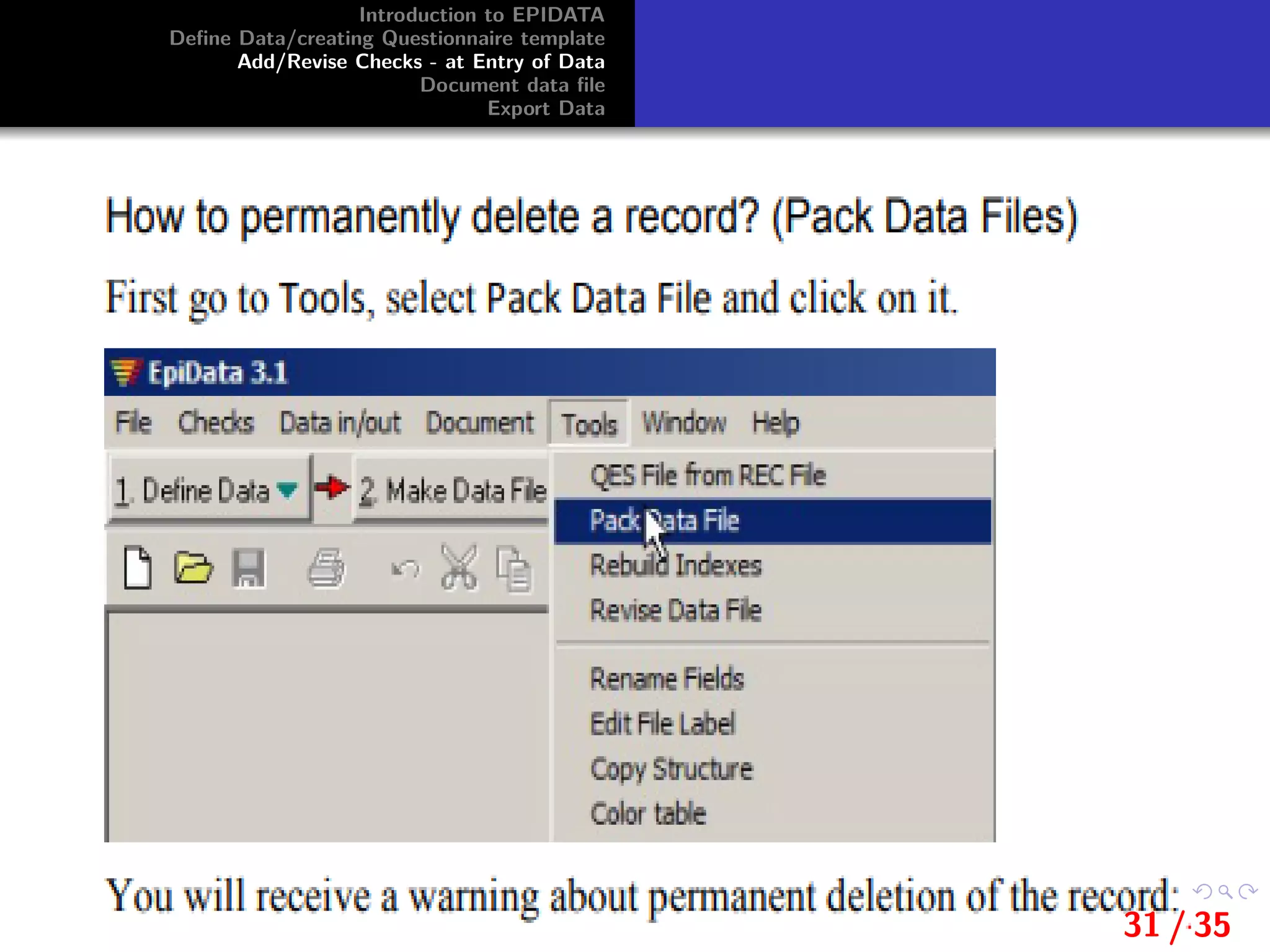
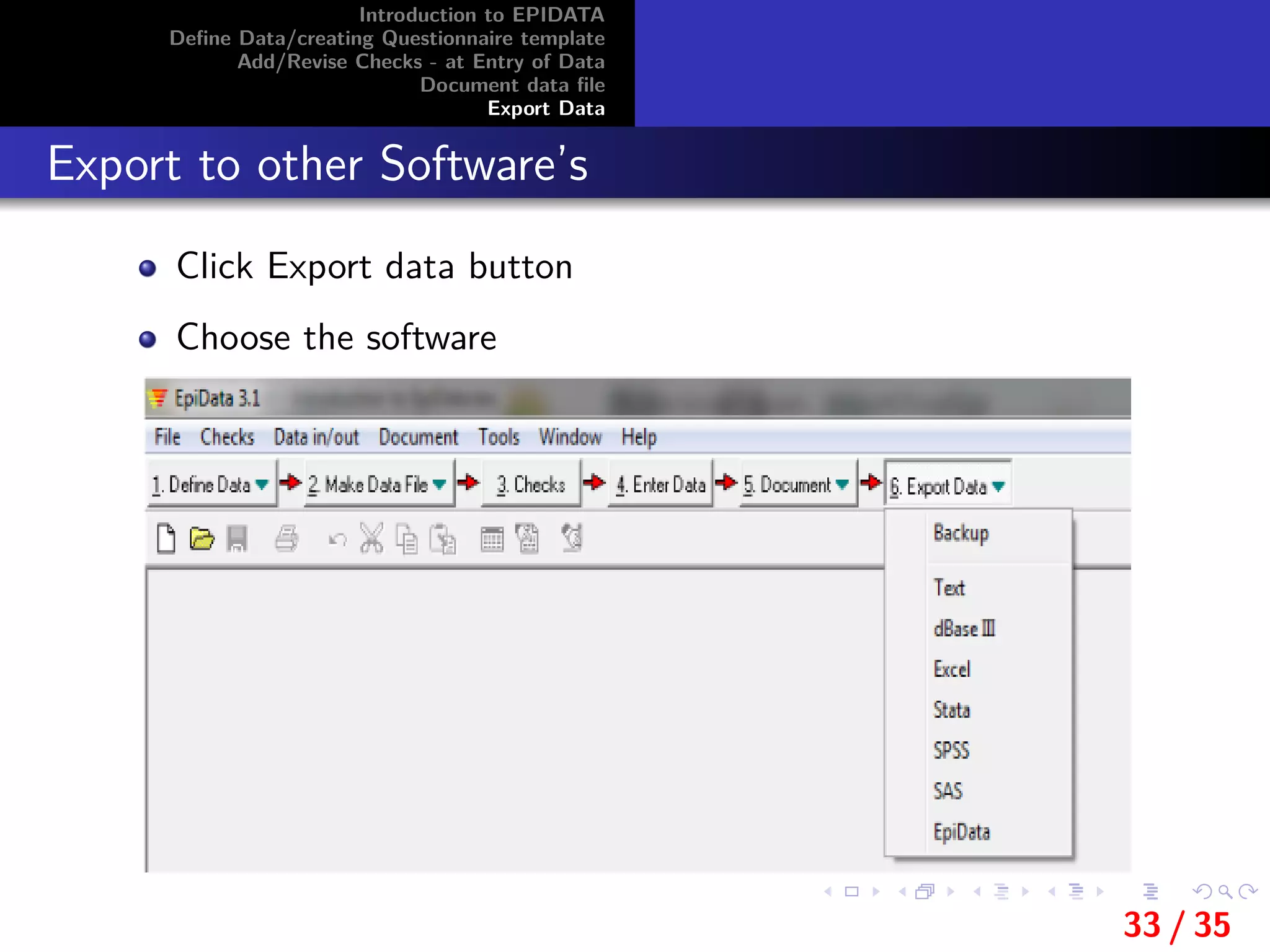
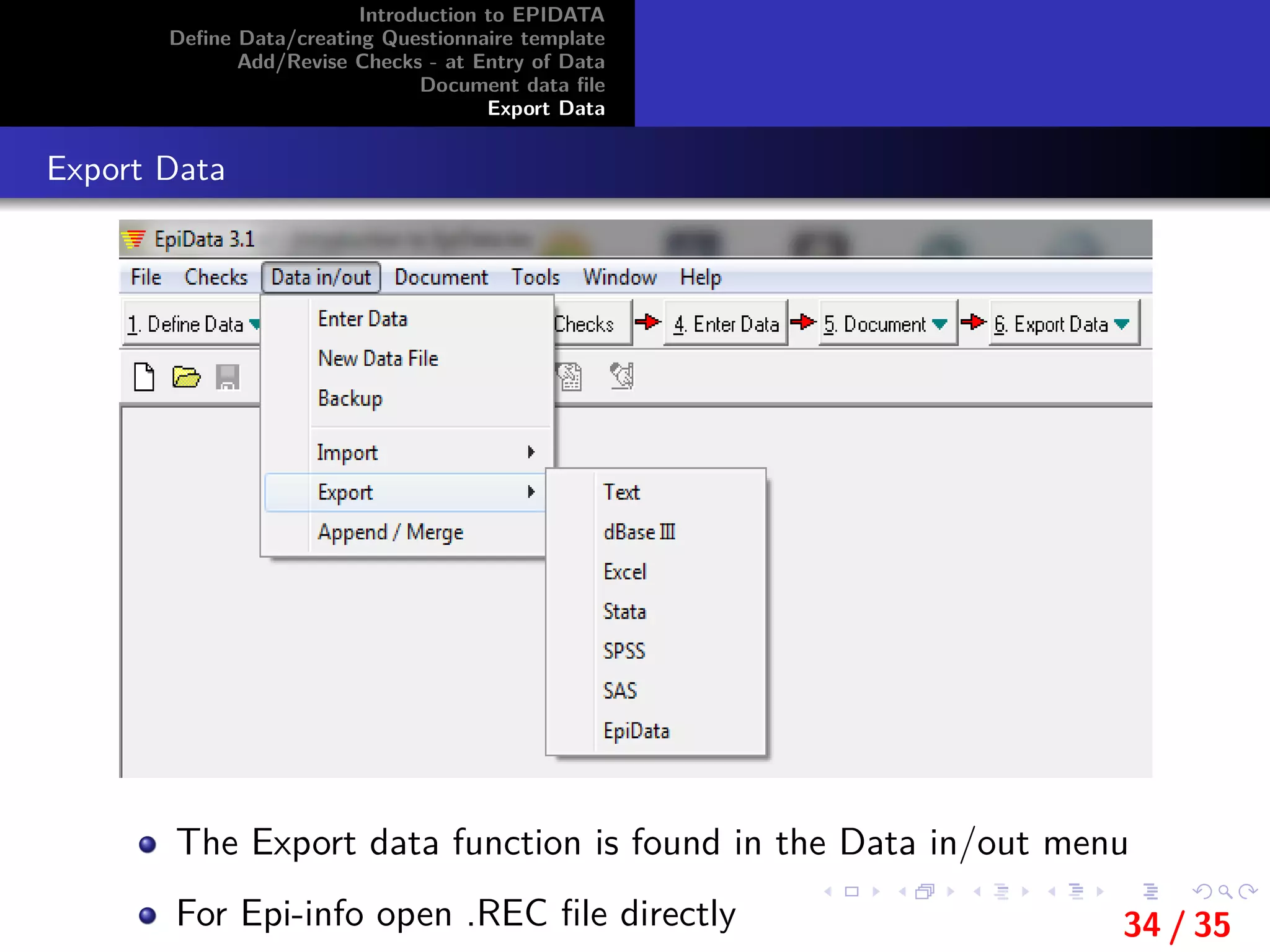
