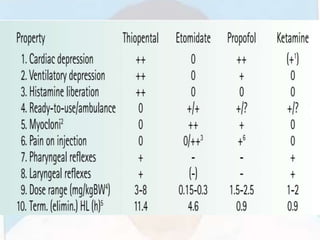
This document provides information about the drug etomidate. It discusses etomidate's history, mechanism of action, effects on body systems, pharmacokinetics, formulations, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing, administration, safety, and relationship to adrenal suppression. The document also outlines cases for discussion and emphasizes that etomidate is the preferred induction agent for hemodynamically unstable patients.