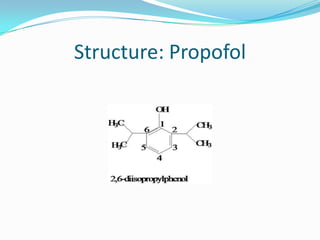
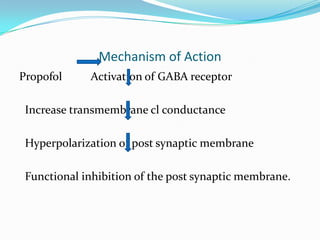
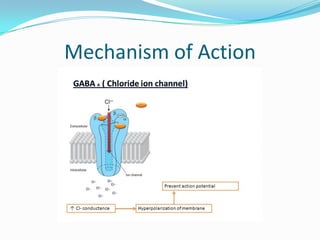
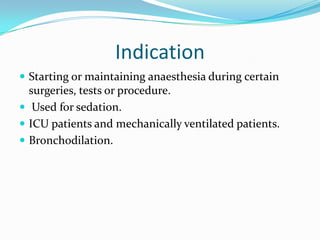
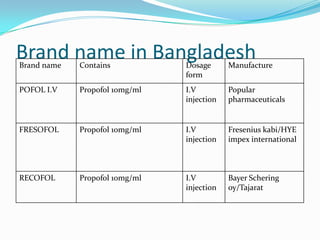
Propofol is an intravenous sedative used for inducing and maintaining general anesthesia. It works by enhancing the effect of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA in the brain. Propofol is formulated as a 1% aqueous solution containing soybean oil, glycerol, and egg lecithin. It has a rapid onset of 15-30 seconds, short duration of 5-10 minutes, and is metabolized in the liver. Common uses include anesthesia induction, sedation, and ventilation in ICU patients. Side effects include nausea, cough, and confusion.