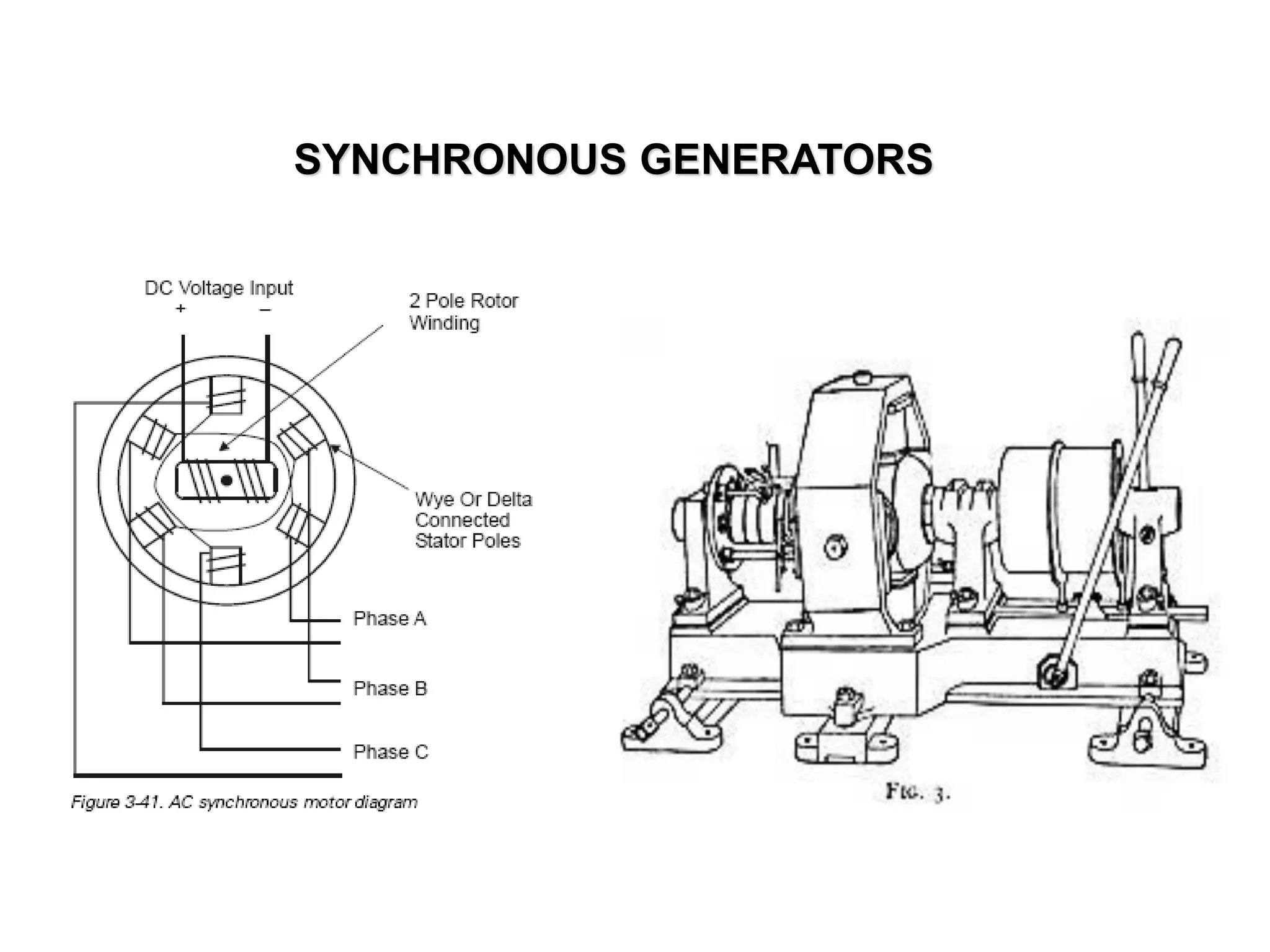
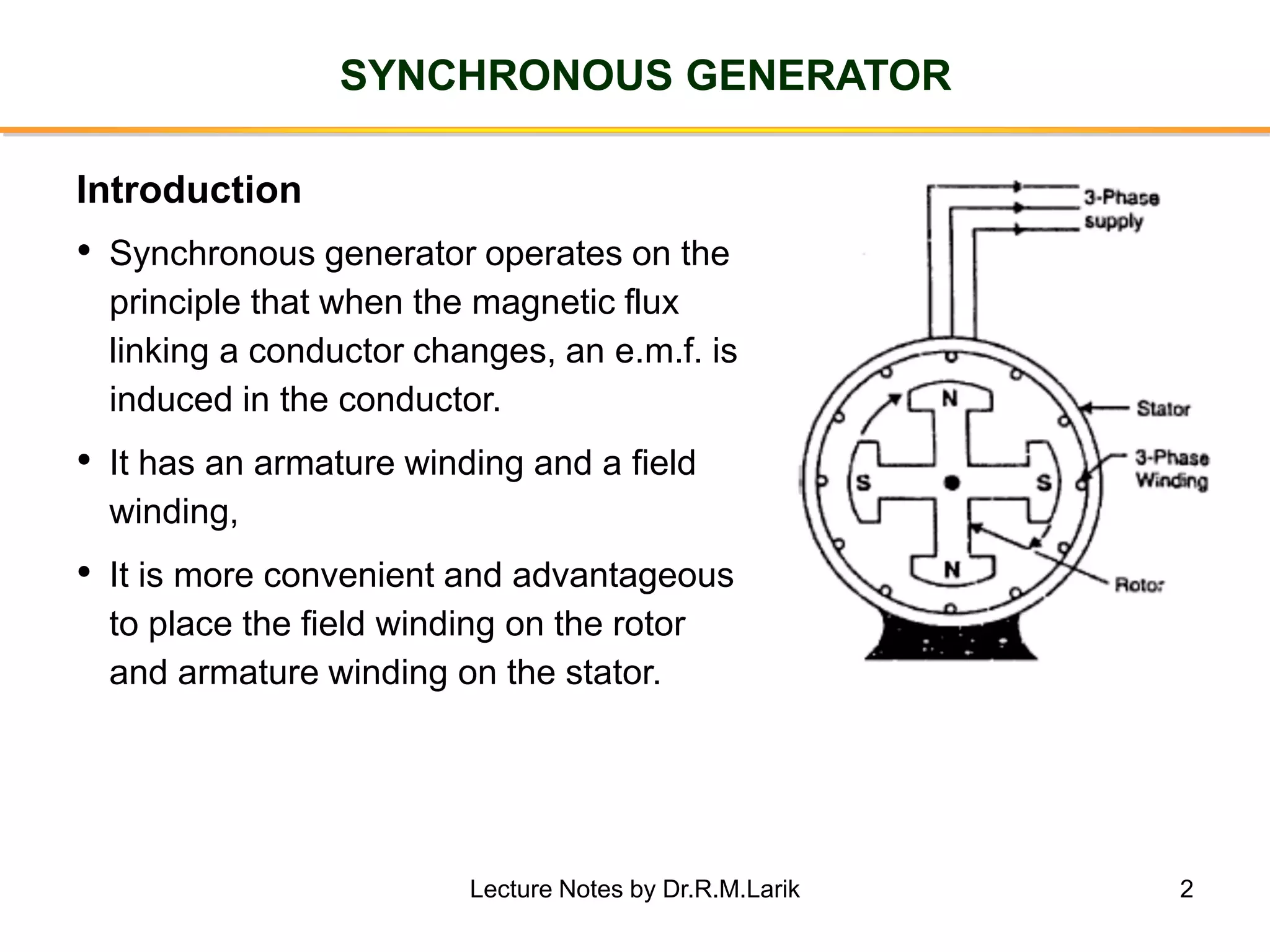
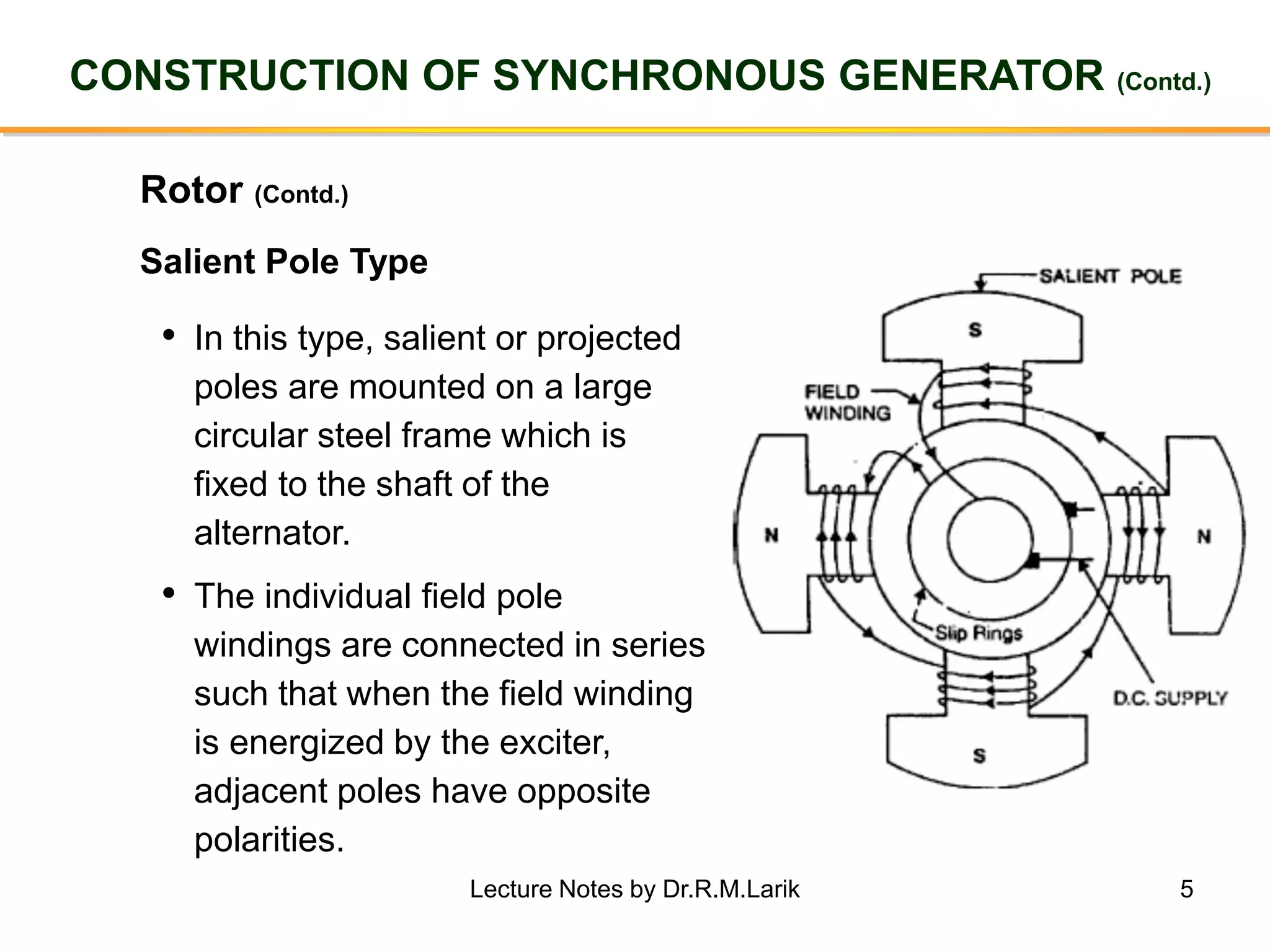
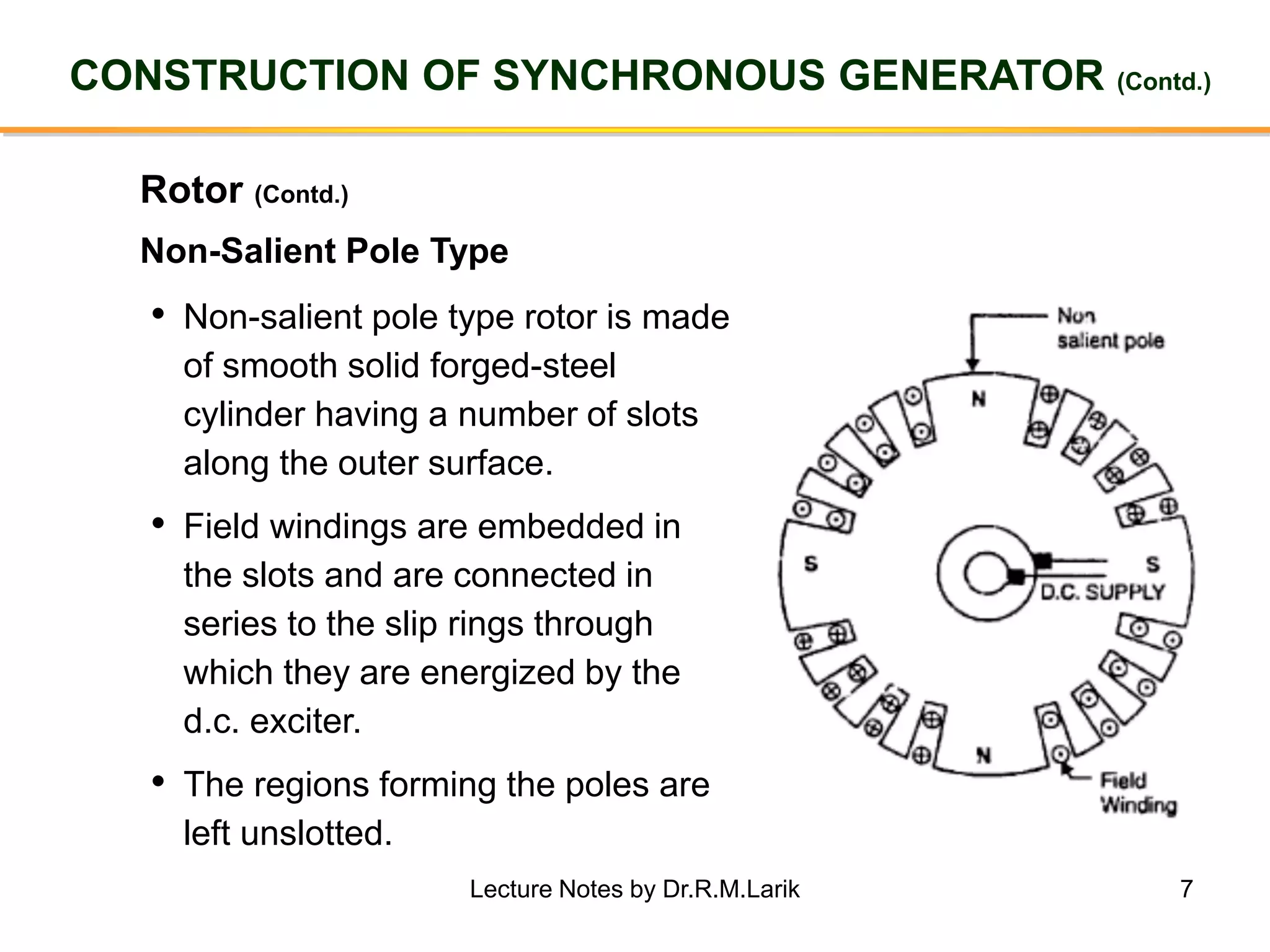
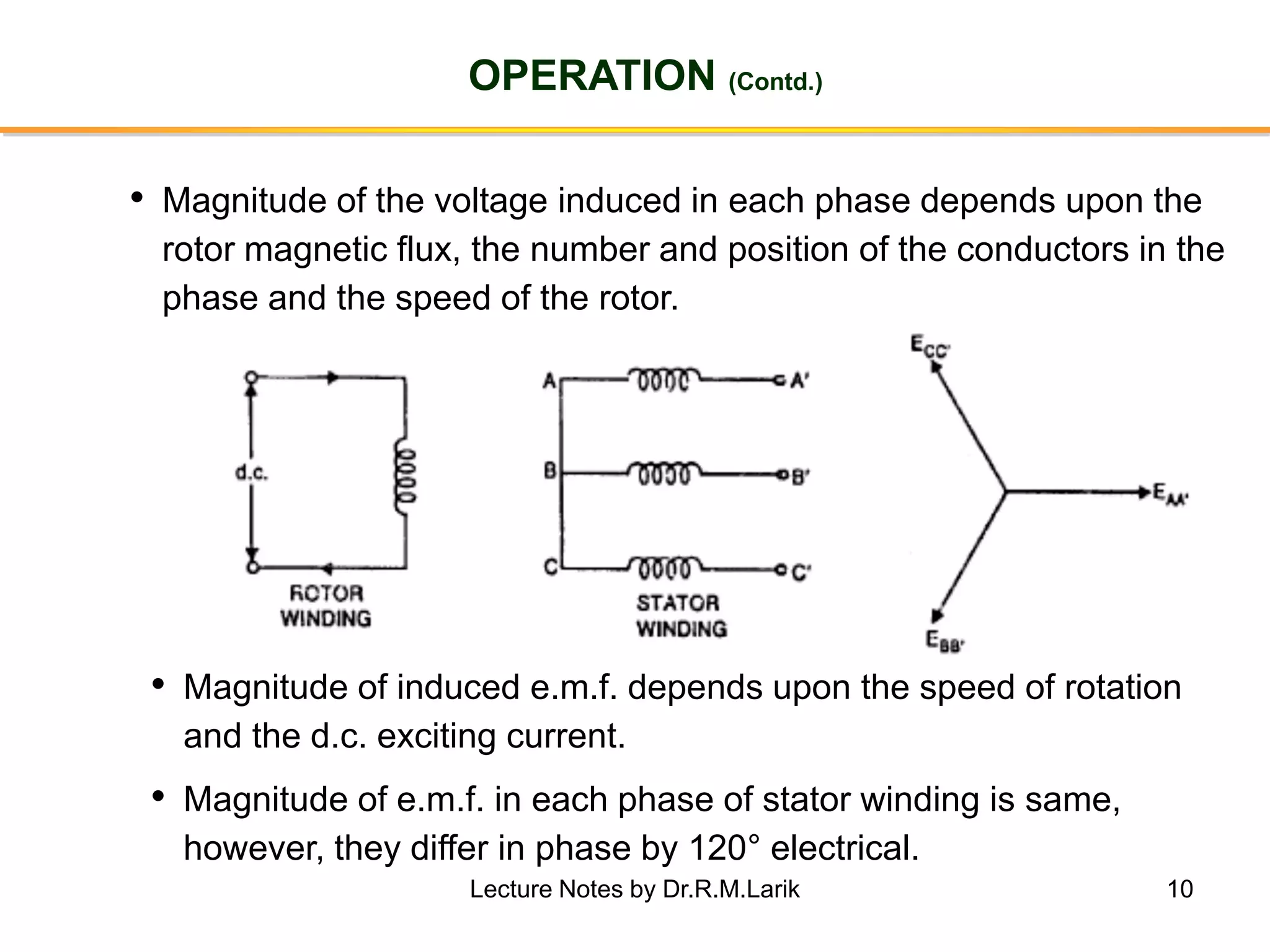
