This document provides an overview of queries in Microsoft Access, including:
- Simple queries allow selecting records from one or more tables using criteria. Calculated fields can be created using the Expression Builder.
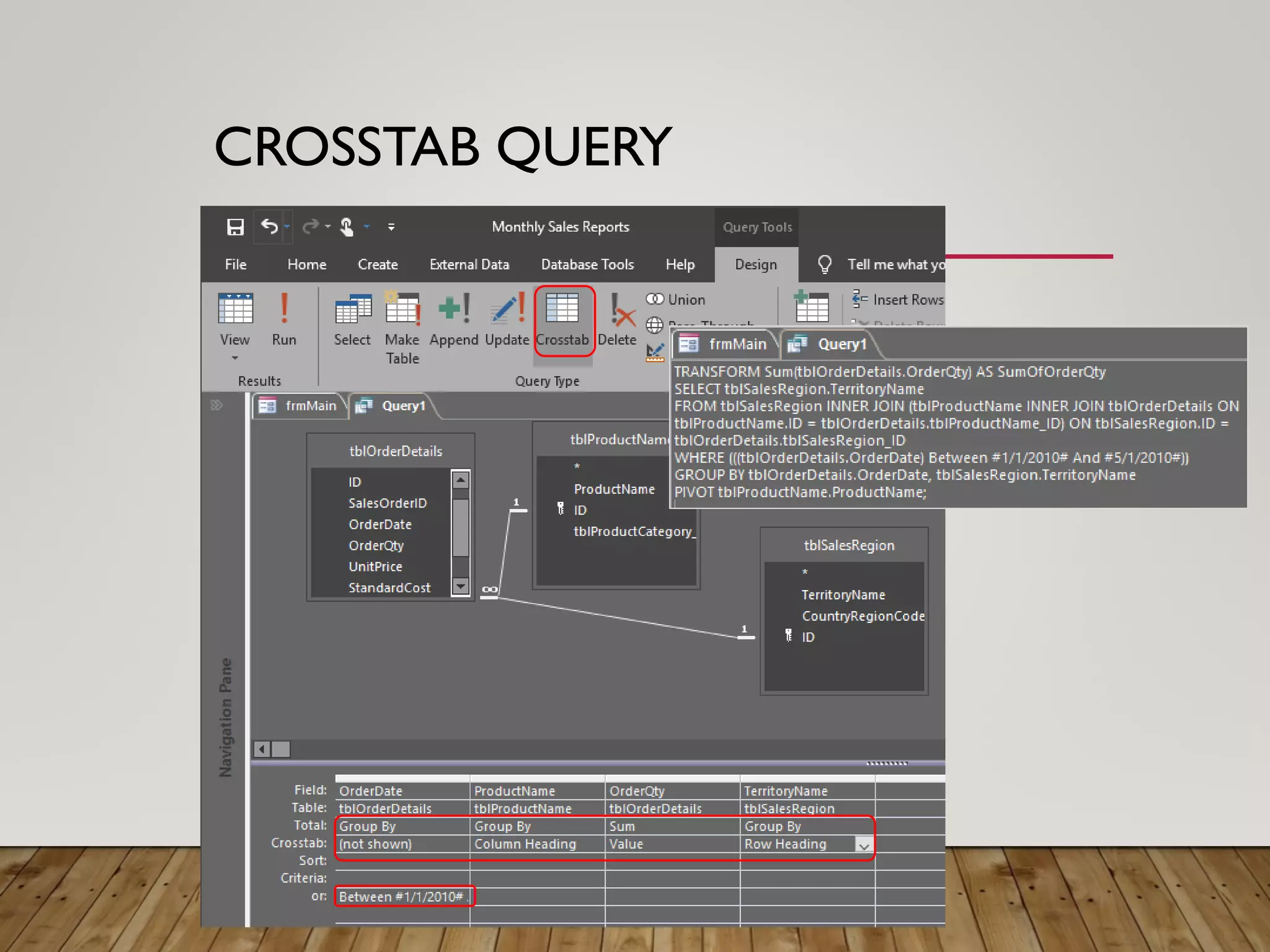
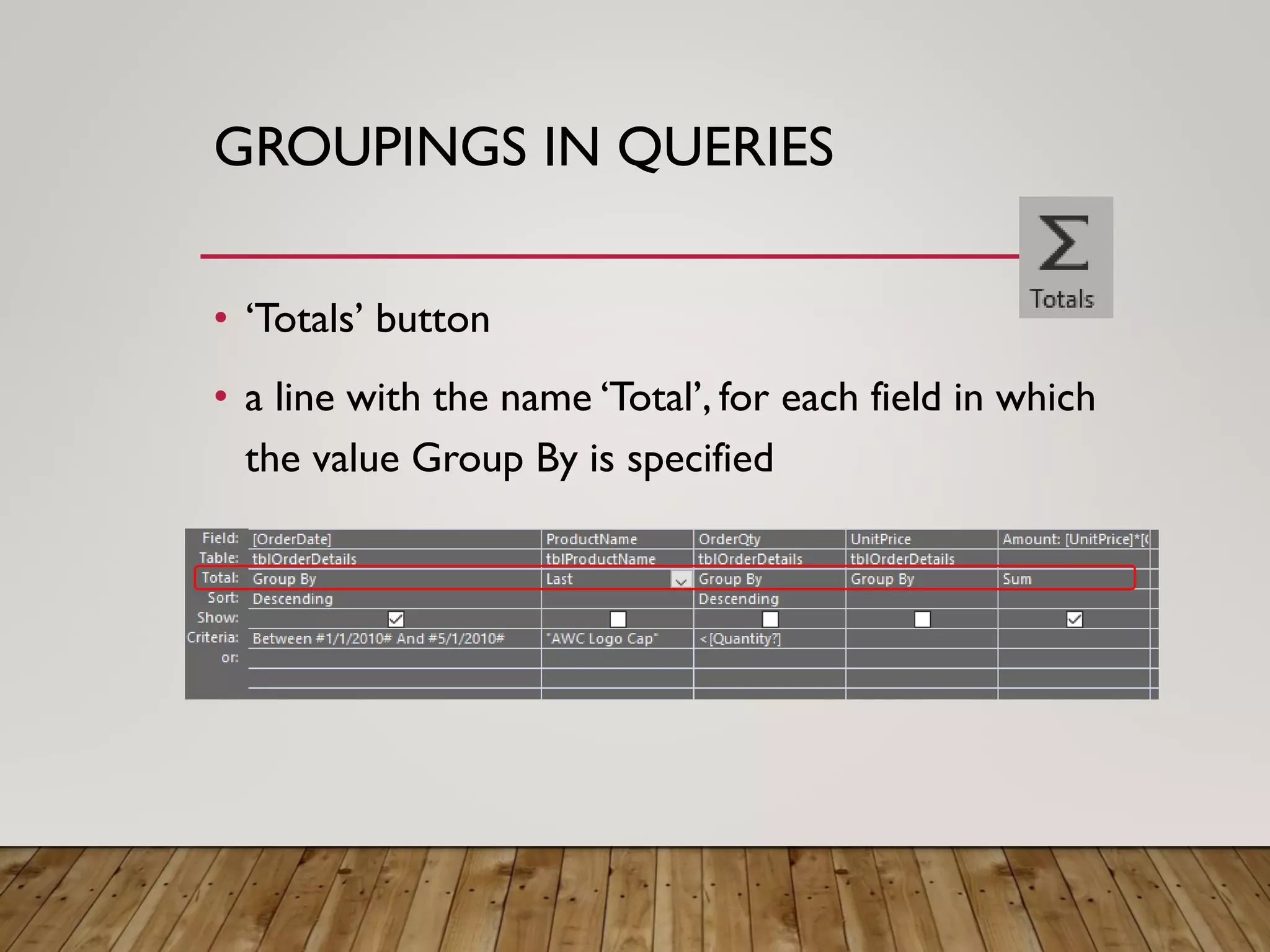
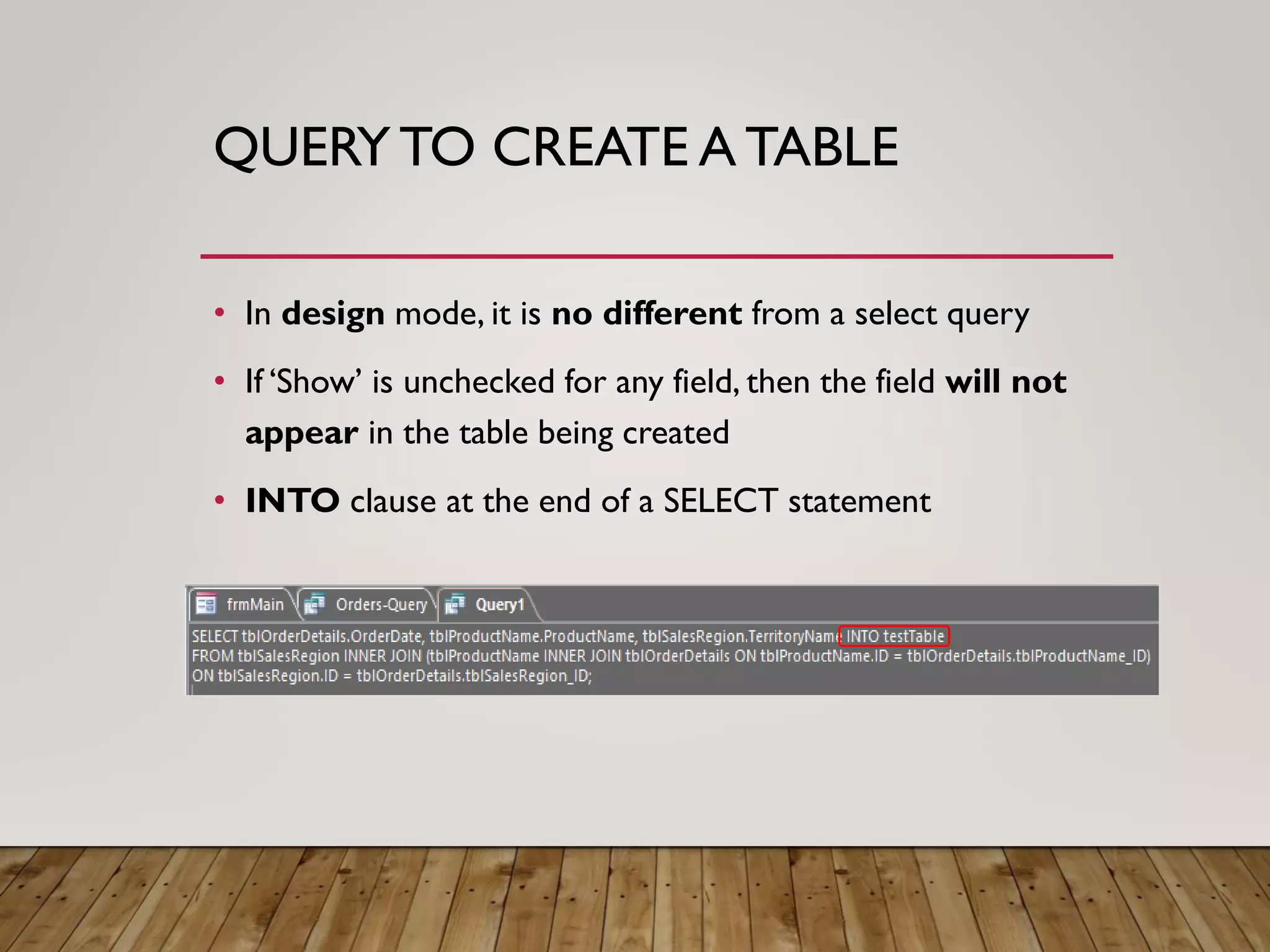
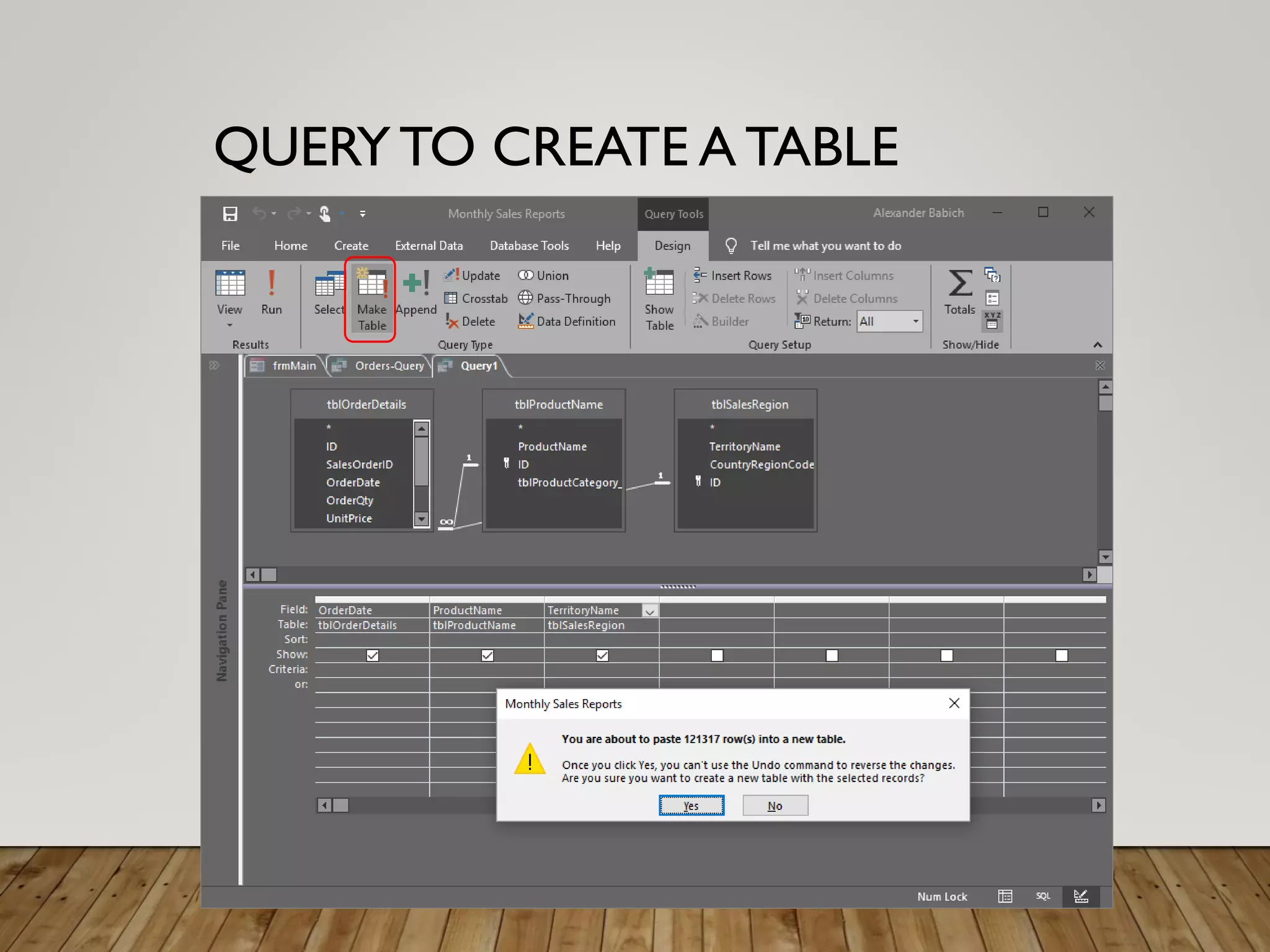
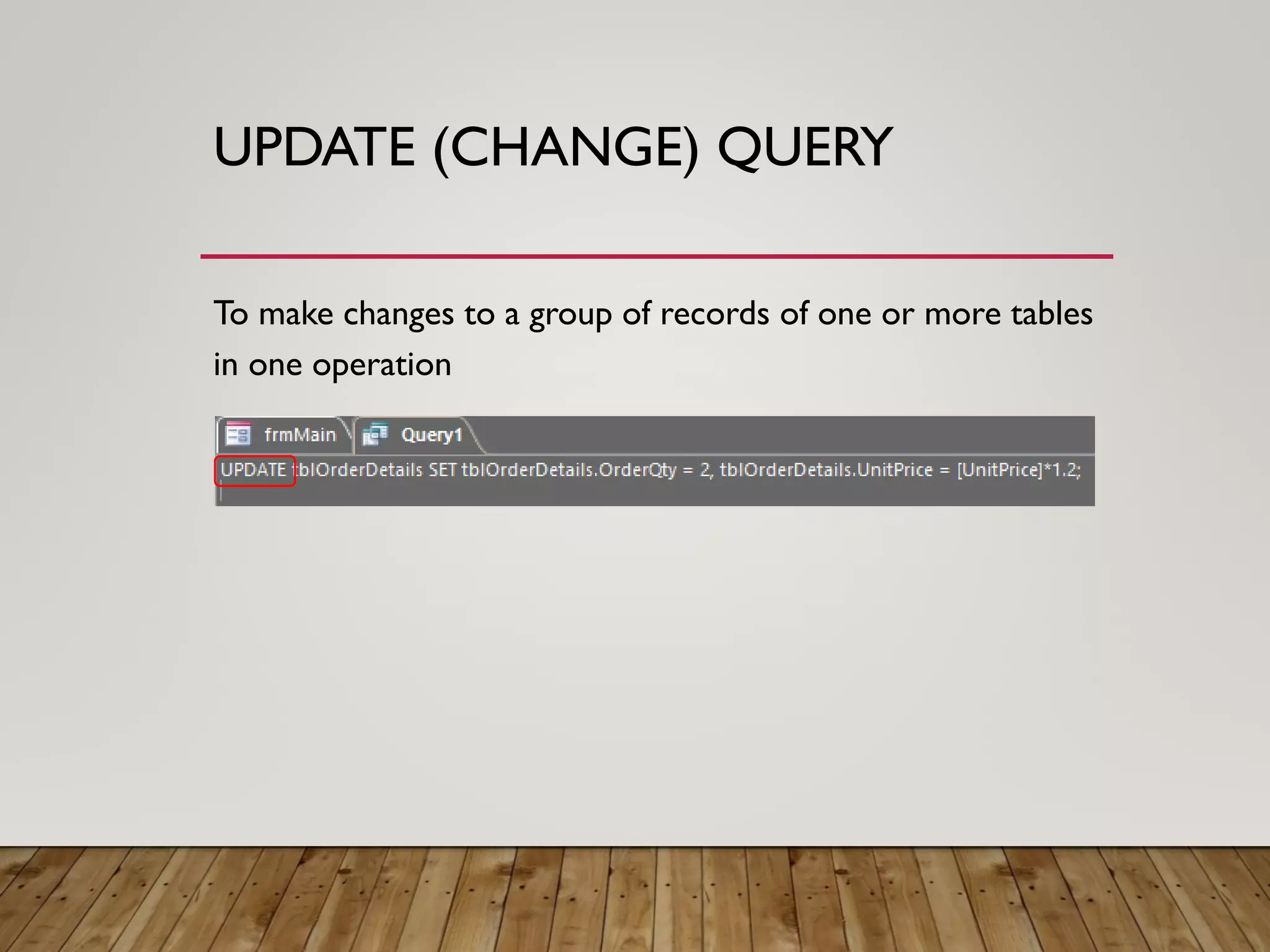
