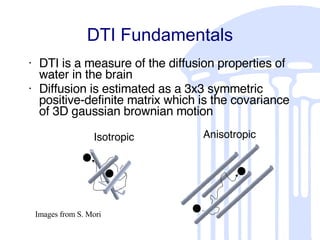
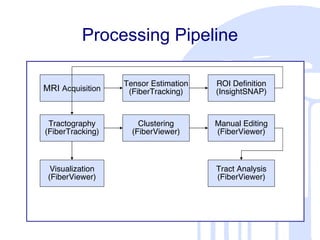
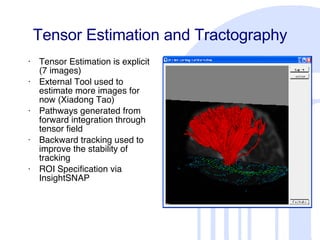
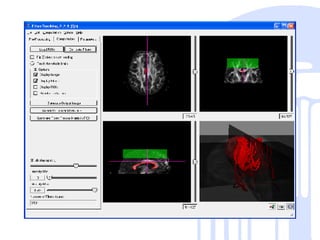
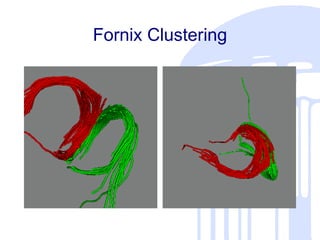
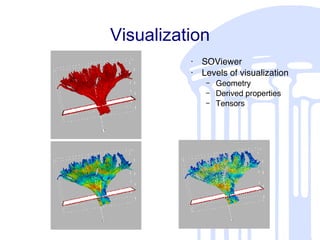
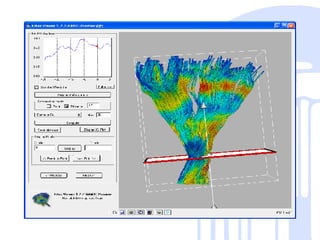
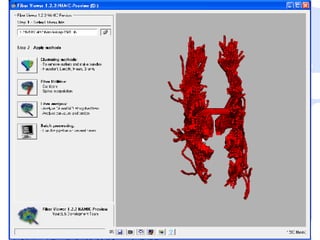
This document summarizes a quantitative diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) fiber tract analysis software suite. It outlines the motivation, open source technologies used, tractography and clustering algorithms, manual editing tools, analysis of fiber tracts, applications, and contributions to open source. The suite processes DTI data through tensor estimation, tractography, hierarchical clustering of fibers, manual editing, visualization, and analysis of fiber properties along tracts. It is being used to study neurodevelopment and is available as open source software.