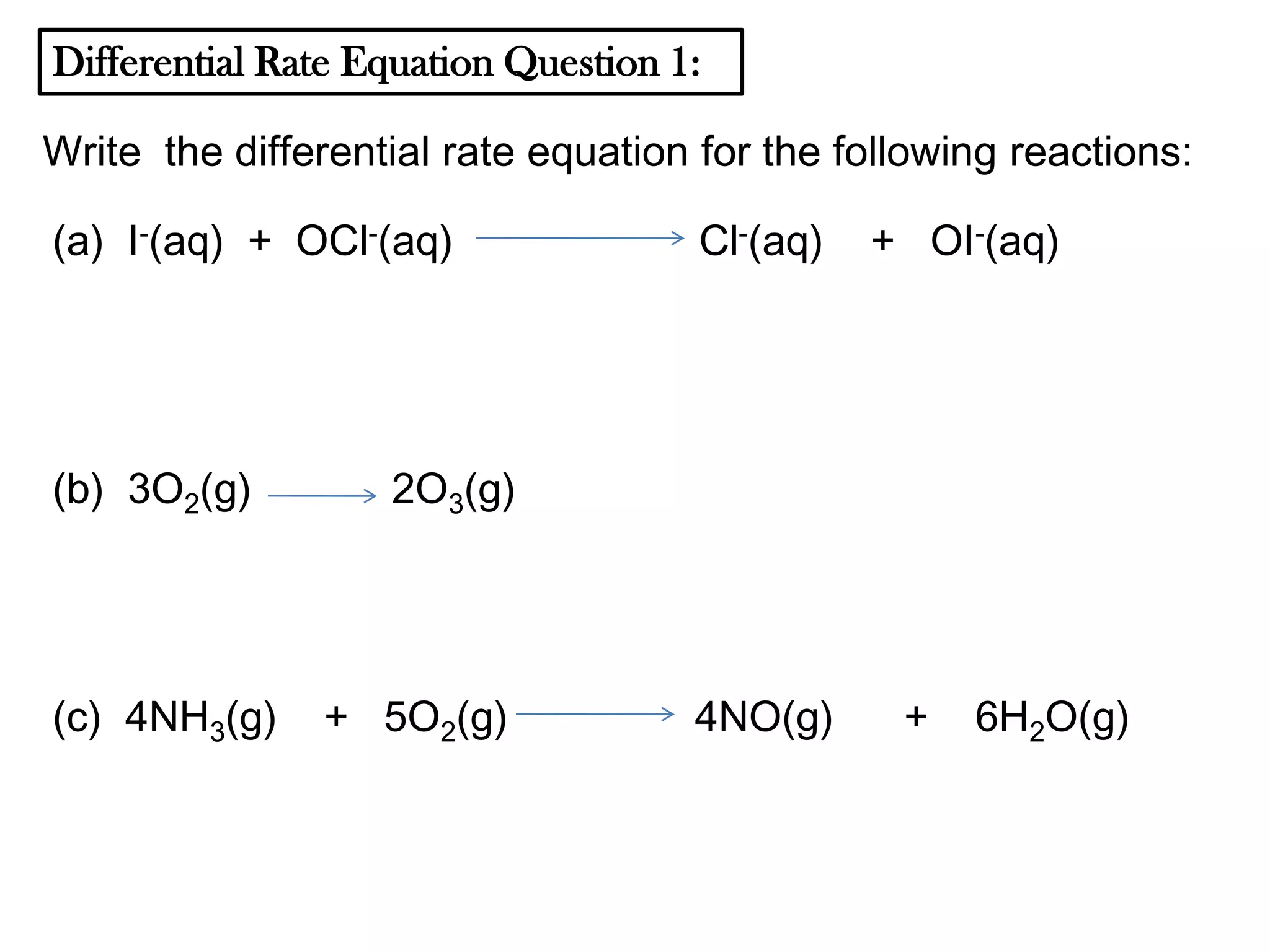
