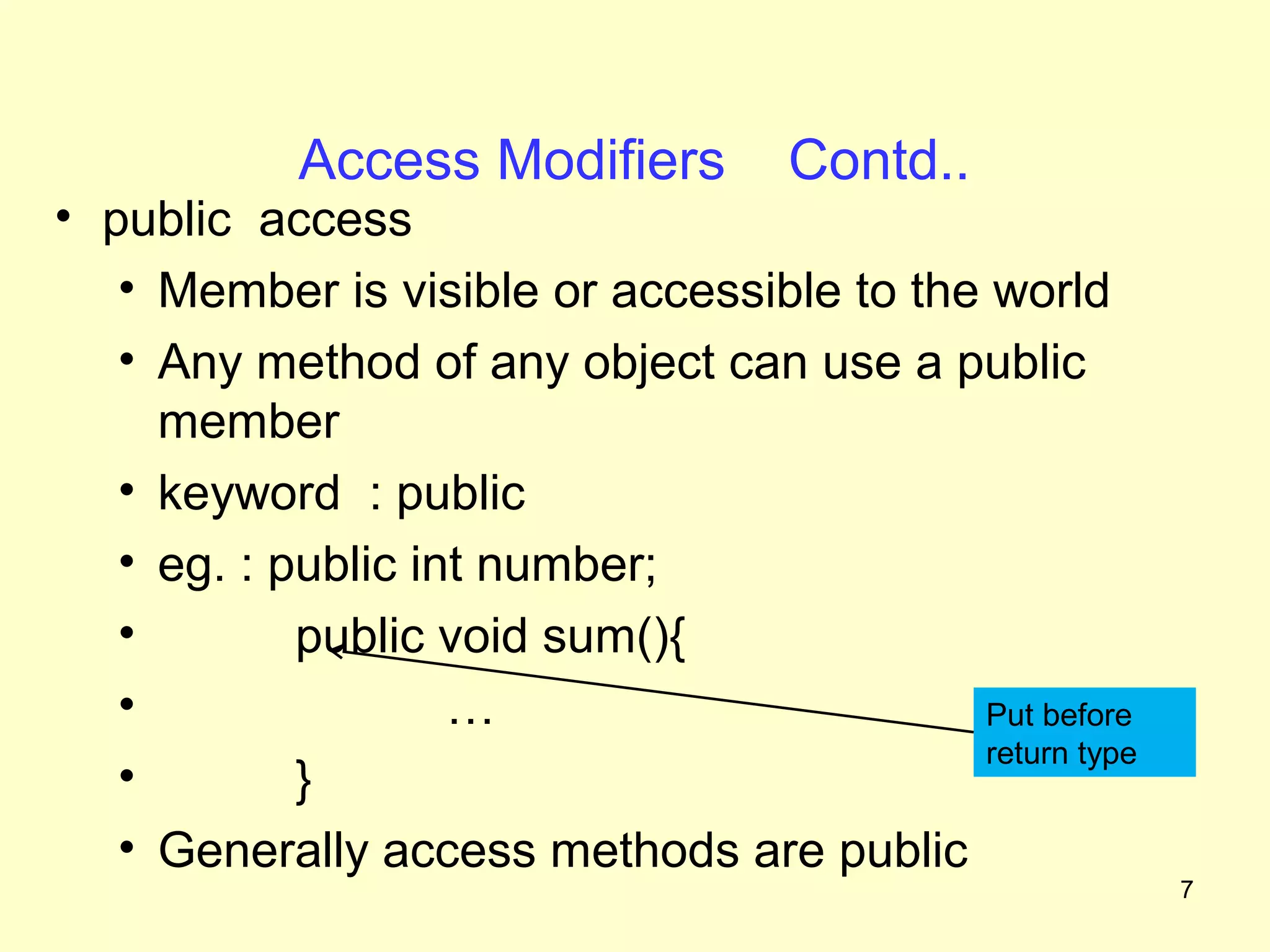
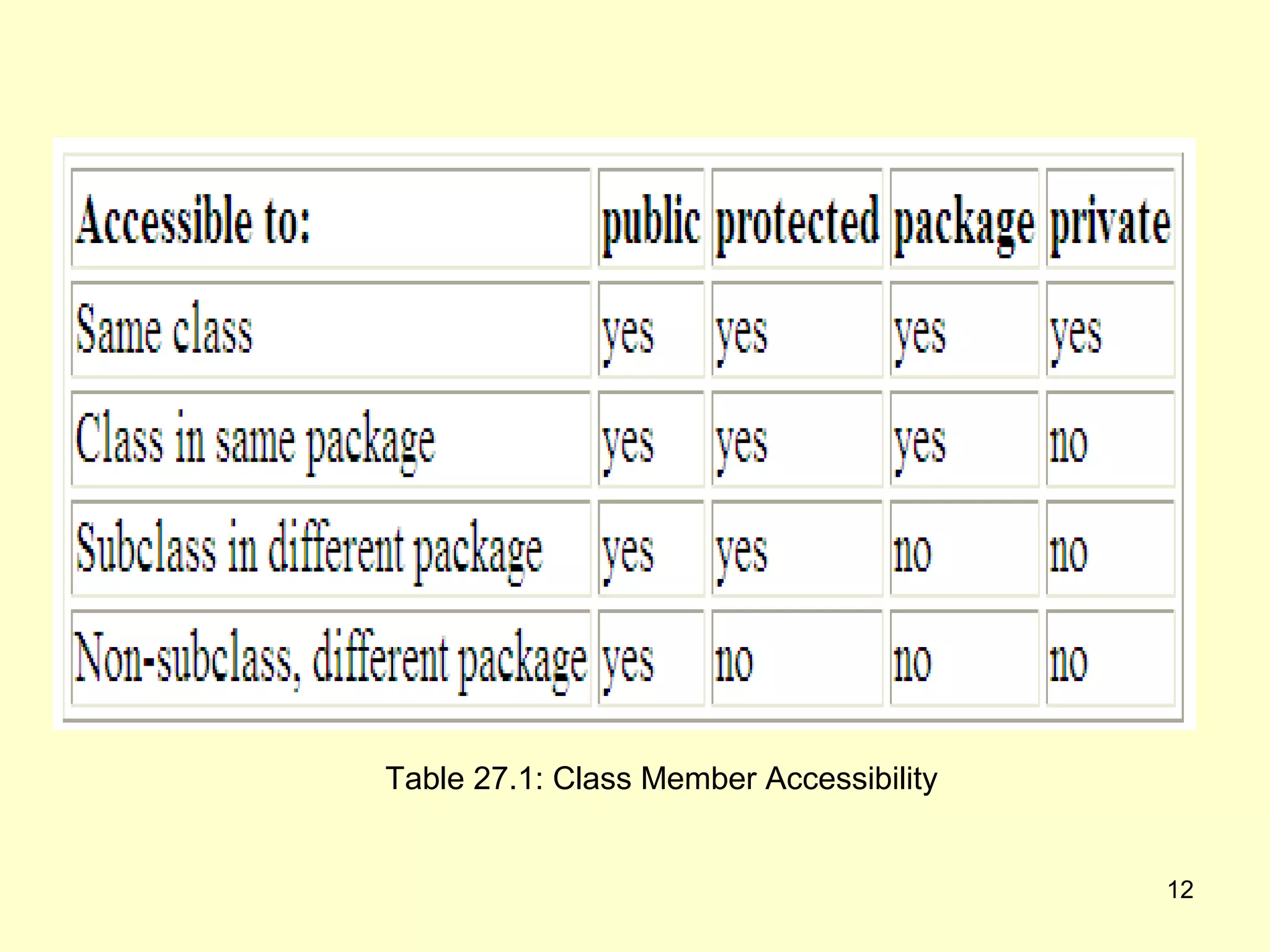
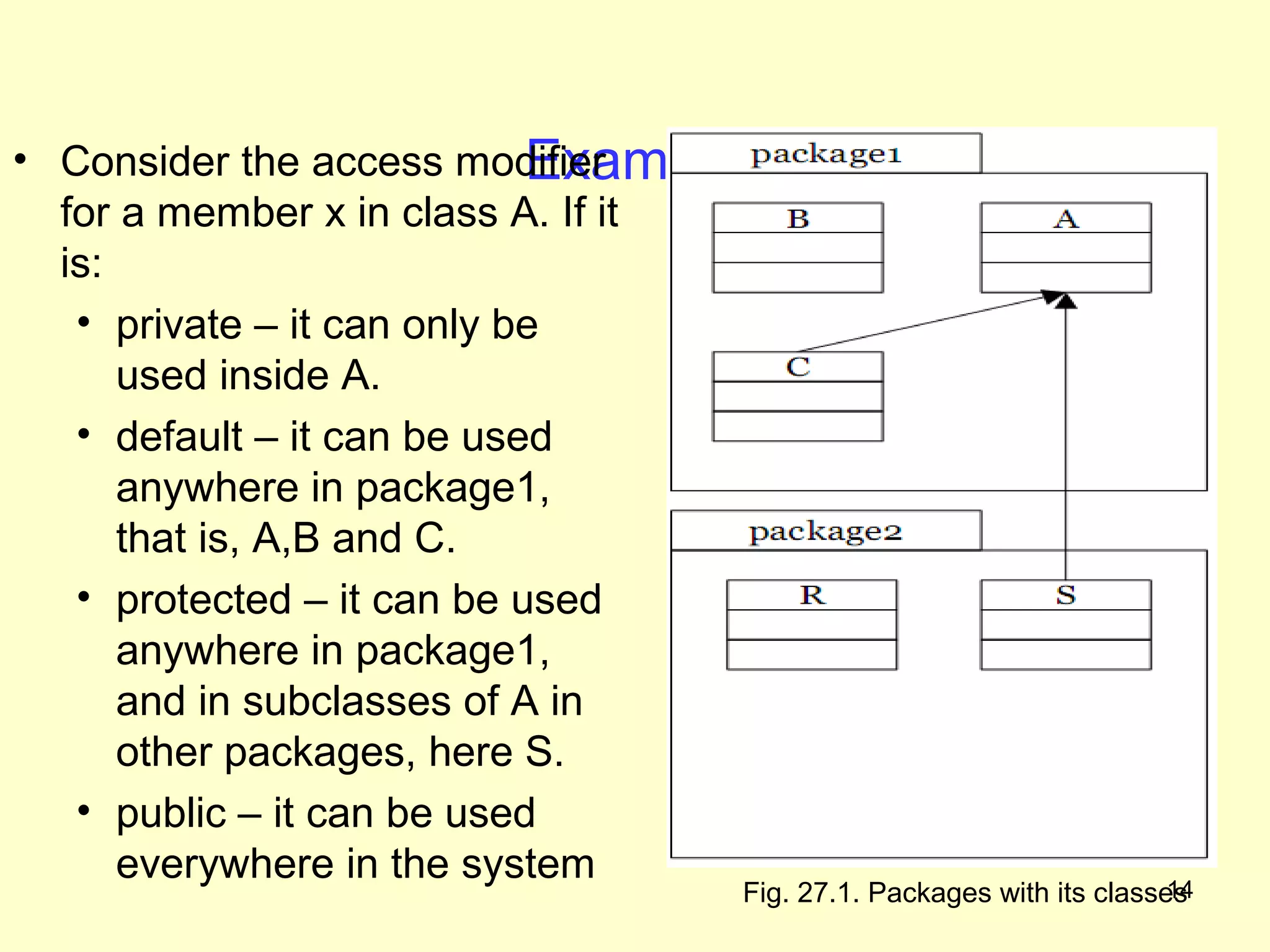
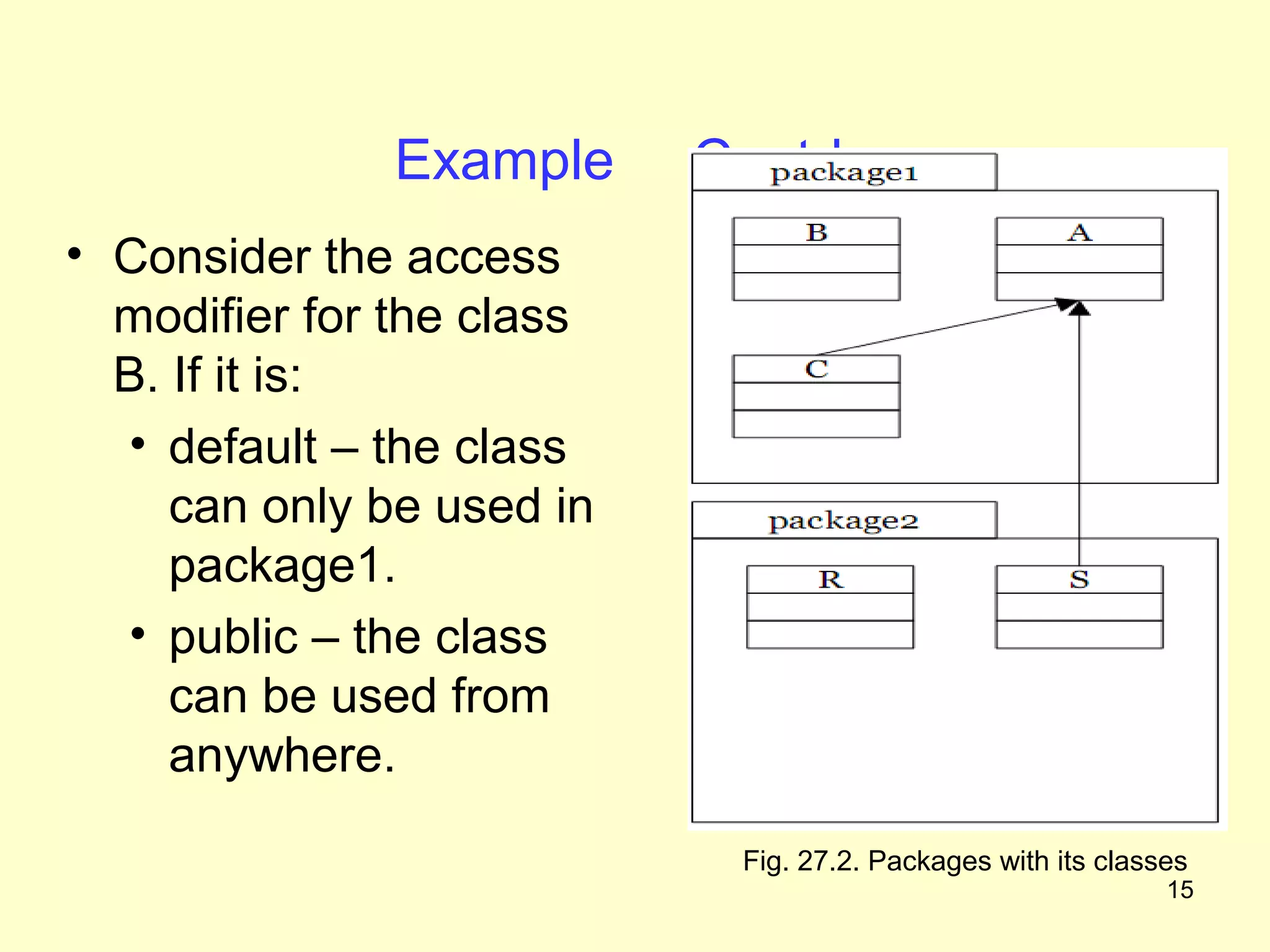
The document discusses access protection and access modifiers in Java. It explains the different access modifiers - public, private, and protected. Public members are accessible everywhere, private members are only accessible within their own class, and protected members are accessible within the class, subclasses, and packages. It provides examples of how to use access modifiers with classes and class members, and recommends generally making data private and accessor methods public. A sample Person class is provided to demonstrate applying access modifiers.