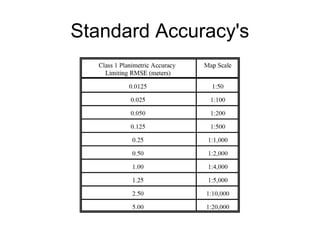
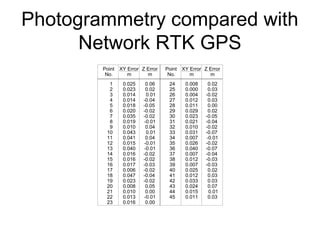
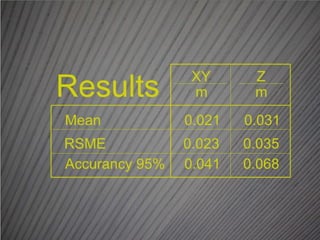
The document compares the accuracy of geospatial data obtained from UAV photogrammetry against network RTK GPS, establishing that UAVs can achieve horizontal and vertical accuracies suitable for various mapping applications. Results indicate that UAVs can perform topographical surveys at scales of 1:200 with impressive accuracy, while reducing time spent on mapping tasks. Overall, UAV photogrammetry is presented as a faster and richer alternative to traditional GPS surveying methods.