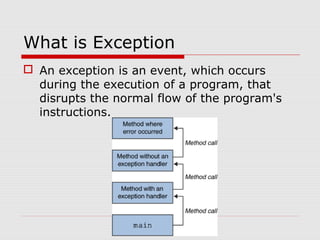
This document discusses exception handling in Java. It defines exceptions as events that disrupt normal program flow. It describes try/catch blocks for handling exceptions and lists advantages like separating error handling code. It discusses different exception types like checked exceptions that must be declared, unchecked exceptions for logic errors, and Errors for JVM problems. It provides best practices like throwing exceptions for broken contracts and guidelines for when to catch exceptions. It also describes antipatterns to avoid, like catching generic exceptions, and exception logging and chaining techniques.