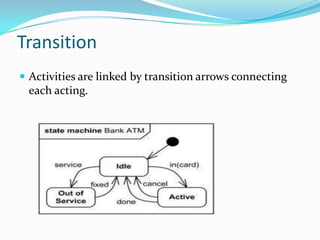
This document describes the key elements of activity diagrams including activities, transitions, guard conditions, decisions, concurrency, and notations. Activities represent steps in a process, transitions connect activities, and guard conditions restrict transitions. Decisions can involve simple true/false tests or choices between options. Activity diagrams can also model the synchronization of concurrent activities and splitting of process flow.