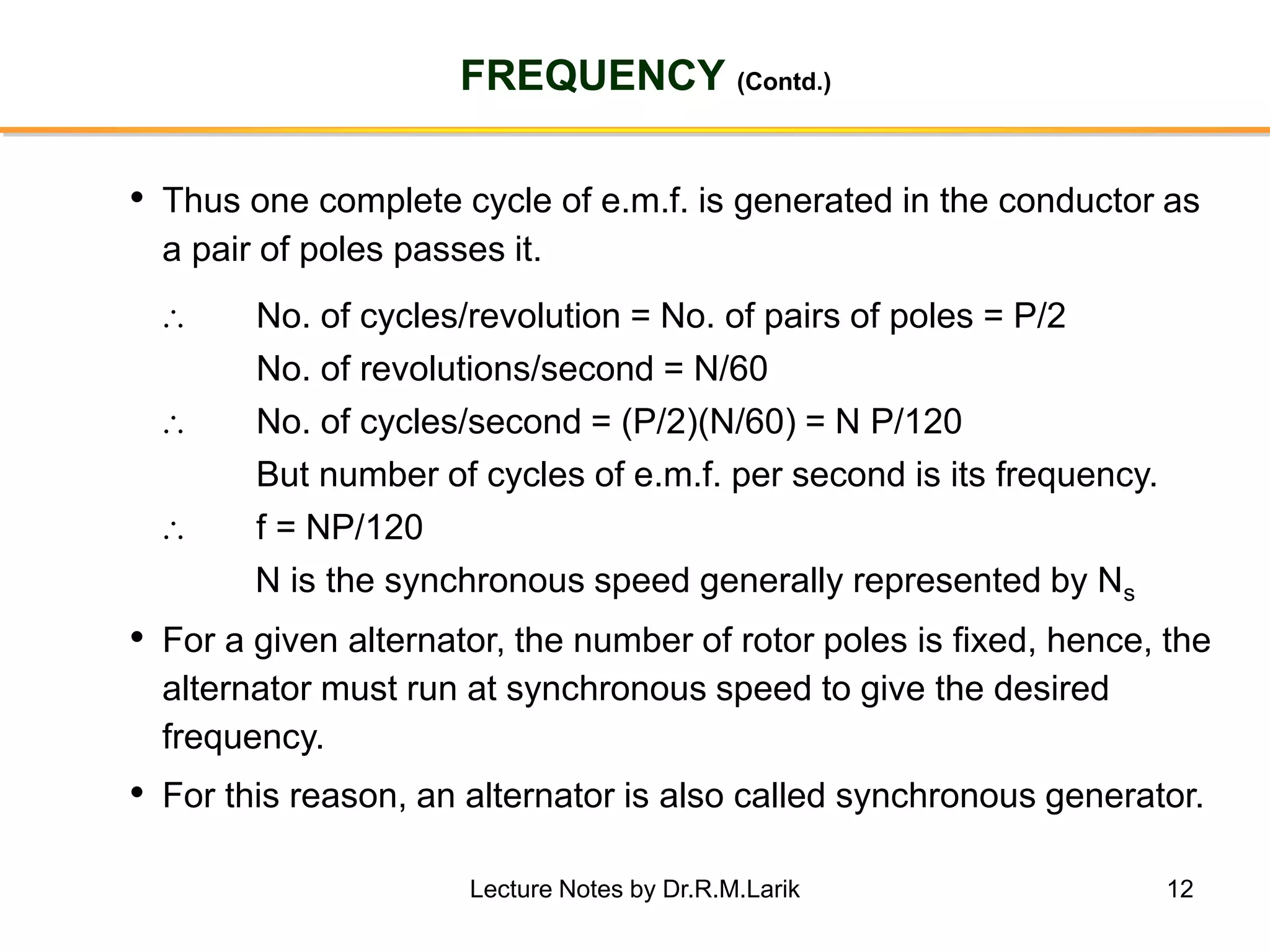
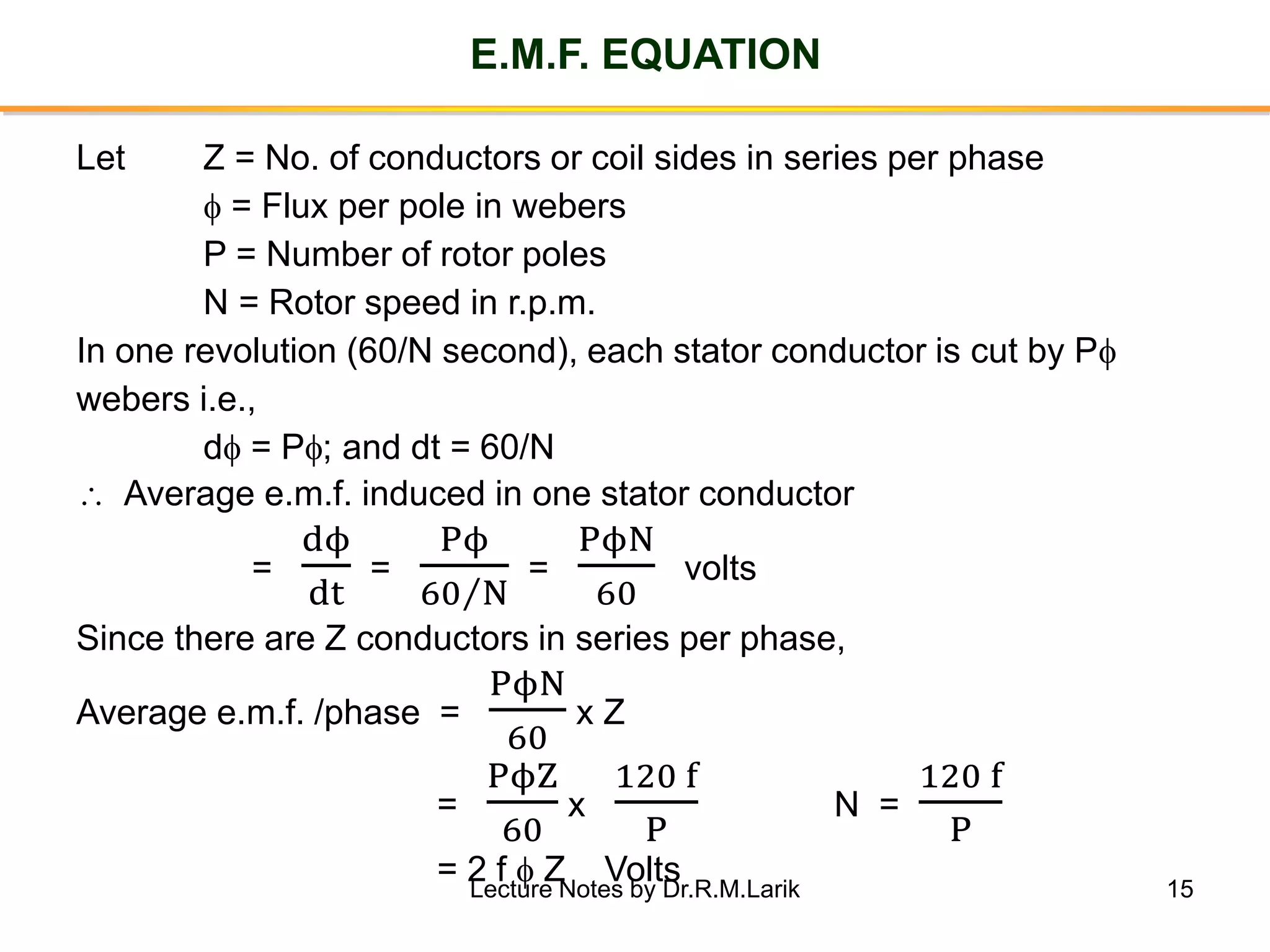
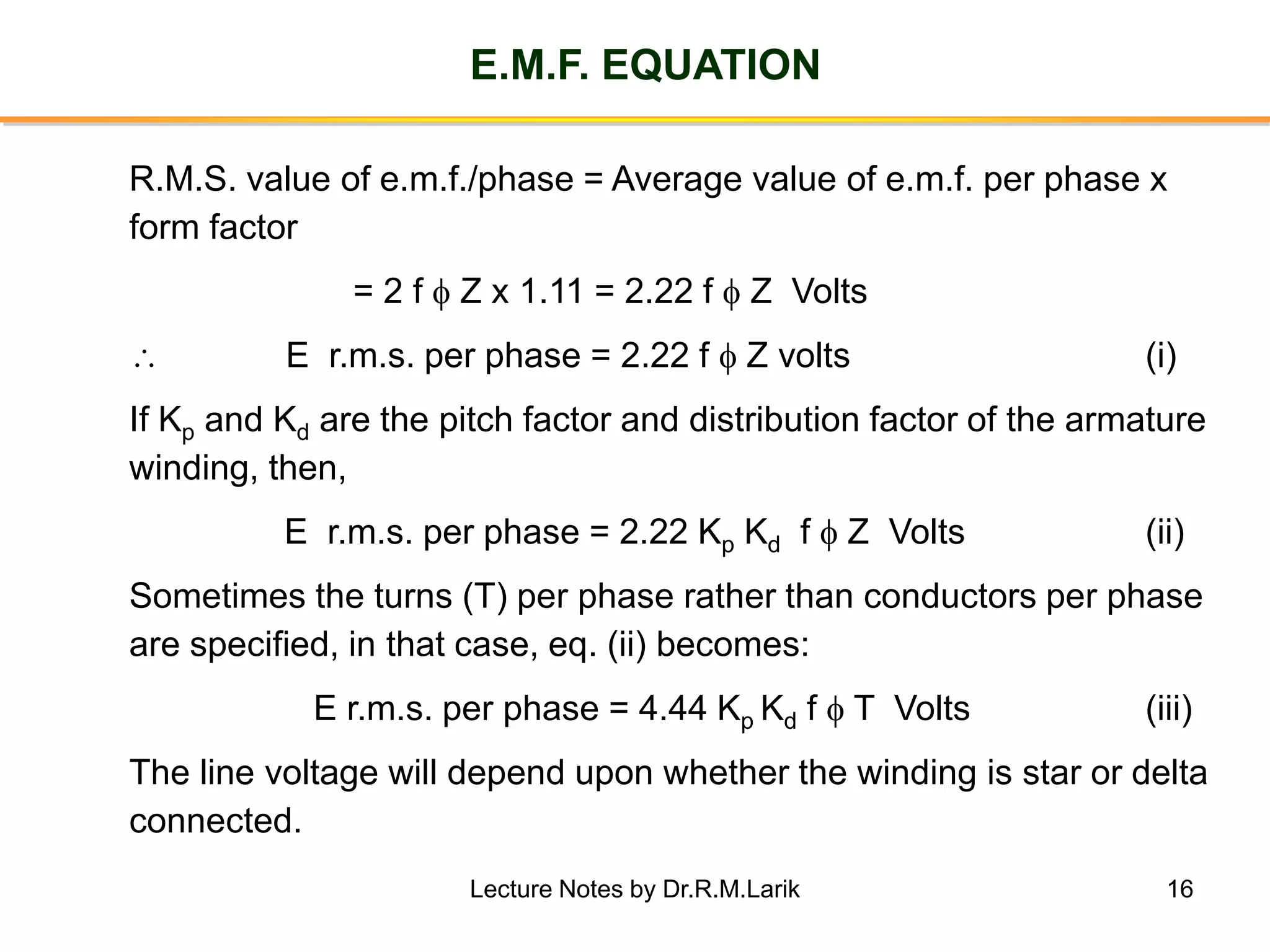
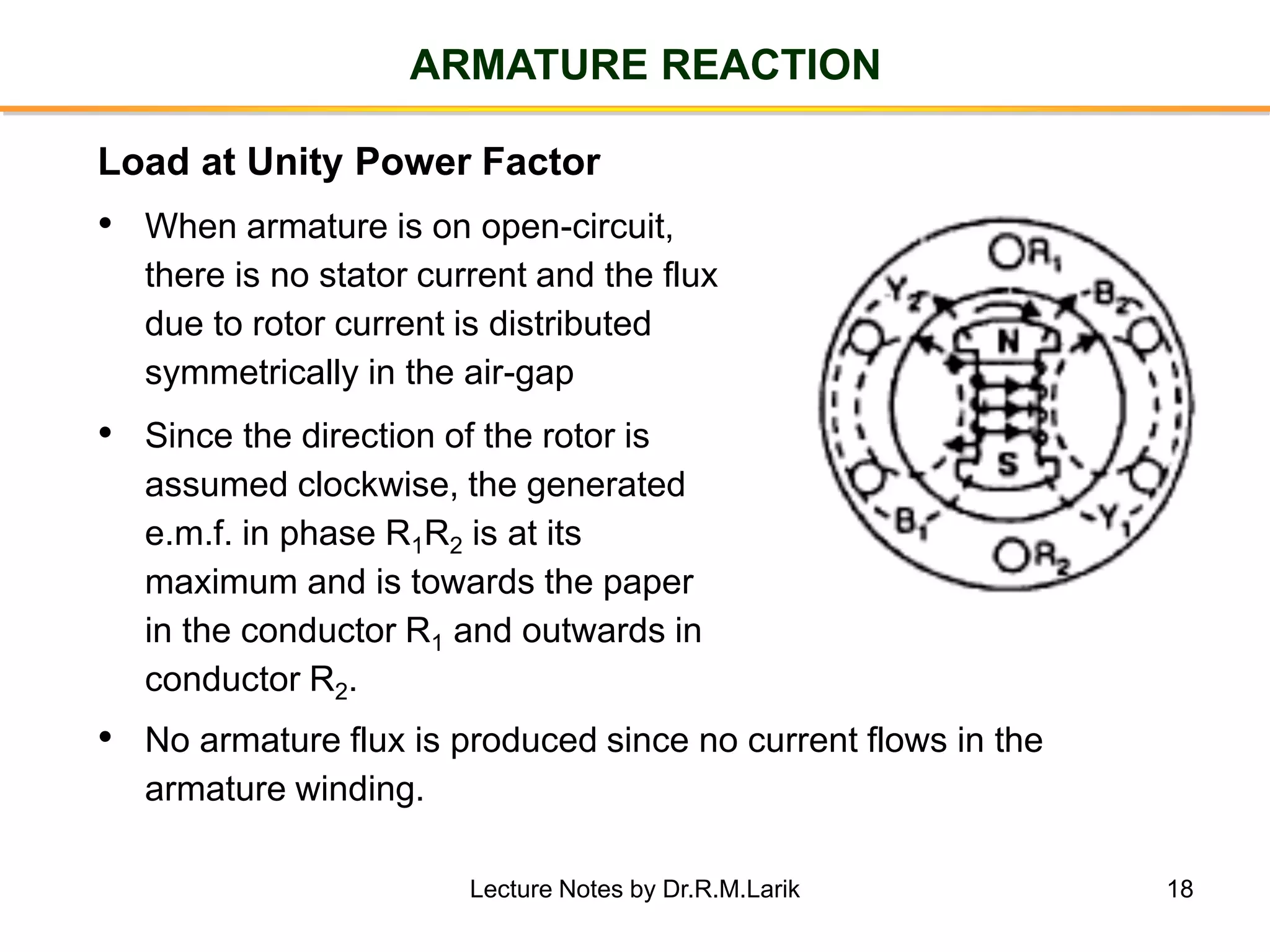
