IMCI combines improved management of common childhood illnesses, prevention of diseases, and promotion of health. It has 3 essential components:
1. Improving health staff skills in managing illnesses through locally adapted guidelines.
2. Strengthening the overall health system.
3. Improving family and community healthcare practices.
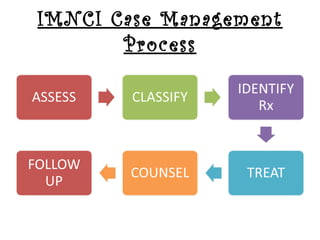
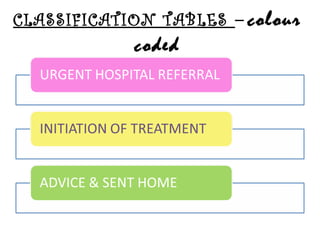
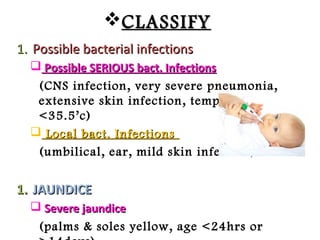
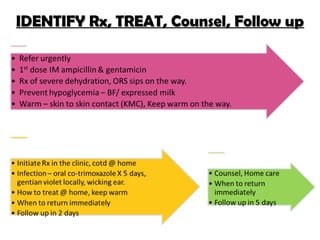
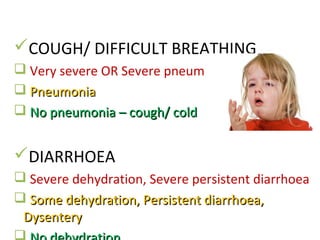
The IMCI process involves assessing children under 5 for general danger signs, classifying their illnesses, identifying treatment and follow up. It focuses on managing problems like cough, diarrhea, fever, ear issues and malnutrition in both young infants and older children. The goal is to treat issues, counsel caregivers, and ensure follow up care.