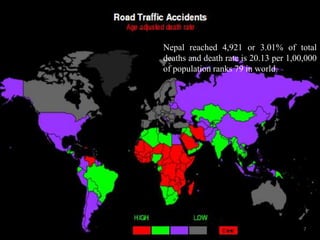
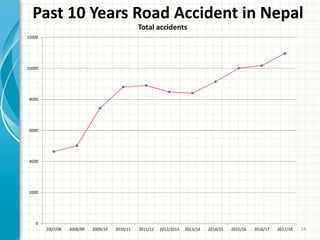
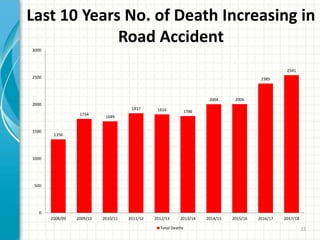
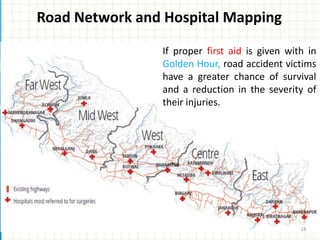
Road traffic accidents occur when a vehicle collides with another vehicle or object on a public road. They are a major public health issue and one of the leading causes of death globally for people aged 5-29. In Nepal, about 7 people die every day from road accidents, which account for 7% of all deaths in the country. The number of accidents and deaths from accidents has been increasing in Nepal over the past decade. Common causes of road accidents include speeding, drunk driving, not wearing seatbelts or helmets, and violating traffic rules. Preventive measures like enforcing speed limits, seatbelt and helmet laws, banning phone use while driving, and improving road infrastructure can help reduce accidents.