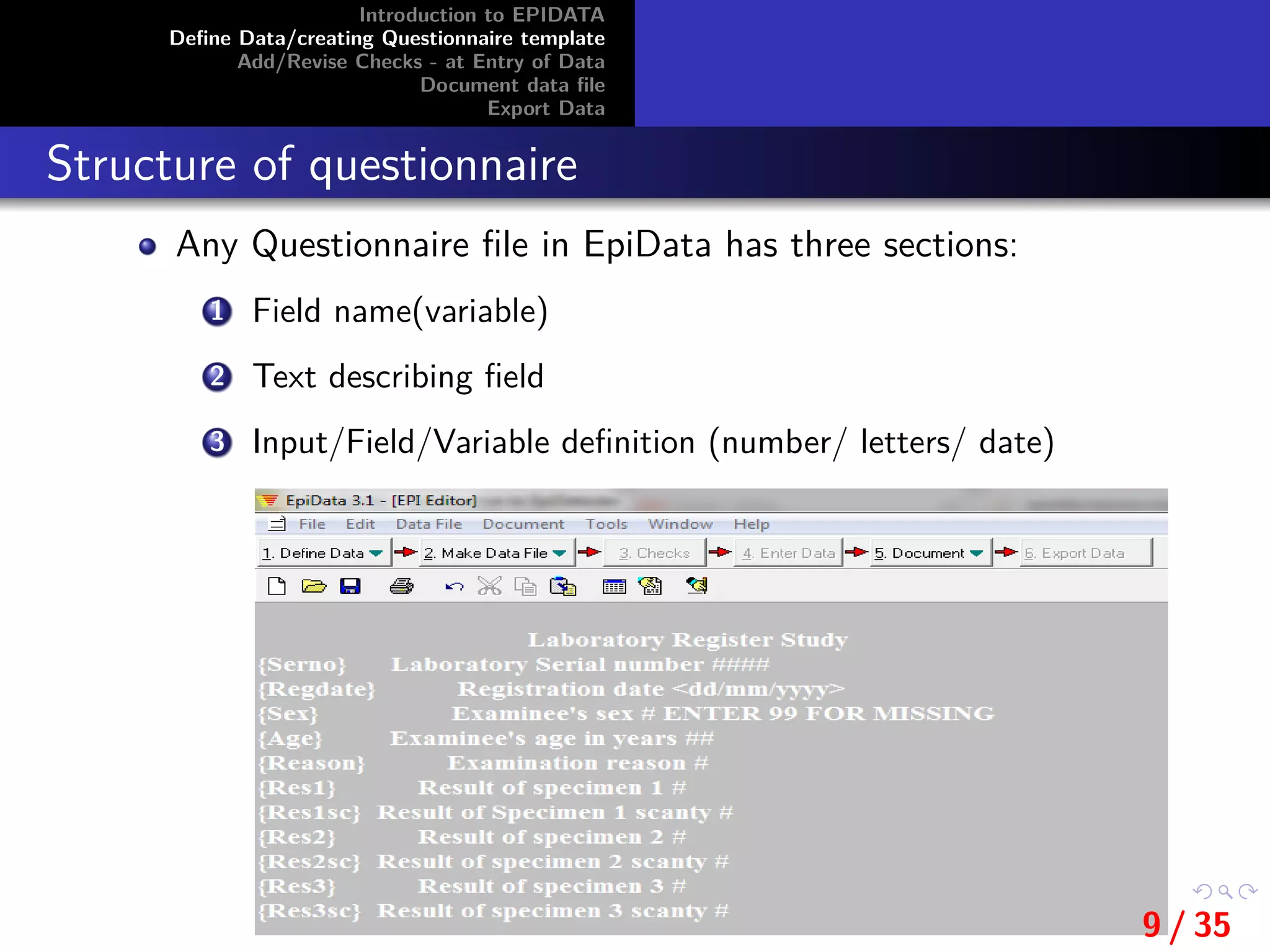
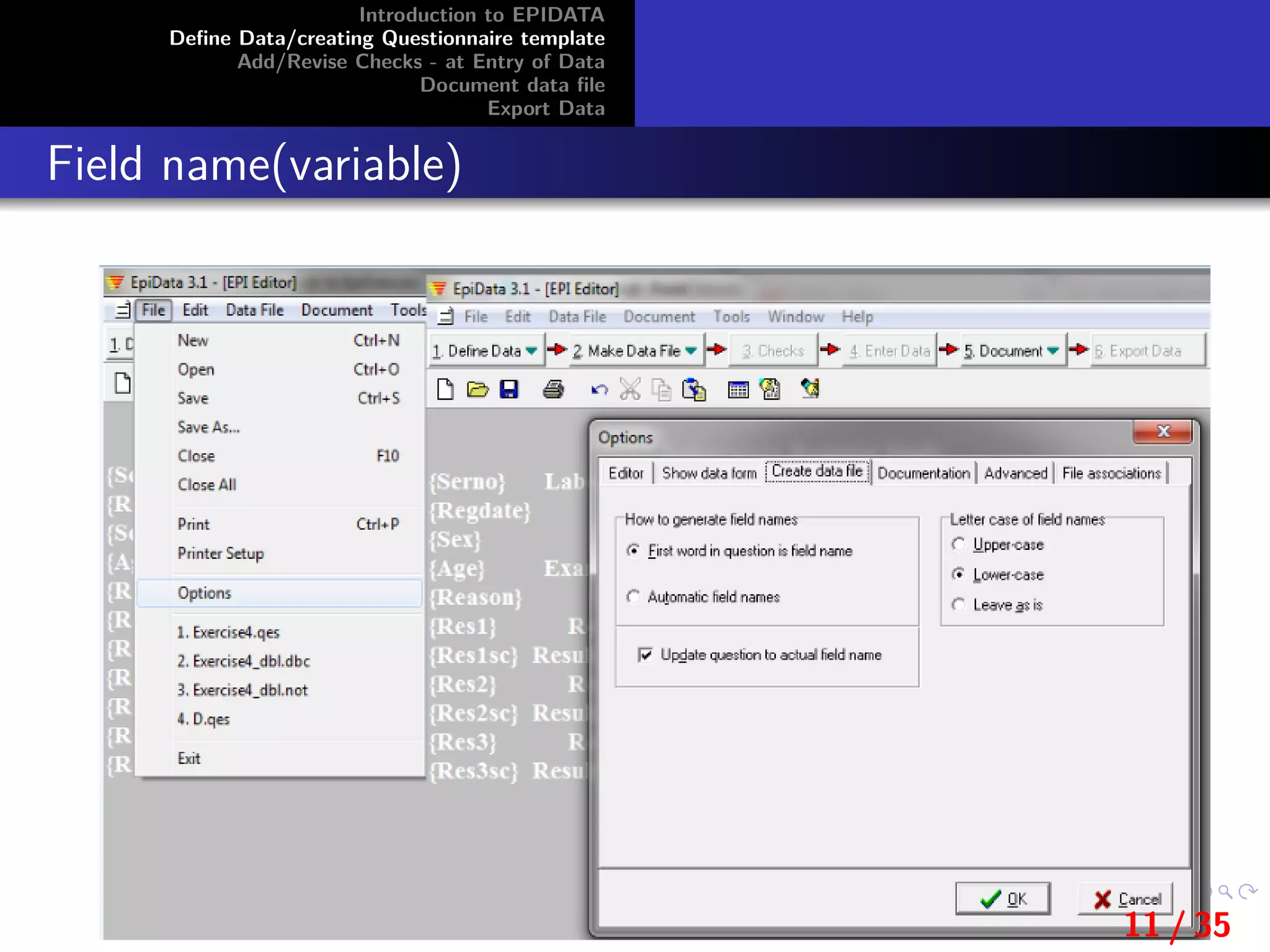
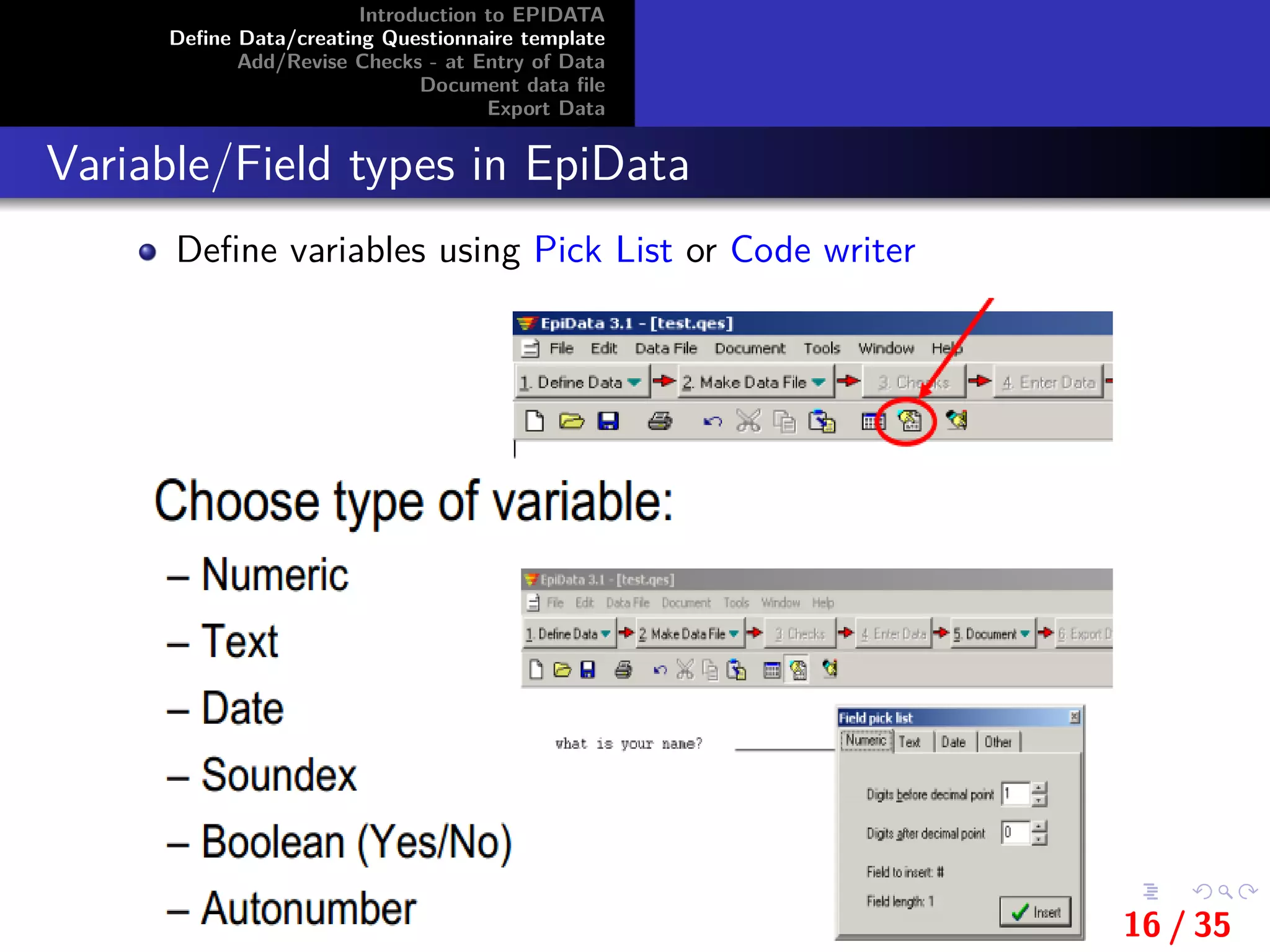
This document provides an introduction and overview of EpiData, including its major functions and file types. It outlines the steps for defining data and creating a questionnaire template in EpiData, including setting variable names, labels, and field types. It also describes how to add and revise checks during data entry and export a data file from EpiData.




















