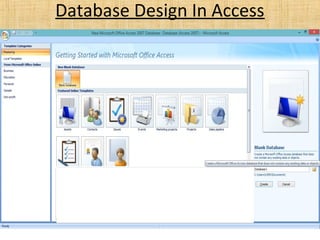
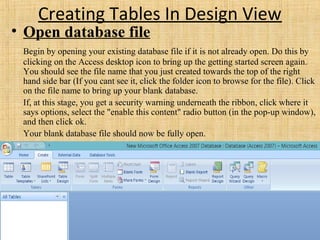
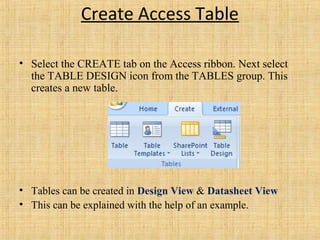
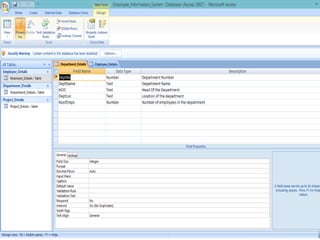
Microsoft Access is a relational database management system used to store and manipulate data. It has a number of key components including tables, queries, forms, reports, macros and modules. Tables are used to store data in rows and columns, while queries are used to manipulate and retrieve data. Forms are used as the interface to add, view and edit data. Reports output data for printing or sharing. Macros automate tasks and modules contain programming code. Relationships link related data across multiple tables. Access supports the SQL query language and uses a .accdb file extension.