The document discusses road accidents, their causes, and preventative measures. It states that human factors like alcohol consumption, distraction, and speeding are the primary causes of accidents, accounting for 69% of total accidents. Vehicle defects and poor road infrastructure account for the remaining 27% and 4% respectively. Some key preventative measures proposed include strict enforcement of speed limits, more stringent licensing tests, mandatory seatbelt and helmet laws, and better road infrastructure like signage and speed breakers. Adopting and enforcing these measures could significantly reduce the millions of deaths and injuries from road accidents worldwide each year.













![[A]. HUMAN FACTORS
Human factors in vehicle collisions include all
factors related to drivers which cause a
collision.
Examples of human factors include driver
behavior, visual and auditory ability, decision-
making ability, and reaction speed during
driving.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roadaccidentstam-2013-28-150712182621-lva1-app6891/75/Road-accidents-tam-2013-28-14-2048.jpg)











![[B]. ROADWAY FACTORS
About 4% of serious crashes are due to the
roadway or its environment.
Poor quality roads laid due to corrupt
contractors, not erupting signal boards at
dangerous turnings, hilly and avalanche like
terrains as seen in north indian states like
Darjeeling causes road collisions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roadaccidentstam-2013-28-150712182621-lva1-app6891/75/Road-accidents-tam-2013-28-26-2048.jpg)



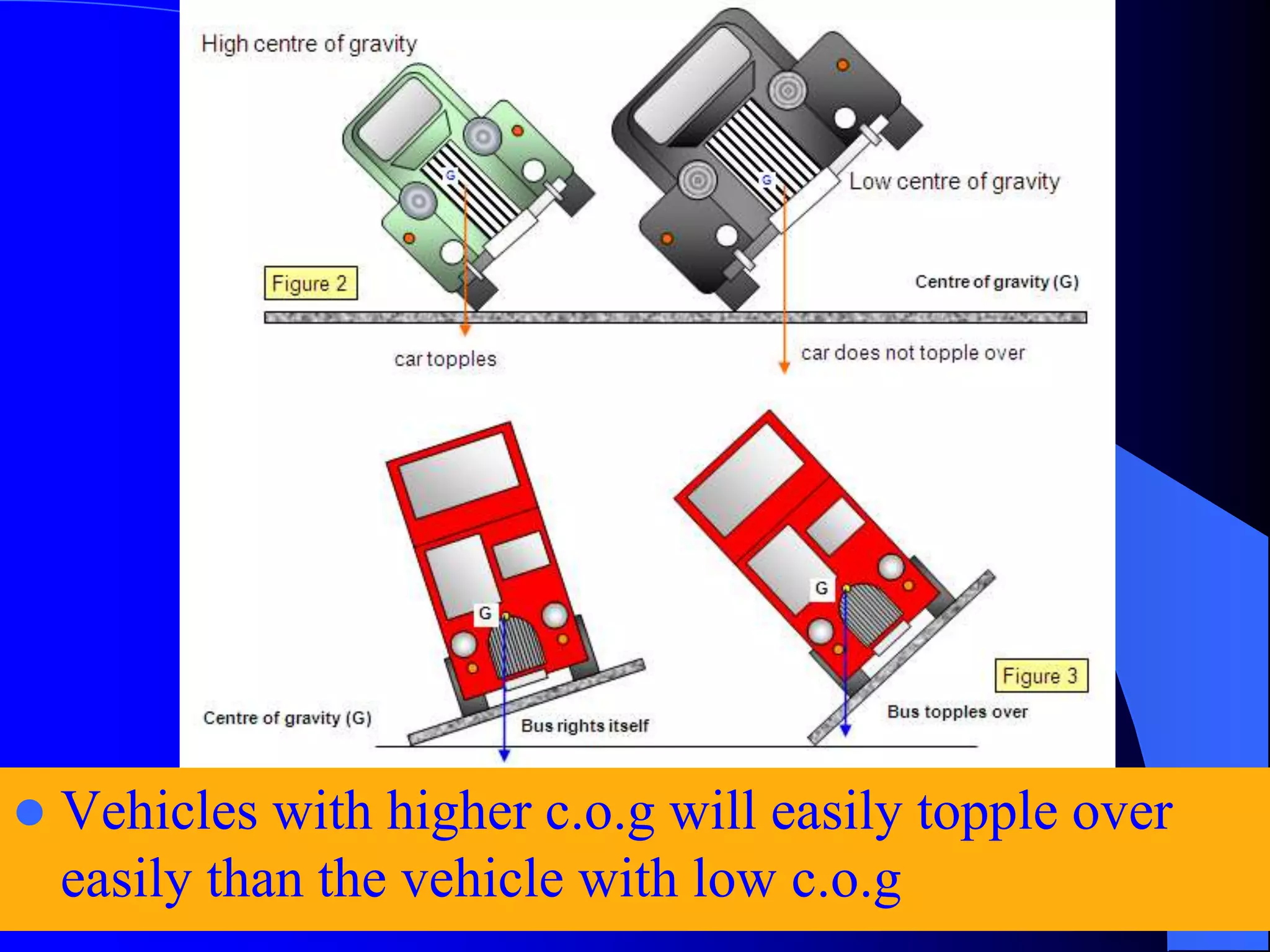
![[C]. VEHICLE FACTORS
Some crash types involving vehicular design and
maintenance tend to have more serious
consequences.
Rollovers have become more common in recent
years, perhaps due to increased popularity of
taller SUVs and minivans.
Rollovers can be fatal, especially if the occupants
are ejected because they were not wearing seat belts](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roadaccidentstam-2013-28-150712182621-lva1-app6891/75/Road-accidents-tam-2013-28-30-2048.jpg)