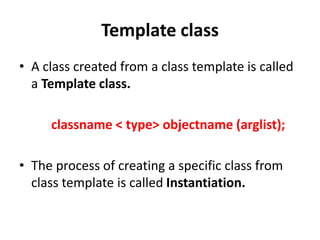
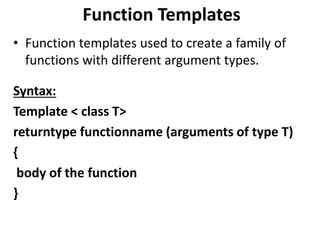
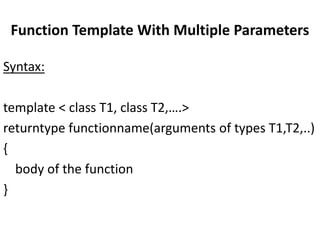
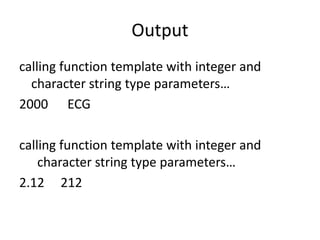
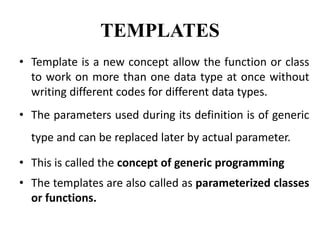
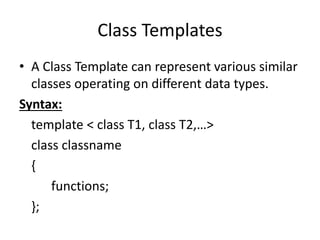
This document discusses templates in C++. Templates allow functions and classes to work with multiple data types without writing separate code for each type. There are two types of templates: class templates, which define a family of classes that operate on different data types, and function templates, which define a family of functions that can accept different data types as arguments. Examples of each template type are provided to demonstrate how they can be used to create reusable and flexible code.


![Eg:
template <class T>
class vector
{
T* v;
int size;
public:
vector (int m)
{
v = new T [size = m];
for ( int i = 0; i <size; i++)
v[i] = 0;
}
vector ( T* a)
{
for ( int i = 0; i <size; i++)
v[i] = a[i];
}
T operator* (vector &y)
{
T sum = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i <size; i++)
sum + = this -> v[i] * y . V [i];
return sum;
}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/templatesinc-200329114231/85/Templates-in-c-6-320.jpg)