The document discusses the significance of pH and solubility in pharmaceutical sciences, highlighting their roles in drug formulation and absorption. It explains how pH influences the solubility and pharmacokinetics of drugs, including the behavior of ionized versus unionized forms. The document also reviews various studies related to pH-dependent solubility profiles of drugs such as diclofenac sodium.

![Introduction
Solubility[1] - It is the property of solid,liquid or
gaseous substance called solute to dissolve in
solid,liquid or gaseous substance.
pH[1] It is defined as negative logarithm of hydrogen
ion concentration in a substance.(Acidic- 0 to 7)
(Alkaline/ Basic-7 to 14).
Formula for calculation of PH[2] -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsolubilityprofile16augustppt-171111200947/85/Ph-and-solubility-profile-2-320.jpg)
![Significance of pH[2] -
It helps to identify a substance either it is acidic or
alkaline in nature.
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, which is the most
acidic, a pH of 7 is neutral, and 14 is the most
alkaline.
Determination of pH of a drug/substance is
very necessary during a pharmaceutical
preparation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsolubilityprofile16augustppt-171111200947/85/Ph-and-solubility-profile-3-320.jpg)
![Significance of Solubility[2] -
Solubility is one of the important parameters
to achieve desired concentration of drug in
systemic circulation for achieving required
pharmacological response .
It plays a major role in parentral formulations.
It differs with different environmental factors
like temperature,pressure etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsolubilityprofile16augustppt-171111200947/85/Ph-and-solubility-profile-4-320.jpg)
![Applications[3]
Solubility is commonly used to describe the
substance, to indicate a substance's polarity, to
help to distinguish it from other substances,
and as a guide to applications of the substance.
Solubility is useful while separating of
mixture.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsolubilityprofile16augustppt-171111200947/85/Ph-and-solubility-profile-5-320.jpg)

![Difference between ionized and unionized drug[4] -
.
An ionized drug will not be absorbed whereas an
unionized drug will be absorbed.
Acidic drugs are in their unionized form in an acidic
environment and basic drugs are unionized in a basic
environment.
Physiologically. an ionized drug will be more available
to tissues than an unionized drug.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsolubilityprofile16augustppt-171111200947/85/Ph-and-solubility-profile-7-320.jpg)
![pka and it’s relation with pH[4] -
pKa explains what the pH needs to be in order for a
chemical species to donate or accept a proton.
The lower the pH, the higher the concentration of
hydrogen ions, [H+]. The lower the pKa, the stronger
the acid and the greater its ability to donate protons.
pH depends on the concentration of the solution.
because a weak acid could actually have a lower pH
than a diluted strong acid. For example, concentrated
vinegar (acetic acid, which is a weak acid) could have
a lower pH than a dilute solution of hydrochloric acid
(a strong acid). On the other hand, the pKa value is a
constant for each type of molecule. It is unaffected
by concentration.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsolubilityprofile16augustppt-171111200947/85/Ph-and-solubility-profile-8-320.jpg)
![RELATION OF Pka WITH SOLUBILITY[4]
PKa values influence behaviour of absorption, binding
and salt selection, as well as influencing other
physicochemical properties such as lipophilicity,
solubility and dissolution.
Lower the Pka value greater will be dissociation
const.Hence, solubility is more.
More the dissociation value then more is the solubility.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsolubilityprofile16augustppt-171111200947/85/Ph-and-solubility-profile-9-320.jpg)
![Papers Published on pH &
solubilization
1-Mosharraf etal; [5] explained that the solubility
vs. pH profiles of Propylparaben has been
determined through two different methods, the
shake-flask (S-F) and the cheqsol methods using
in both instances the appropriate Henderson–
Hasselbalch (H–H) equation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsolubilityprofile16augustppt-171111200947/85/Ph-and-solubility-profile-10-320.jpg)


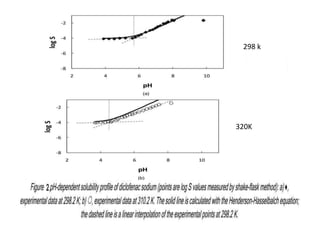
![2- R. J. Prankerd[6] explained the solubilities of sparingly
soluble drug-compounds in water was measured at
constant temperatures (298.2 and 310.2 K) by shake-flask
method. Drug presented in this work is diclofenac sodium
. In the current experimental condition the Henderson-
Hasselbalch (HH) relationship was used to predict the
pH-dependent solubility profiles of choosen drug at two
temperatures. For this purpose pH dependent profile of
drug were determined at temperature of 298.2 K and
310.2 K.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsolubilityprofile16augustppt-171111200947/85/Ph-and-solubility-profile-13-320.jpg)

![3-Khan MA etal;[7] studied to illustrate the effect of
pH on dissolution profile of diclofenac sodium
sustained release tablets .Here the drug content in
each tablets was 100mg. The eqiupments used
were UV/visible Spectrophotometer,tablet
dissolution test apparatus,paddle and Friability test
apparatus and characterized for physical
examinations.% of drug release was studied.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsolubilityprofile16augustppt-171111200947/85/Ph-and-solubility-profile-16-320.jpg)
![[7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsolubilityprofile16augustppt-171111200947/85/Ph-and-solubility-profile-17-320.jpg)



