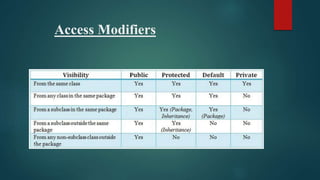
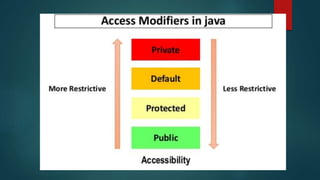
Access specifiers in Java determine the visibility and accessibility of classes, methods, and variables. There are four levels of access specifiers in Java: default, private, protected, and public. The default access level is accessible only within the same package. Private is accessible only within the same class, protected is accessible within the same package and subclasses, and public has the widest scope and is accessible everywhere.




![1.]DEFAULT ACCESS SPECIFIER:
No keyword is required to specify default
access specifier
When no access modifier is specified for a
class, method or data member it is said to be
having the default access specifier by default.
Default access specifier are accessible within the
same package.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accessmodifiersinjava-200812074217/85/Access-modifiers-in-java-6-320.jpg)
![2. ]PRIVATE ACCESS SPECIFIER:
The private access specifier is specified using the
keyword private.
The methods or data members declared as private
are accessible only within the class in which they are
declared.
Any other class of same package will not be able to
access these members.
Classes or interface can not be declared as private.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accessmodifiersinjava-200812074217/85/Access-modifiers-in-java-7-320.jpg)
![PRIVATE Example
1.class A{
2.private int data=40;
3.private void msg(){System.out.println("Hello java");}
4.}
5.
6.public class Simple{
7. public static void main(String args[]){
8. A obj=new A();
9. System.out.println(obj.data);//Compile Time Error
10. obj.msg();//Compile Time Error
11. }
12.}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accessmodifiersinjava-200812074217/85/Access-modifiers-in-java-8-320.jpg)

![PRIVATE Example – setter & getter
class Data {
private String name;
// getter method
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
// setter method
public void setName(String name) {
this.name= name;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] main){
Data d = new Data();
// access the private variable using the getter and setter
d.setName(“Ganpat Univ");
System.out.println(d.getName());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accessmodifiersinjava-200812074217/85/Access-modifiers-in-java-10-320.jpg)
![3. ]PROTECTED ACCESS
SPECIFIER:
The protected access specifier is specified
using the keyword protected.
The methods or data members declared as
protected are accessible within same package
or sub classes in different package.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accessmodifiersinjava-200812074217/85/Access-modifiers-in-java-11-320.jpg)
![PROTECTED Example
class Animal {
// protected method
protected void display() {
System.out.println("I am an animal");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an object of Dog class
Dog d = new Dog();
// access protected method
d.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accessmodifiersinjava-200812074217/85/Access-modifiers-in-java-12-320.jpg)
![PROTECTED Example
package p1;
//Class A
public class A
{
protected void display()
{
System.out.println("Learning JAVA");
}
}
package p2;
import p1.*; //importing all classes in package p1
//Class B is subclass of A
class B extends A
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
B obj = new B();
obj.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accessmodifiersinjava-200812074217/85/Access-modifiers-in-java-13-320.jpg)
![.4]PUBLIC ACCESS SPECIFIER:
The public access specifier is specified using the
keyword public.
The public access specifier has the widest scope
among all other access modifiers.
Classes, methods or data members which are
declared as public are accessible from every where in
the program. There is no restriction on the scope of
a public data members.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accessmodifiersinjava-200812074217/85/Access-modifiers-in-java-14-320.jpg)