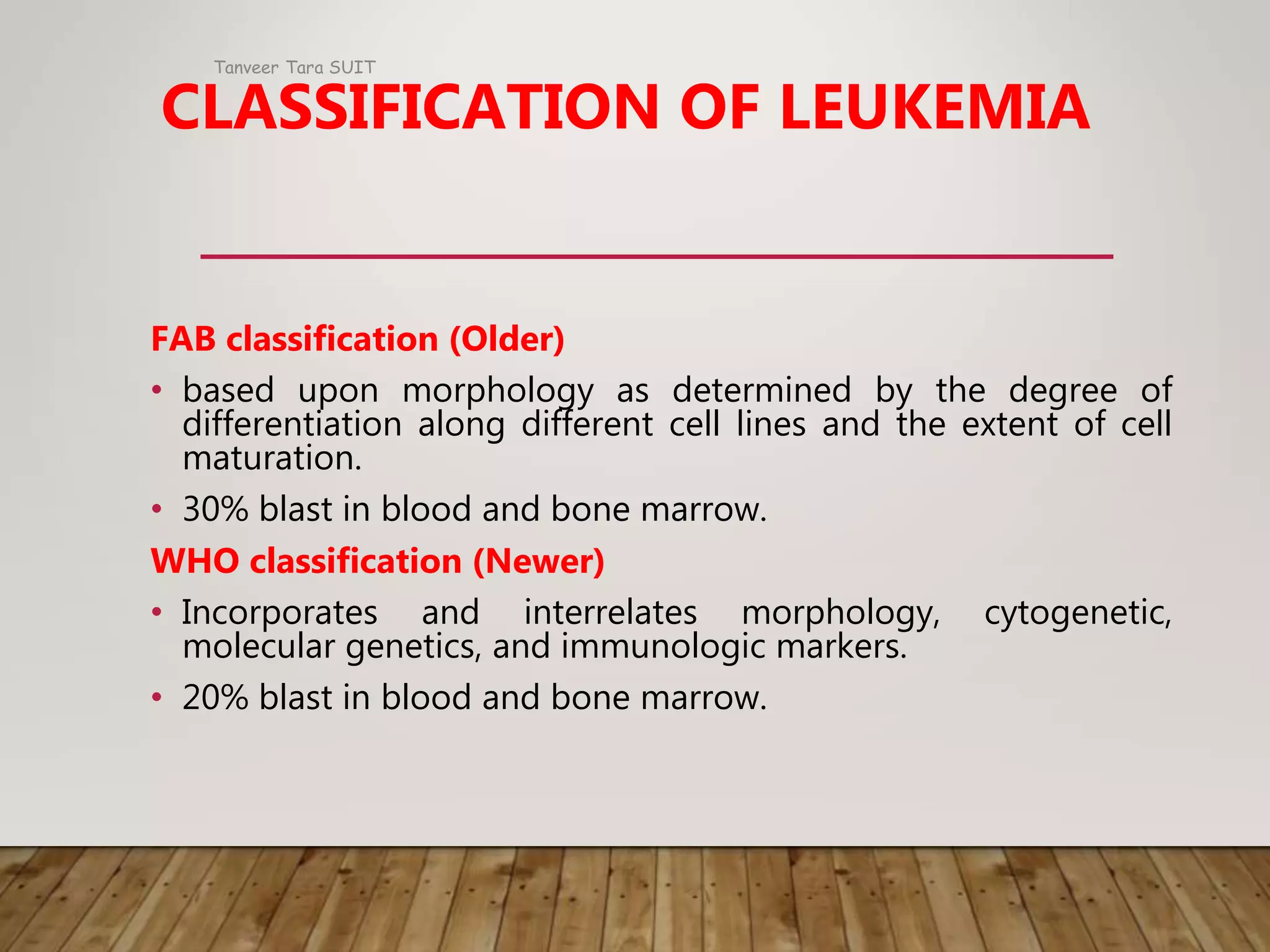
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells. The main pathological changes in AML involve abnormal proliferation, blocked differentiation, and abolished apoptosis of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Benzene exposure can cause AML and other hematological malignancies. AML is classified based on the type of cells affected and how quickly the disease progresses. The disease involves accumulation of genetic mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, leading to increased proliferation, reduced apoptosis, and a block in cellular differentiation. Clinical manifestations include marrow failure, tissue infiltration, and leukostasis. Prognostic factors include age, white blood cell count, specific genetic mutations, and disease characteristics