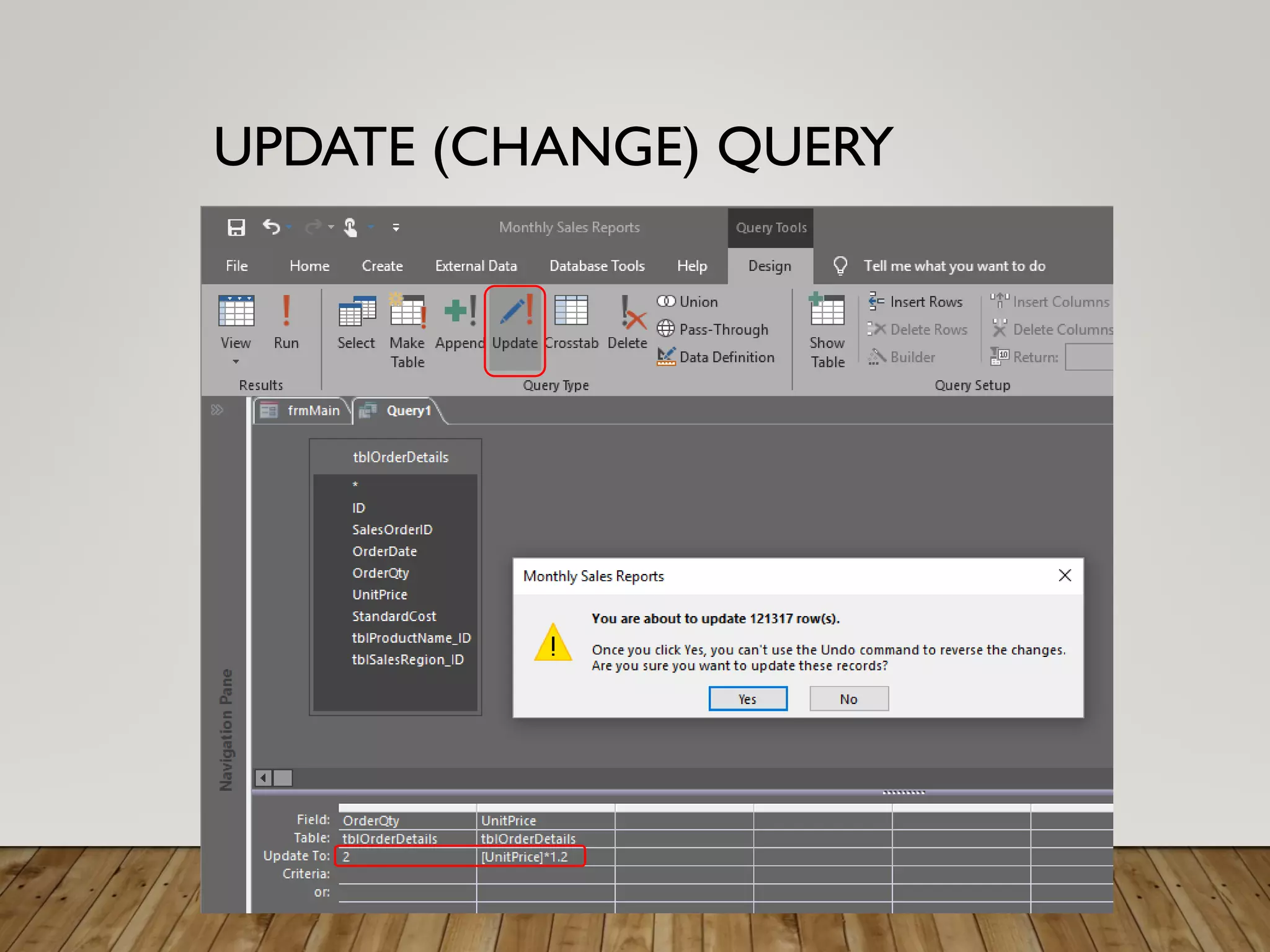
- More complex queries include grouping data, creating tables from queries, updating data, adding new records, and deleting records. Crosstab queries summarize and reformat data.
- The module teaches the concepts of queries, building queries visually, writing selection criteria, and using calculated fields and expressions. However, it does not cover everything about queries.










![SELECTION CRITERIA
boolean expression
• >30
• =‘Smith‘,‘Smith’
• =10, 10
• Like [prompt]
• Or, And
• Between, Is, In](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/access03-190201171117/75/Access-03-12-2048.jpg)









![DELETE (CHANGE) QUERY
Query to delete all records from the table (clearing the table)
DELETE * FROM [...];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/access03-190201171117/75/Access-03-28-2048.jpg)