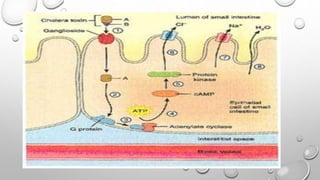
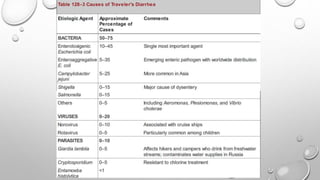
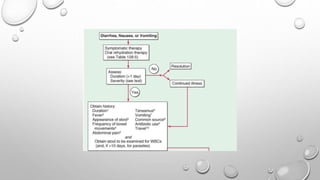
Acute diarrheal diseases are a leading cause of illness and death worldwide, with over 4.6 billion cases per year. A wide variety of infectious agents can cause acute diarrhea, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites. The main pathogenic mechanisms are toxin production, invasion and destruction of intestinal cells, and penetration of the intestinal mucosa. Treatment focuses on oral rehydration and antibiotics depending on the suspected pathogen. Proper hygiene and vaccines can help prevent acute diarrheal diseases.