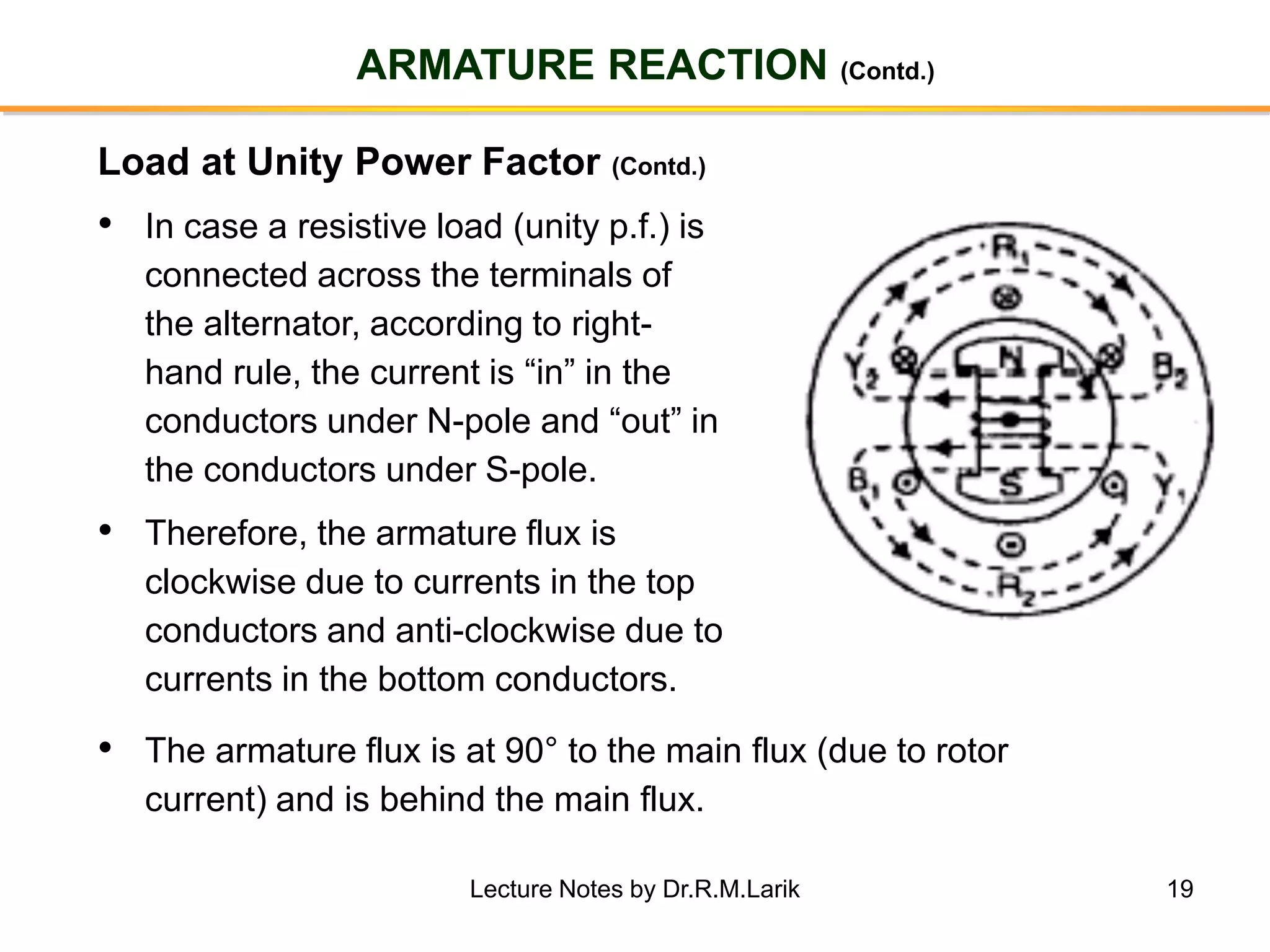
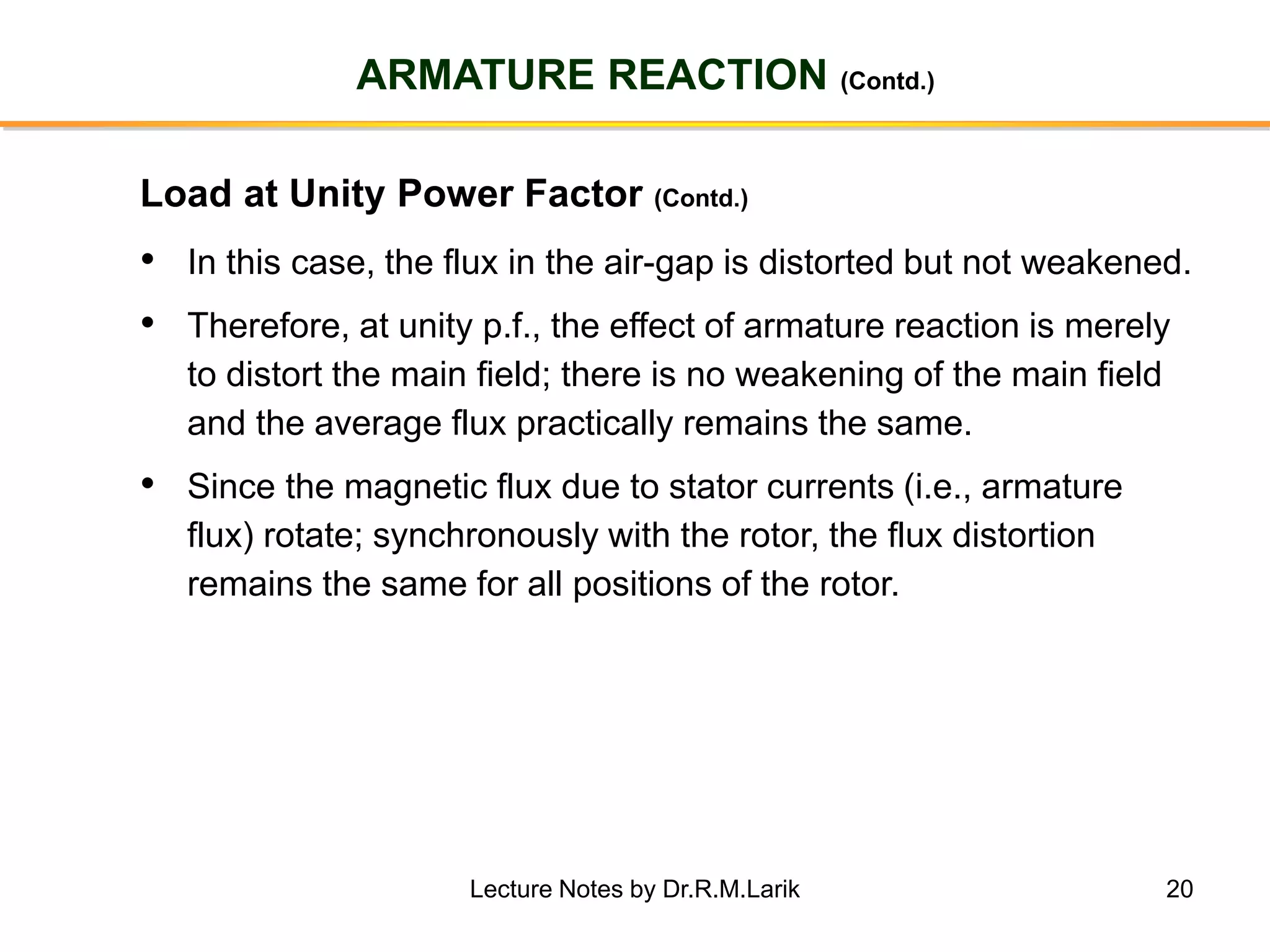
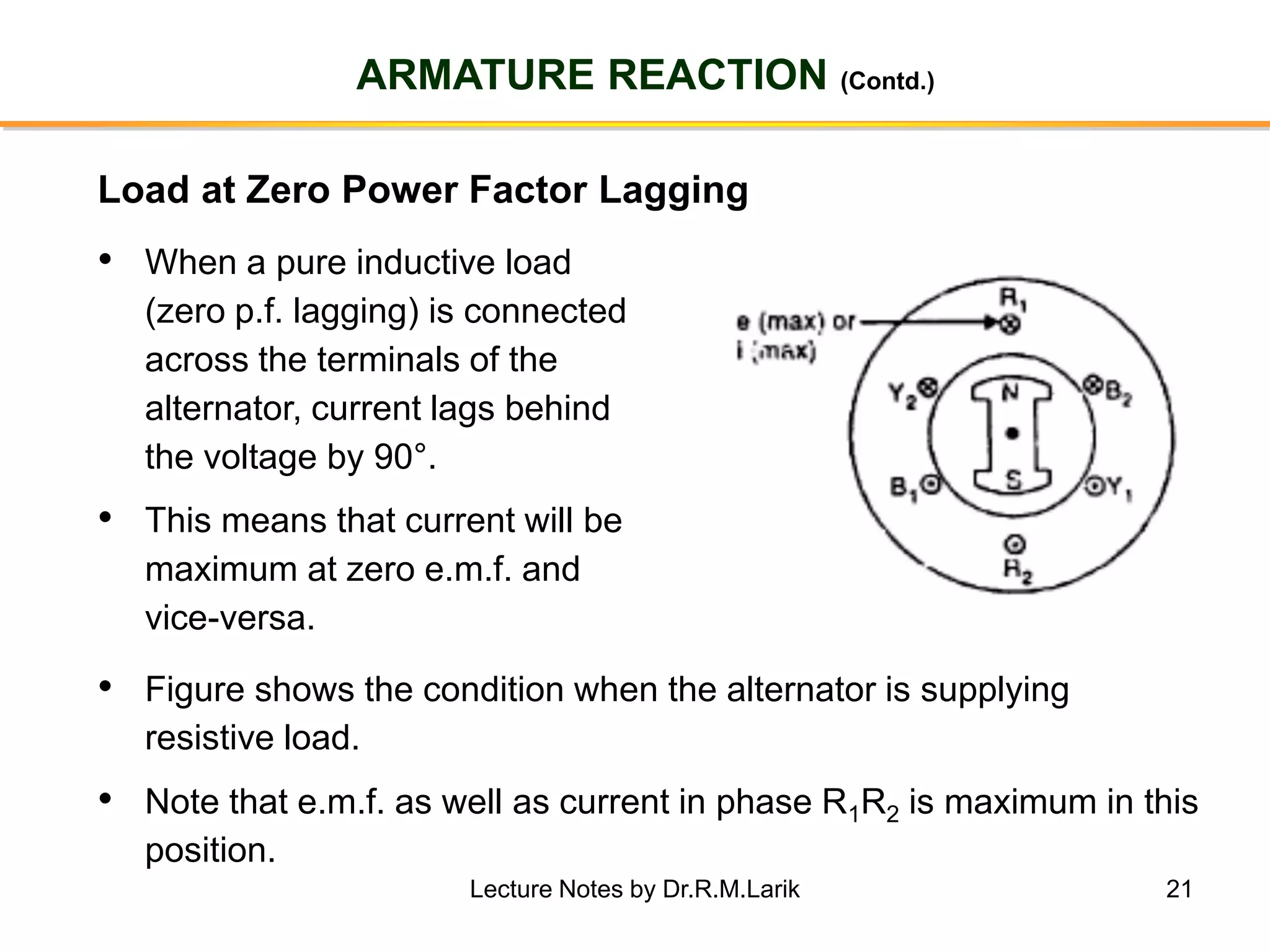
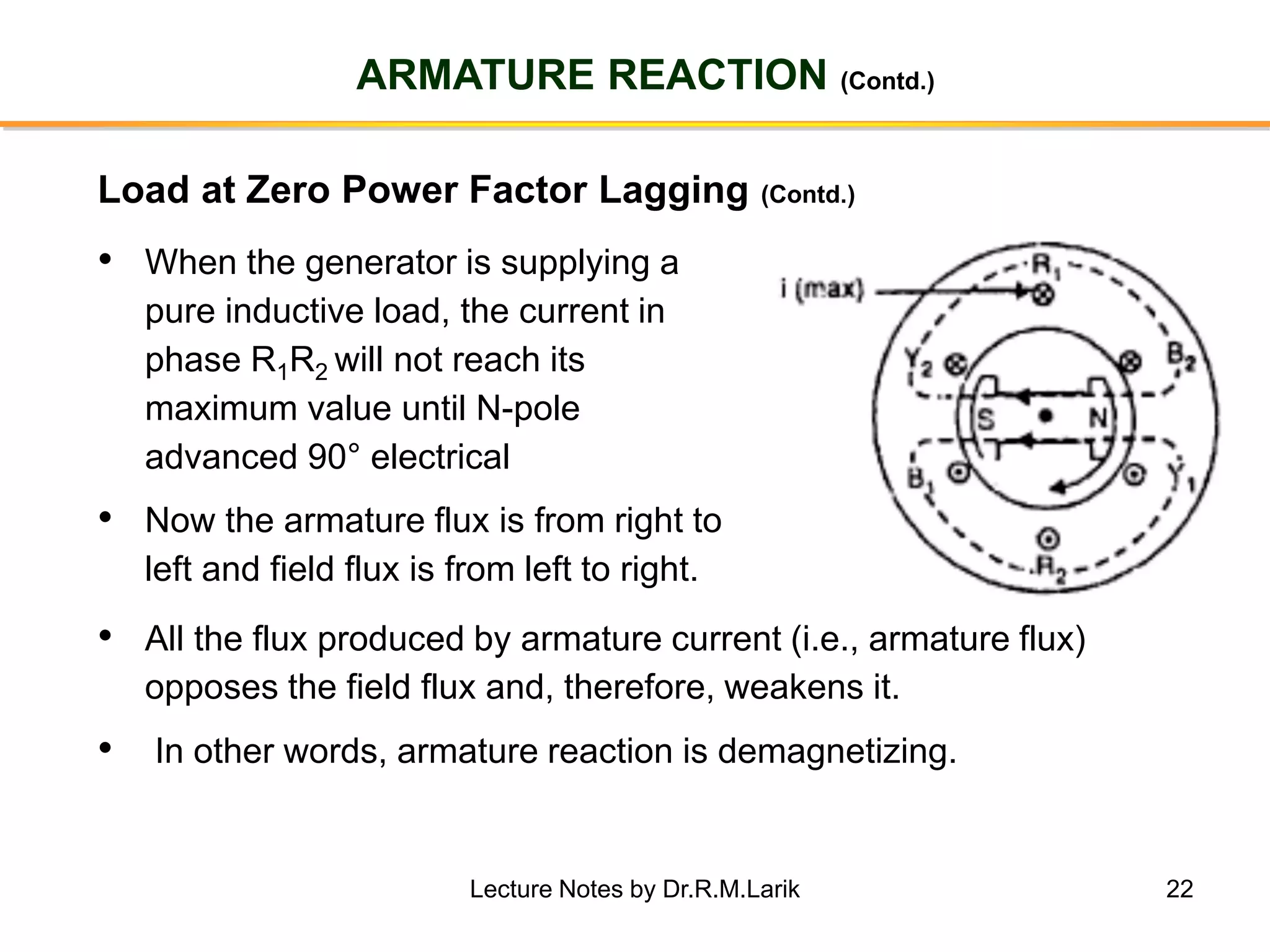
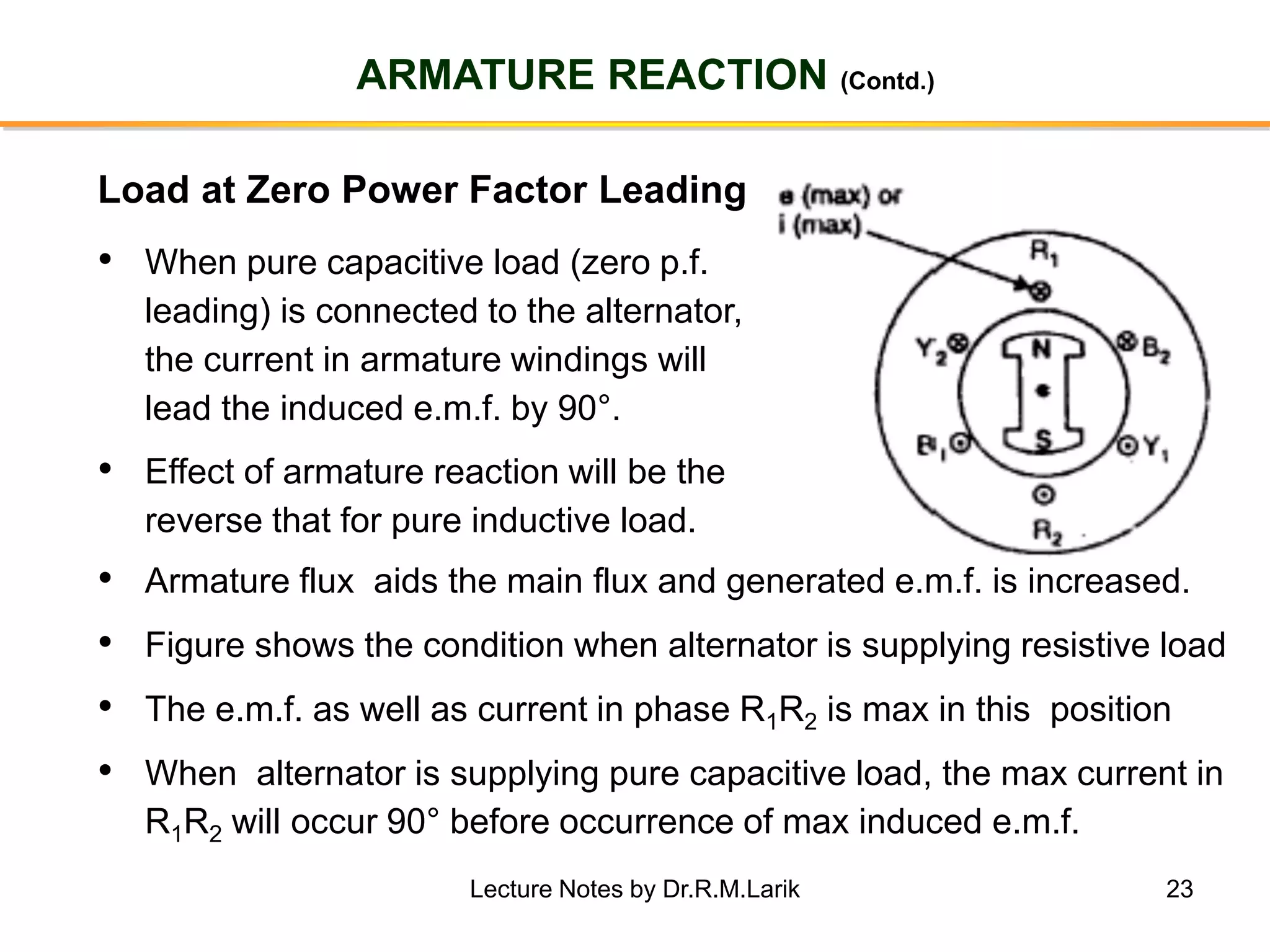
