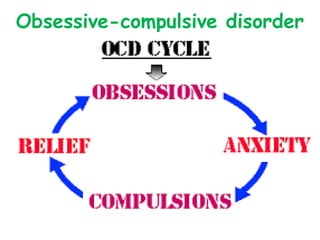
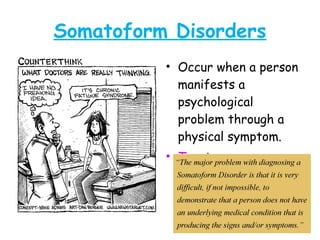
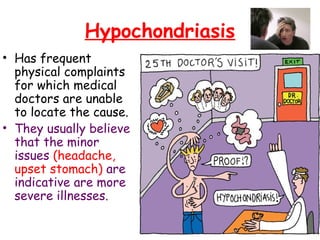
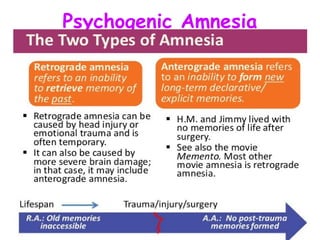
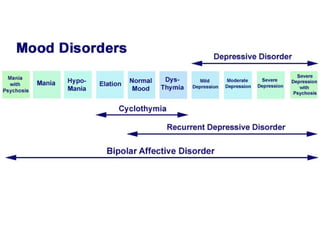
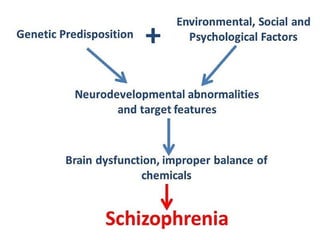
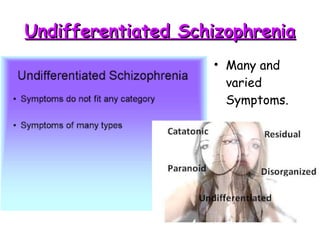
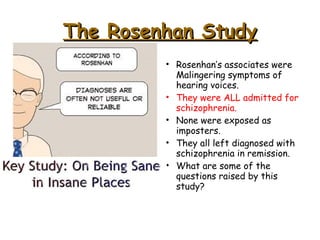
Abnormal psychology involves the study of psychological disorders, which are behaviors judged to be inappropriate, distressing, or dysfunctional. Psychological disorders are studied and treated by psychologists and psychiatrists using various theoretical perspectives including psychodynamic, behavioral, cognitive, and biological approaches. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) provides standardized criteria for classifying and diagnosing mental disorders. Major classes of disorders include anxiety disorders, mood disorders like depression, dissociative disorders, personality disorders, and psychotic disorders like schizophrenia.