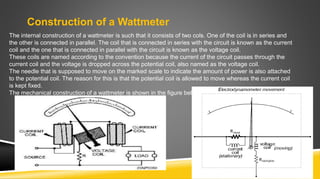
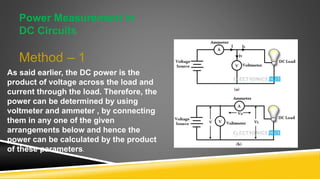
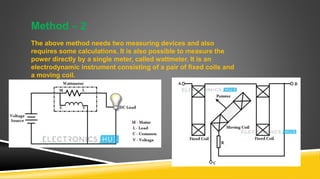
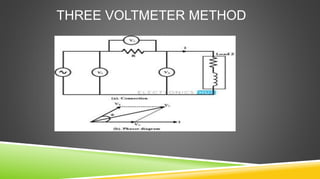
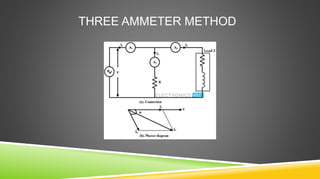
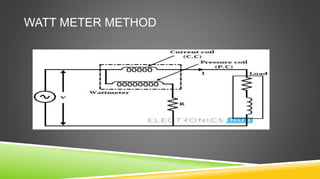
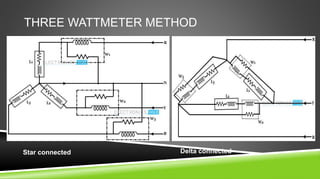
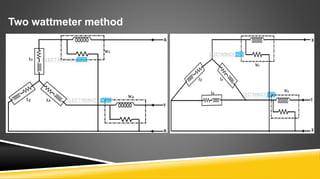
The document provides an introduction to wattmeters, instruments used for measuring electric power in watts, detailing their construction, operation, and historical development. It explains how wattmeters work with both DC and AC circuits and describes different methods for measuring power in single-phase and three-phase systems. Additionally, the document outlines various applications of wattmeters in industrial and electrical circuit measurements.