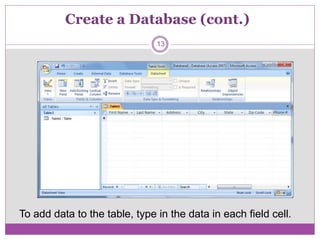
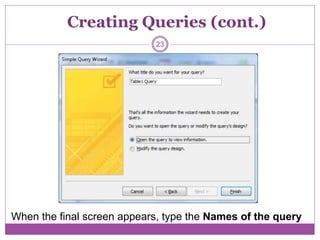
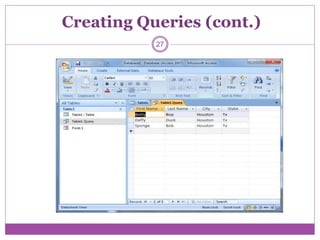
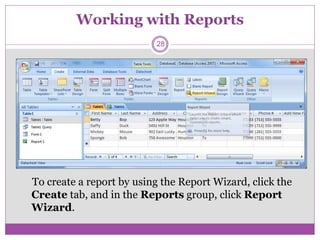
Microsoft Access is a database program that allows users to create and manage databases. It has features like tables to organize data, queries to search and filter data, forms to enter and view data, and reports to analyze and present data. The basic units of a database in Access are fields, records, and tables. Fields make up records, and related records are organized into tables. Access supports relational databases where data across multiple tables is linked through primary and foreign keys.