![Introduction to EPIDATA
Define Data/creating Questionnaire template
Add/Revise Checks - at Entry of Data
Document data file
Export Data
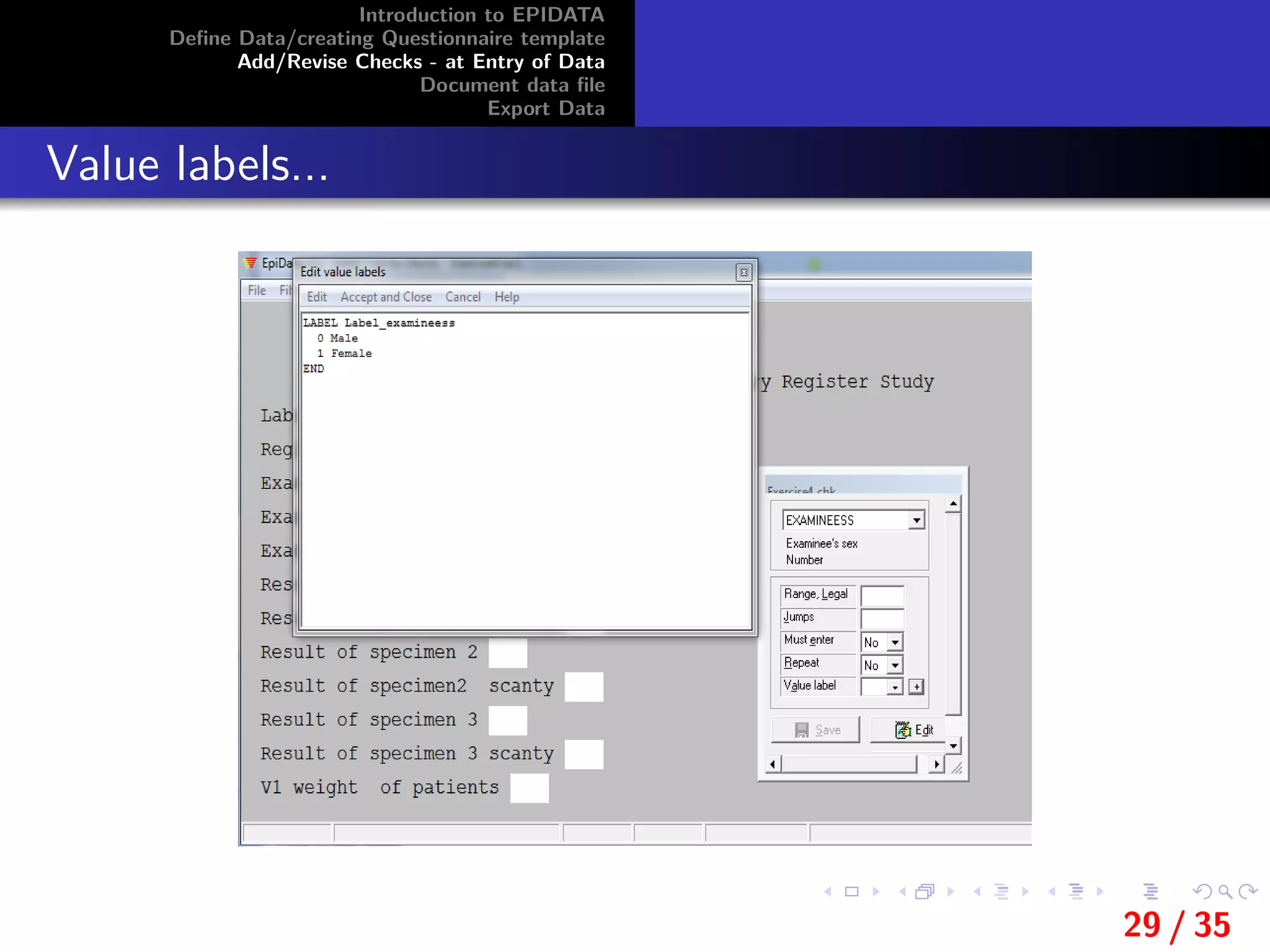
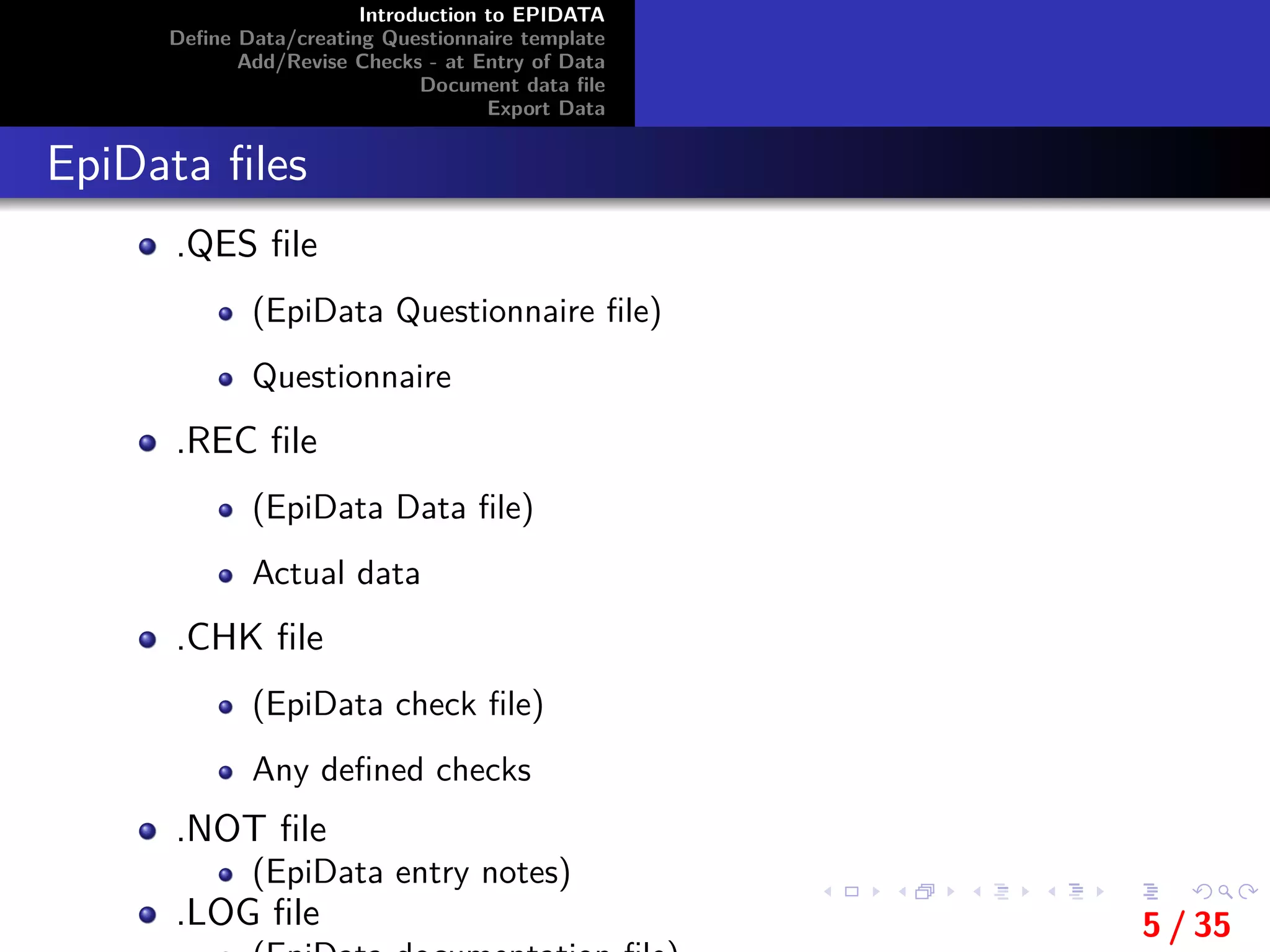
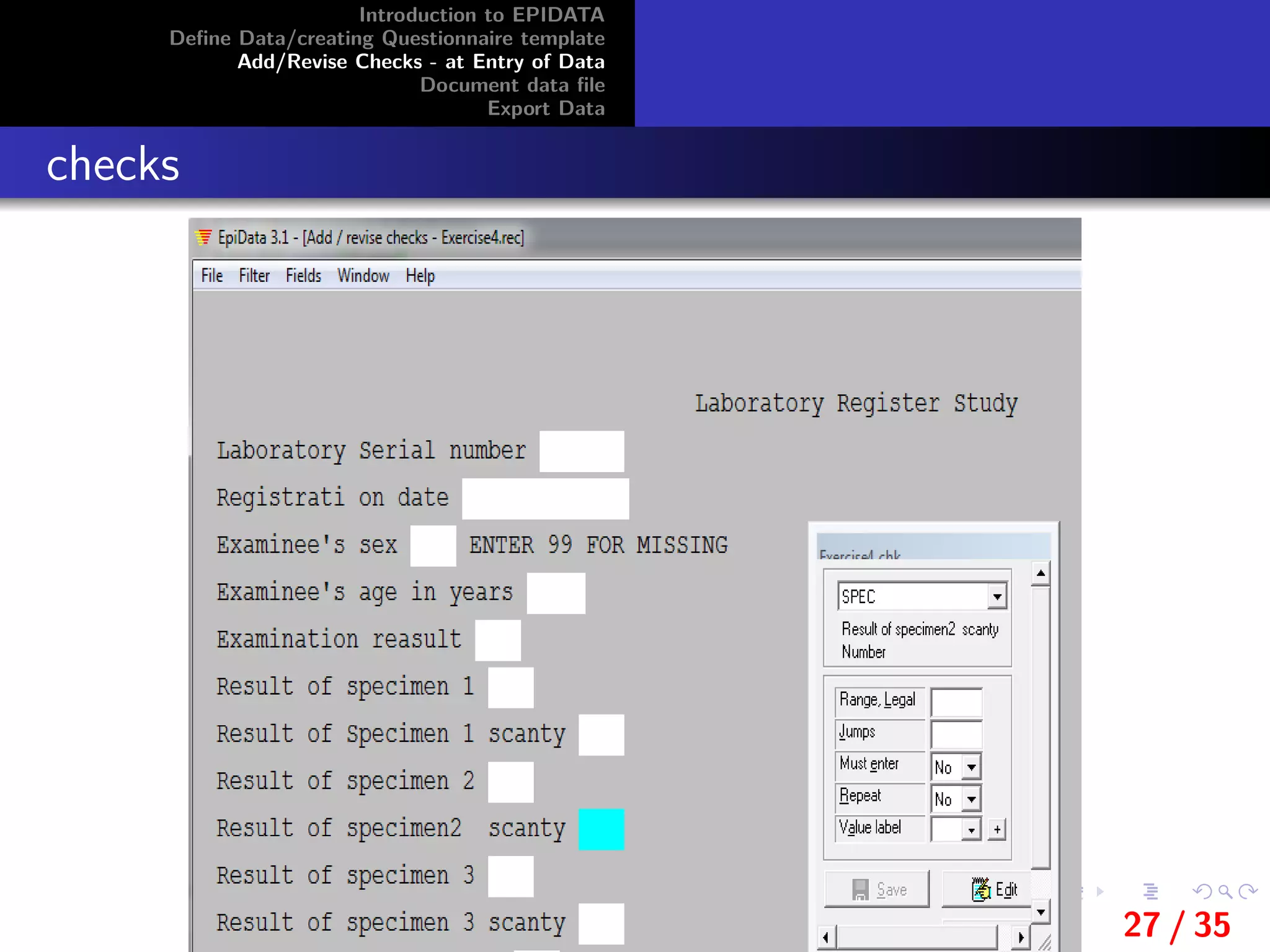
Value labels
Value labels are a set of values combined with text itemsthat
explain the meaning of each value.
For example: A field is created to enter information on the sex
of the informants’.
a value of 0 in the field means that the informant is male and
that a value of 1 means the informant is female.
The value labels in this example would be:
0 Male
1 Female
If a value label is defined then a ’translation table’ can be
shown during data entry if the user presses [F9]or the [+] key
on the numeric keypad).
28 / 35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoepidata-191224140117/75/Introduction-to-epi-data-29-2048.jpg)