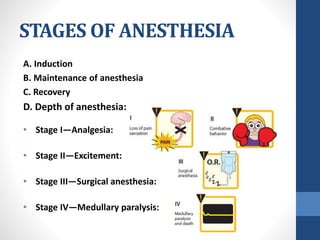
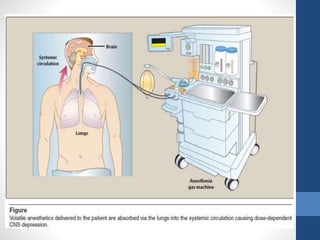
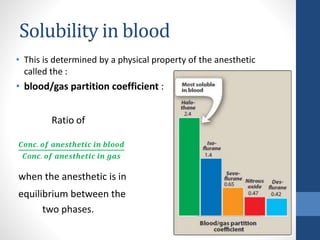
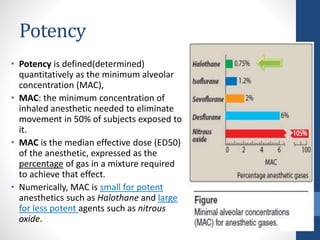
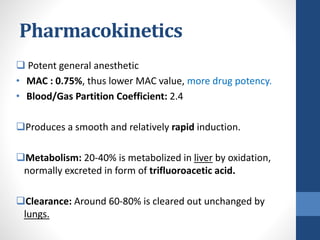
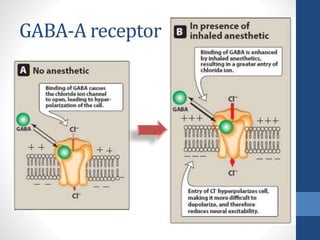
Halothane is an inhalational general anesthetic containing bromine that provides a long duration of action. It produces a smooth induction and rapid recovery from anesthesia. While potent, it has disadvantages like being a strong respiratory and cardiovascular depressant that can cause hypotension, arrhythmias, and hepatitis with oxidative metabolism in the liver. It also carries a risk of the serious complication of malignant hyperthermia in susceptible individuals. Due to these adverse effects, halothane has been replaced by other anesthetics with fewer complications in most countries.