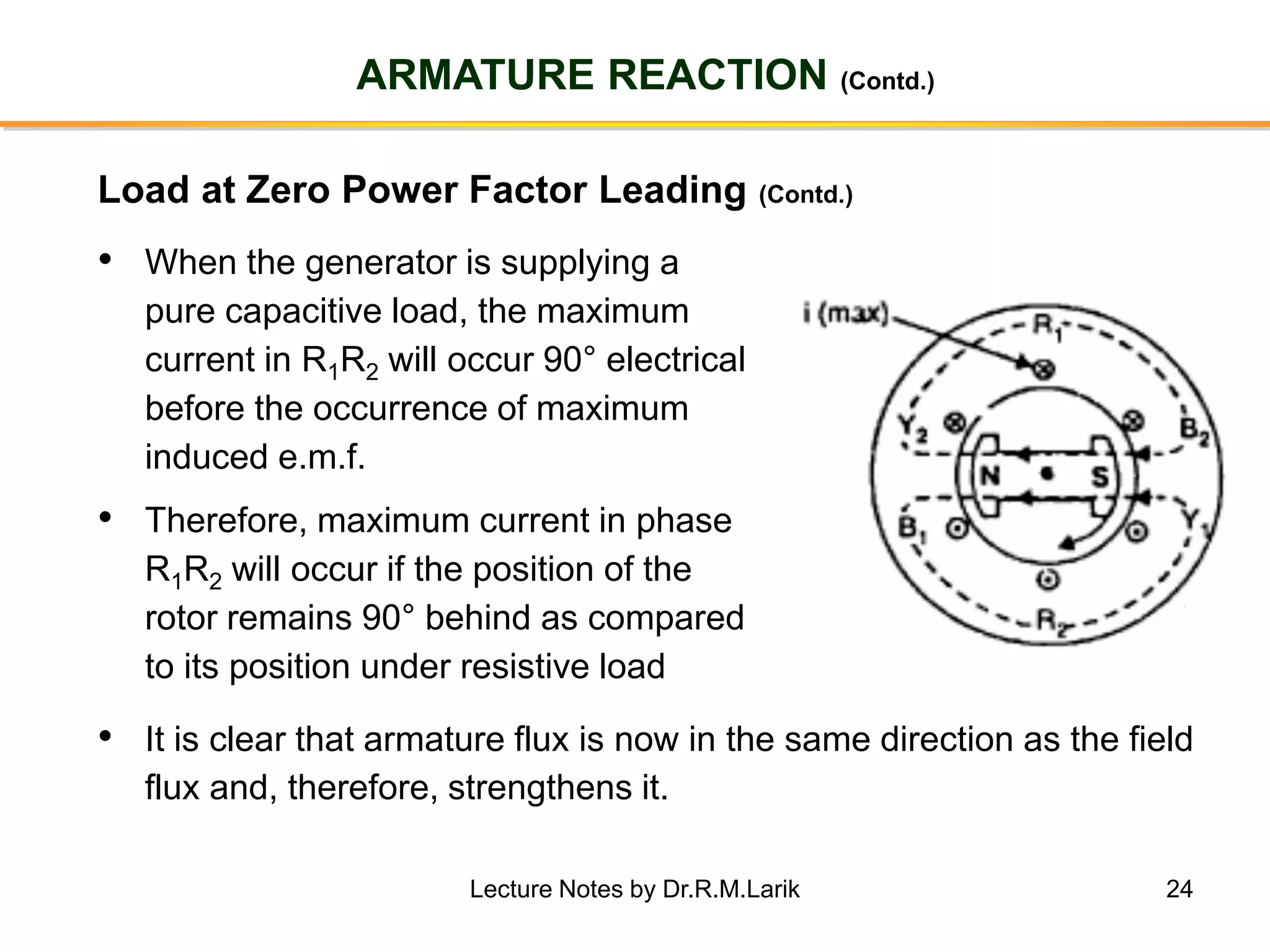
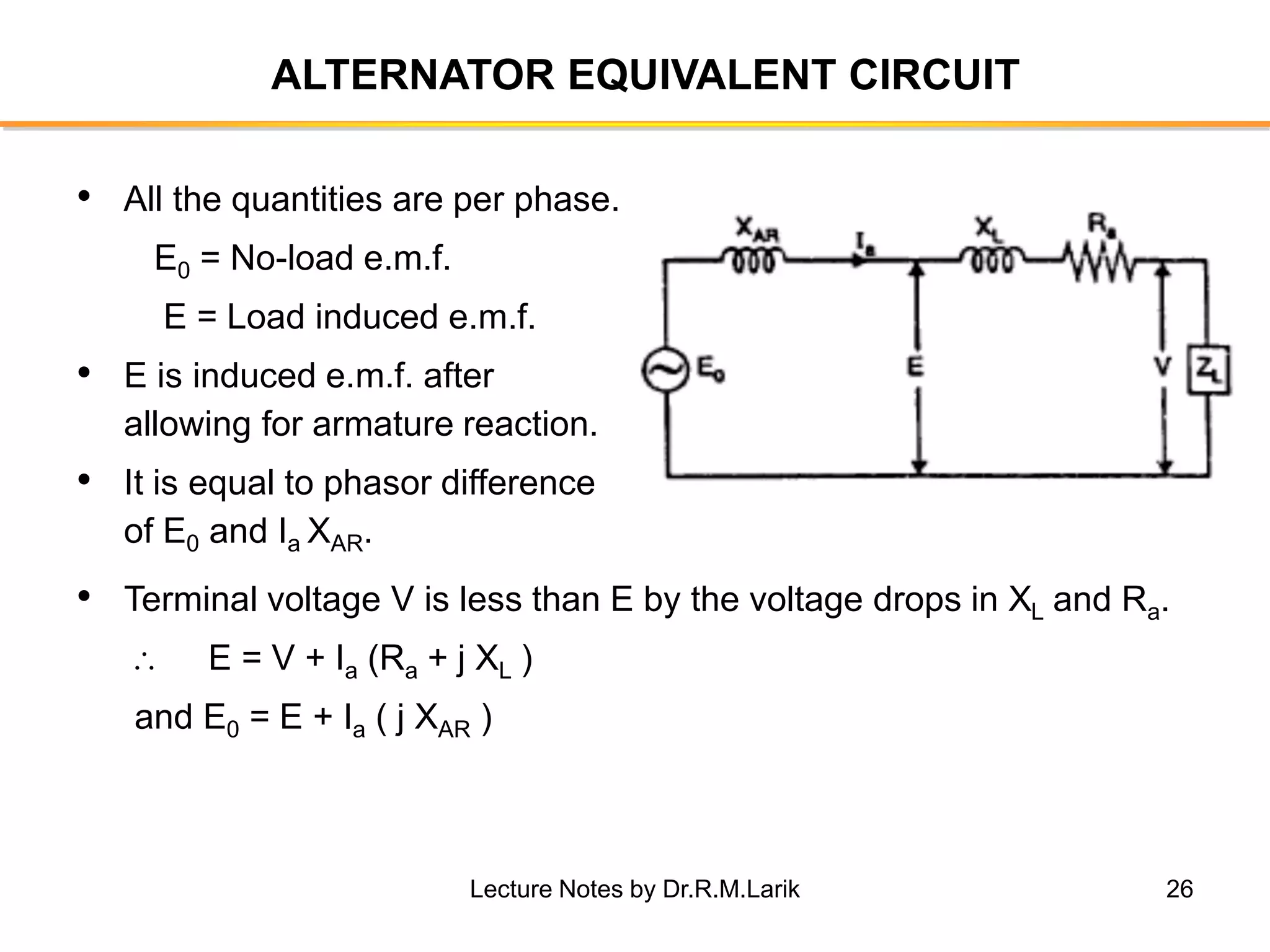
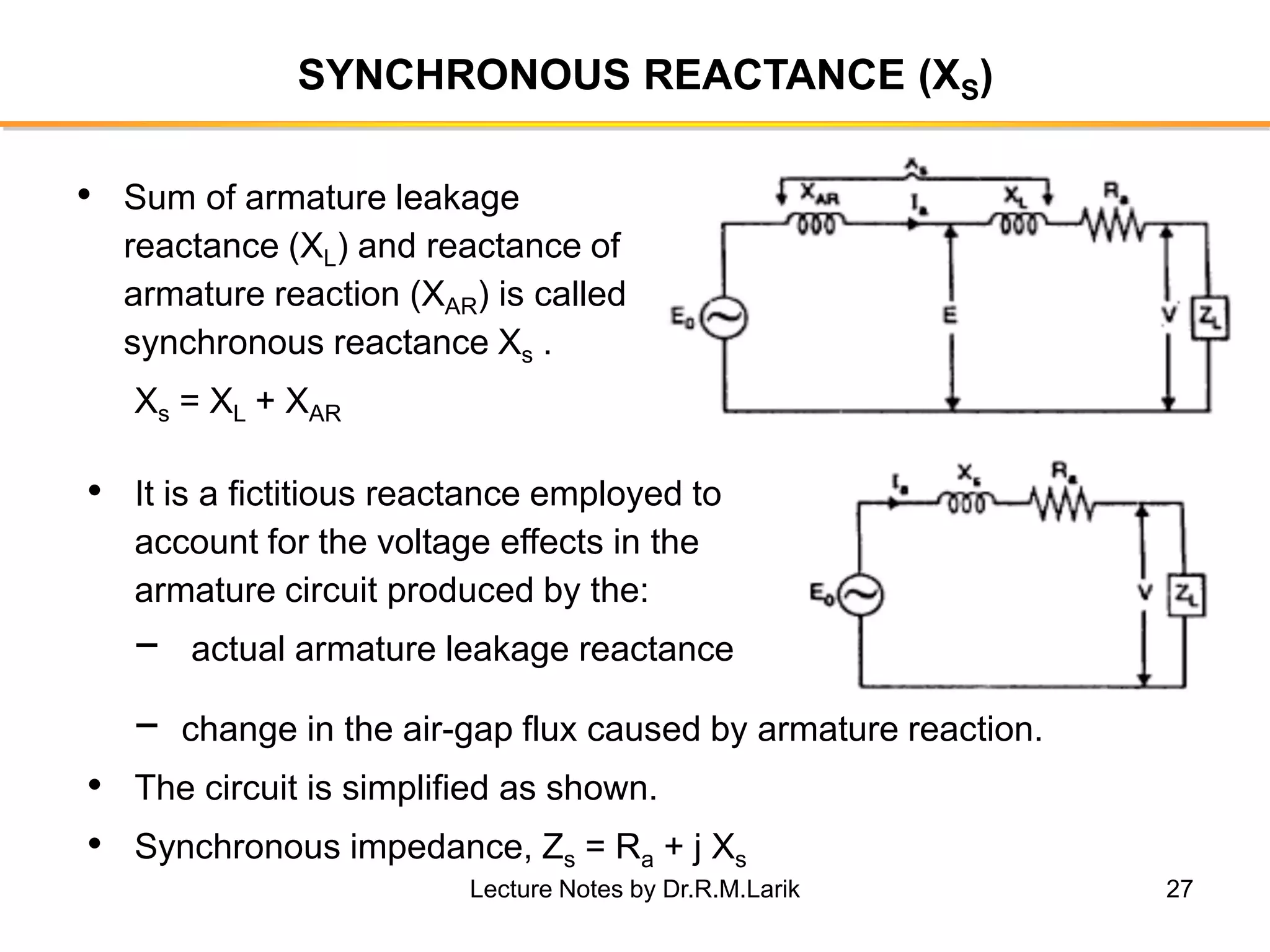
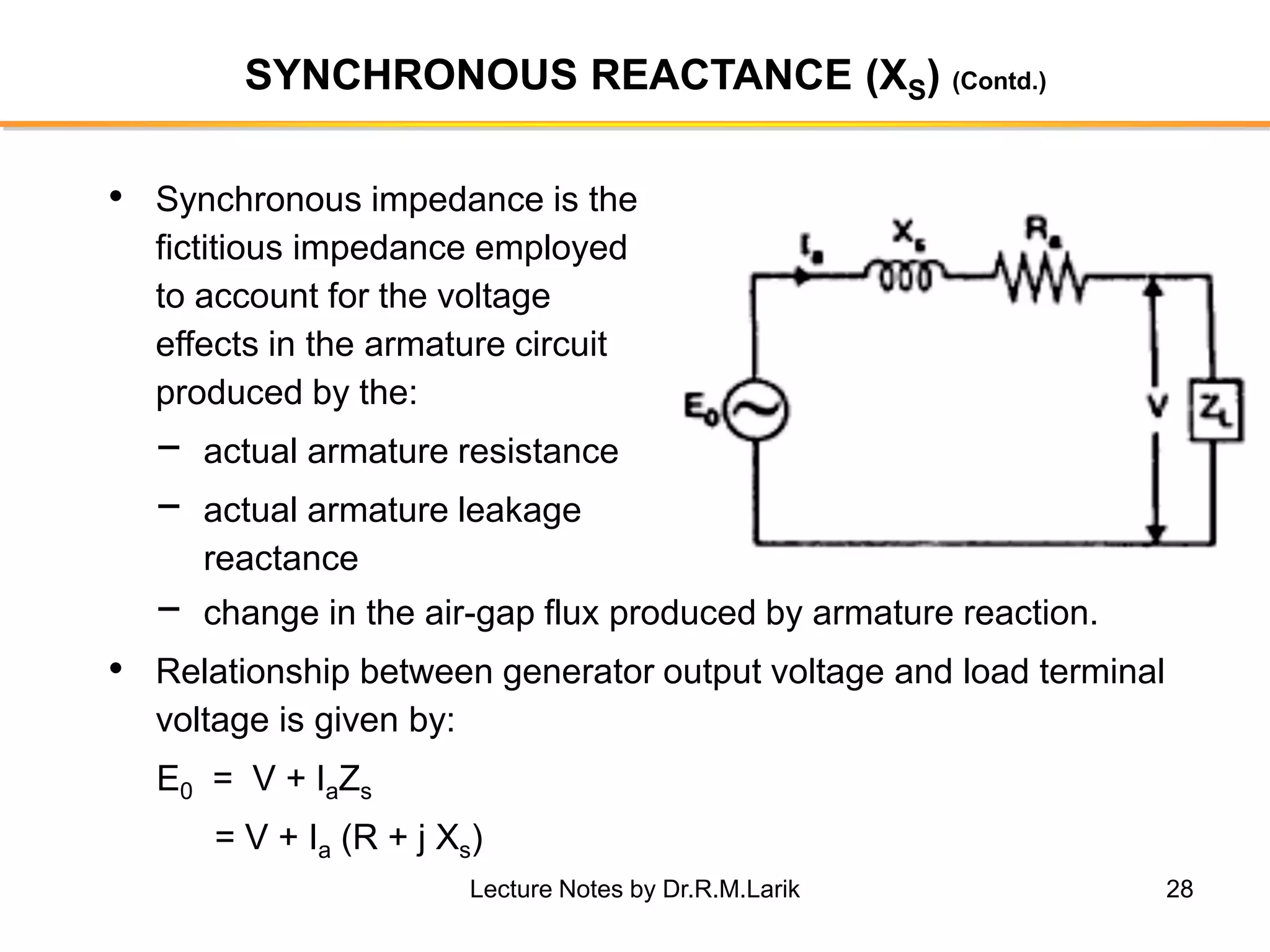
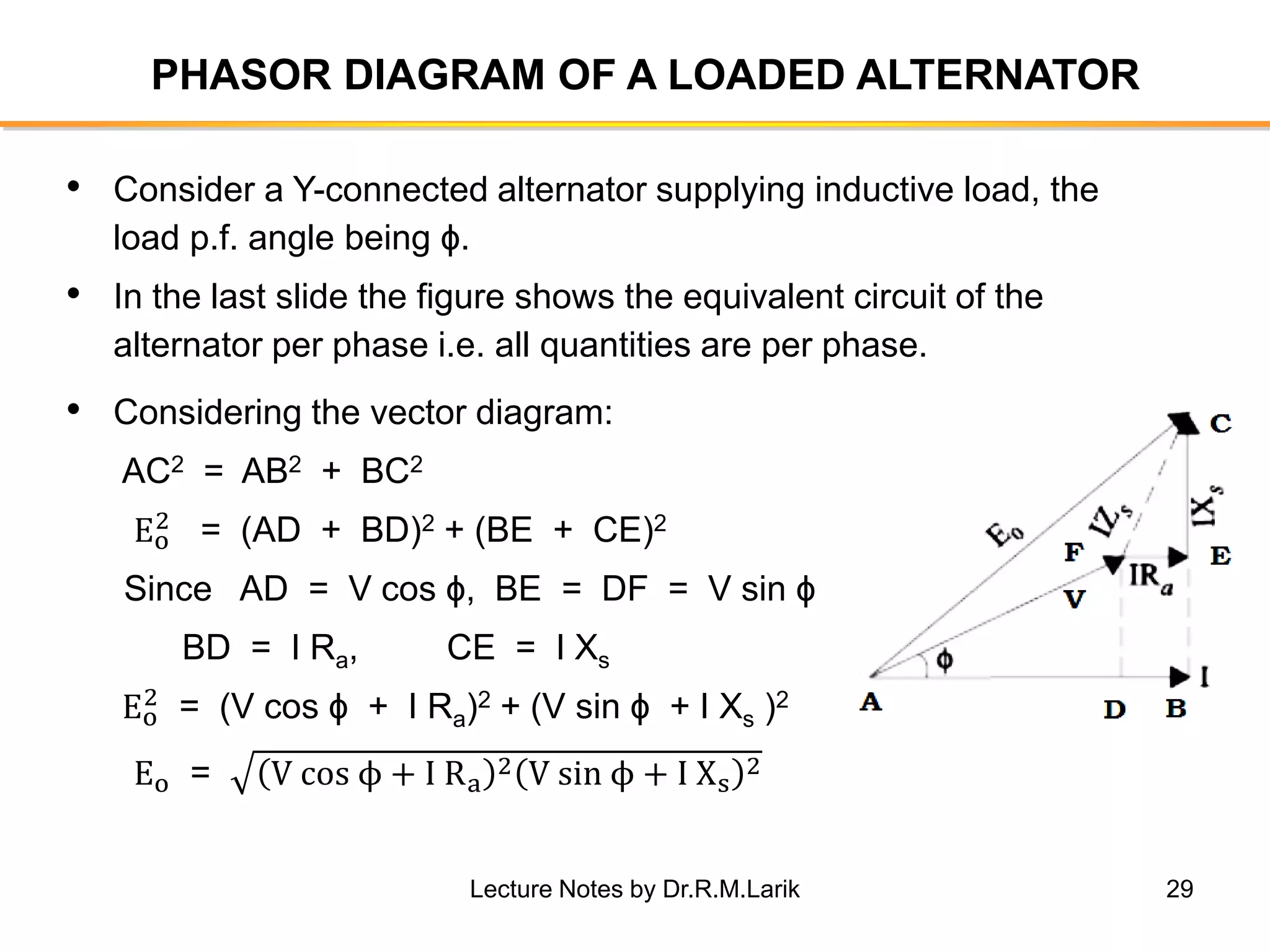
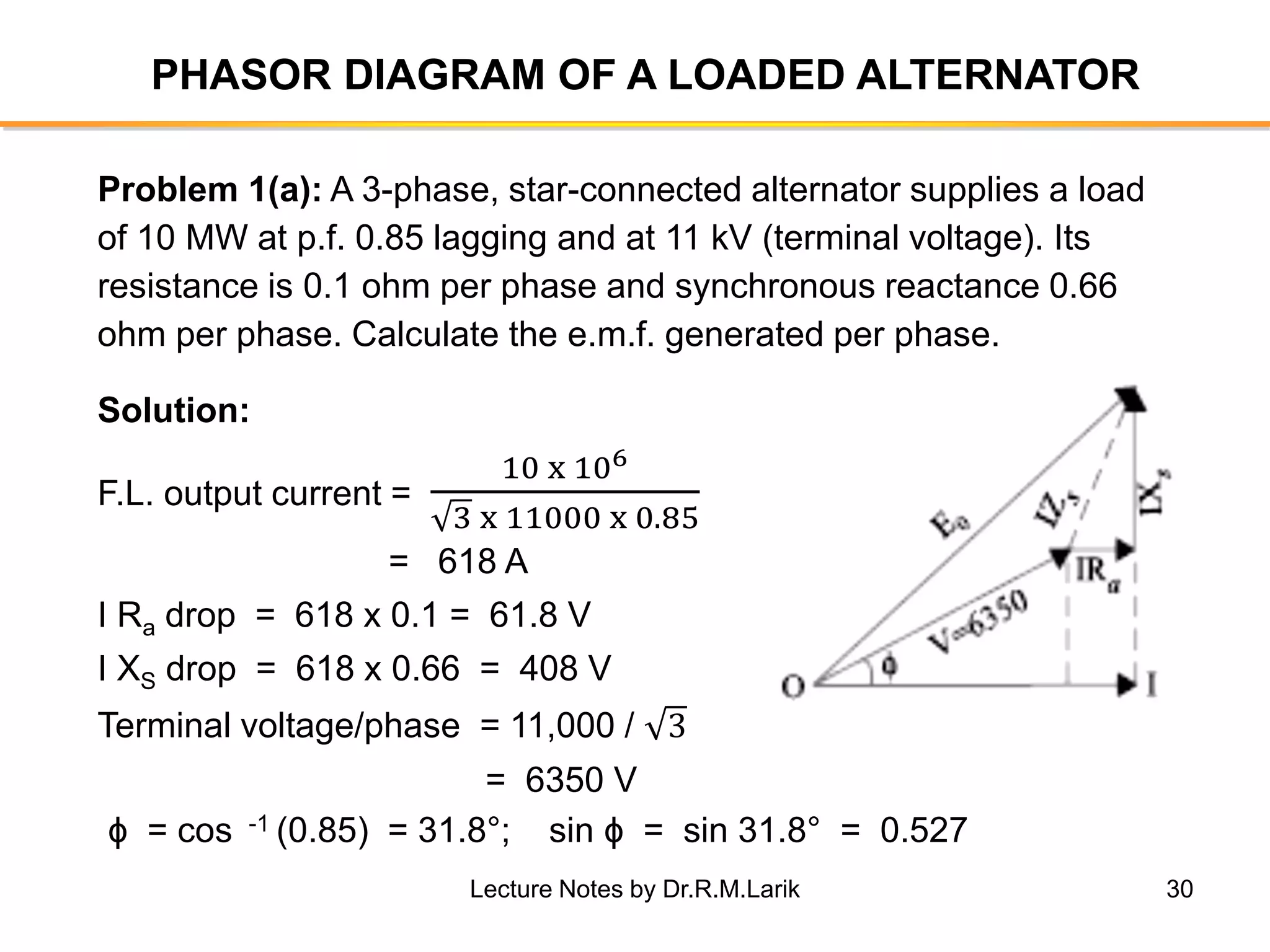
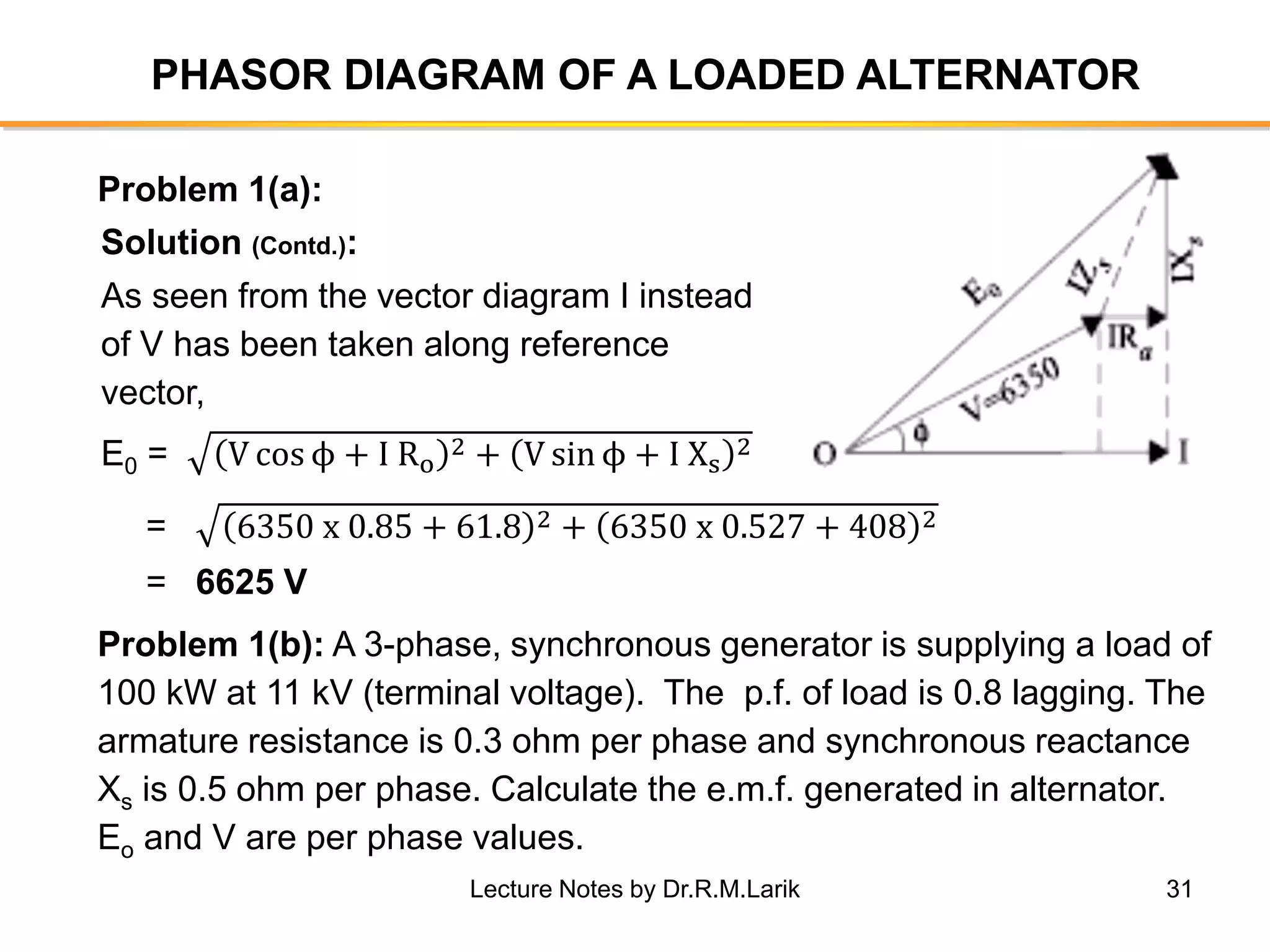
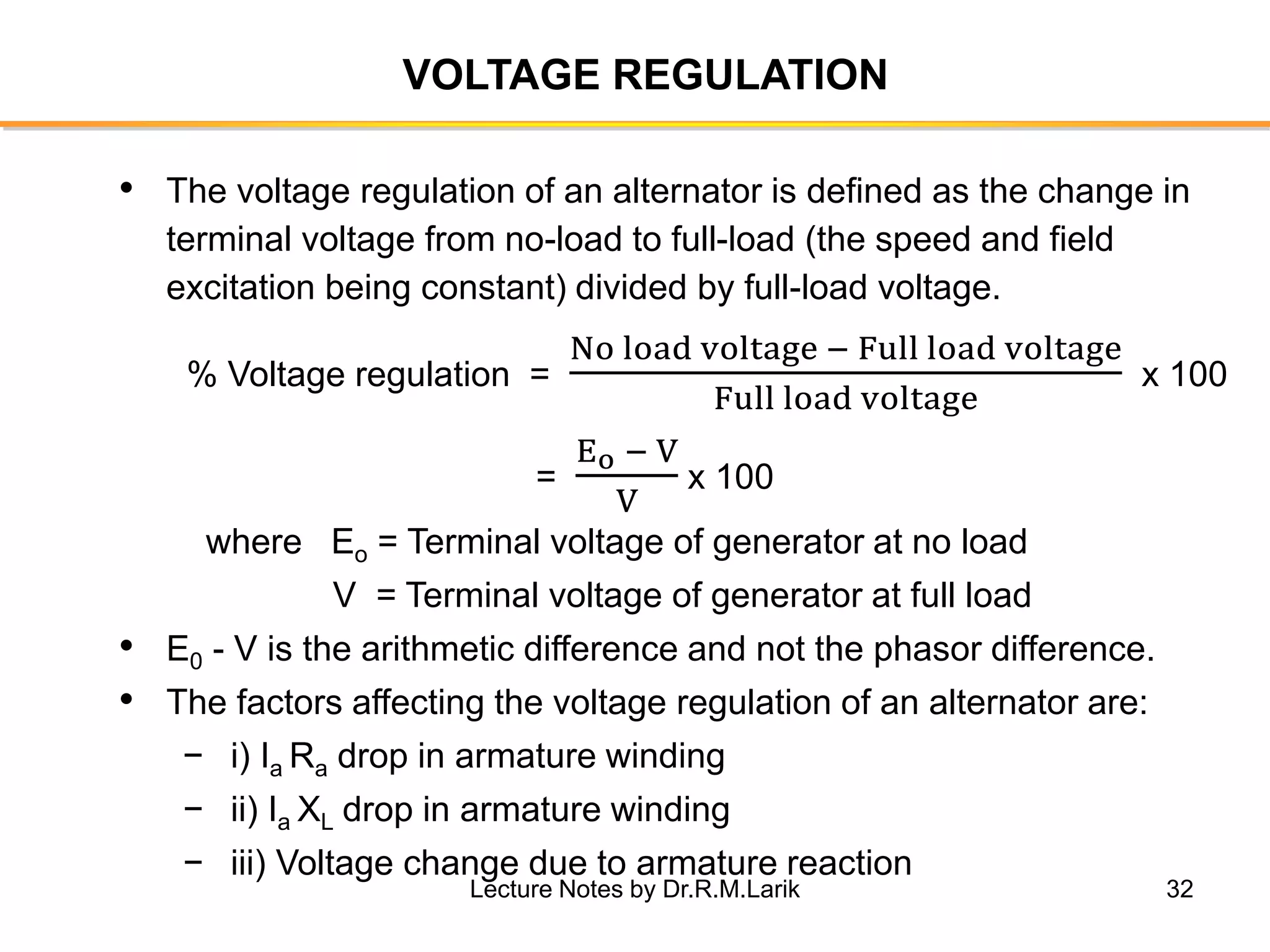
Synchronous generators operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. They have a stationary armature winding and a rotating field winding supplied by a direct current source. It is advantageous to have the field winding on the rotor and armature winding on the stator because it allows for easier insulation of the high voltage winding and direct connection to the load. The frequency of the induced voltage depends on the number of rotor poles and its rotational speed. Armature reaction is the effect of the armature magnetic field on the main rotor field, distorting or strengthening it depending on the load power factor.