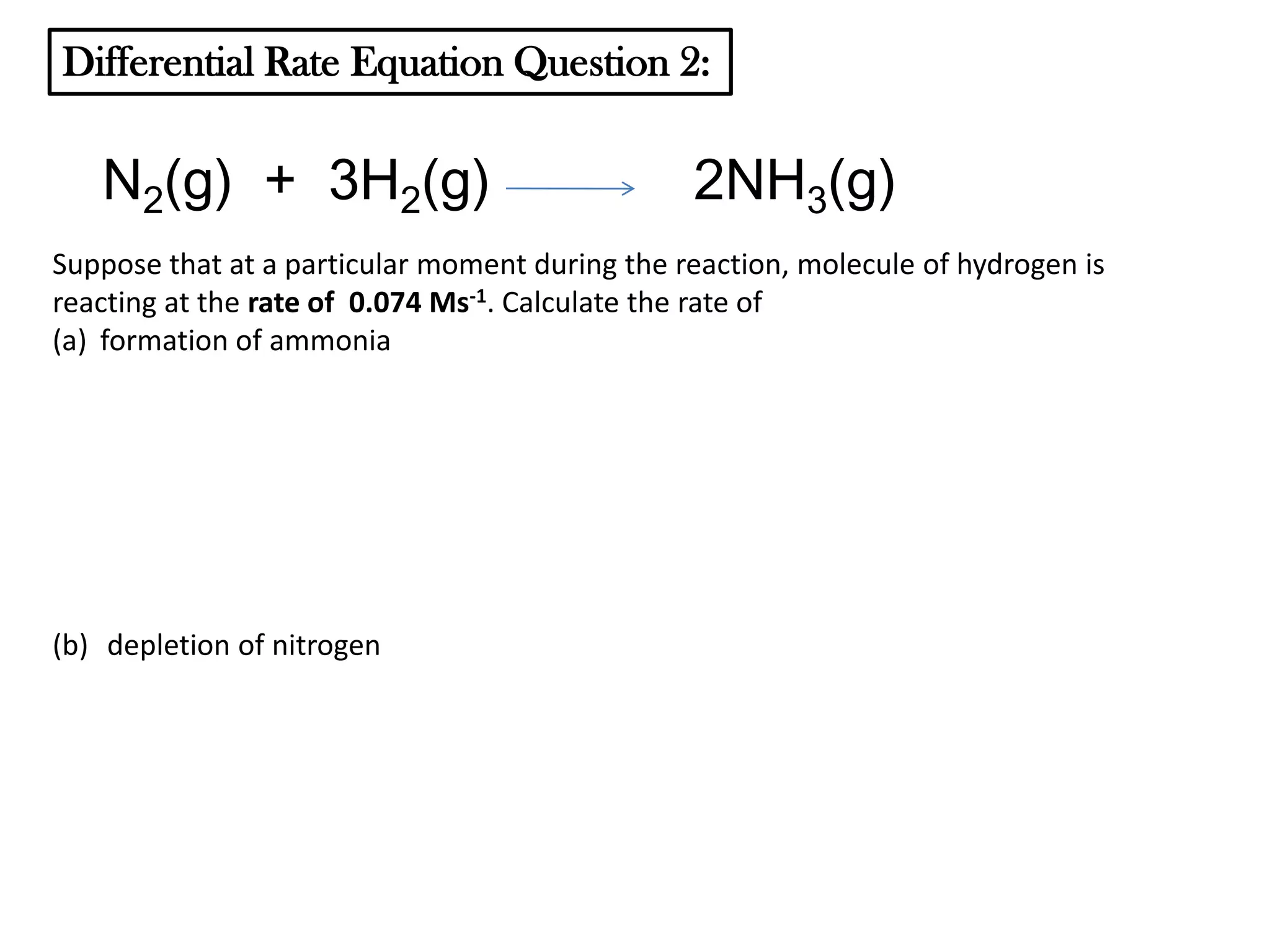
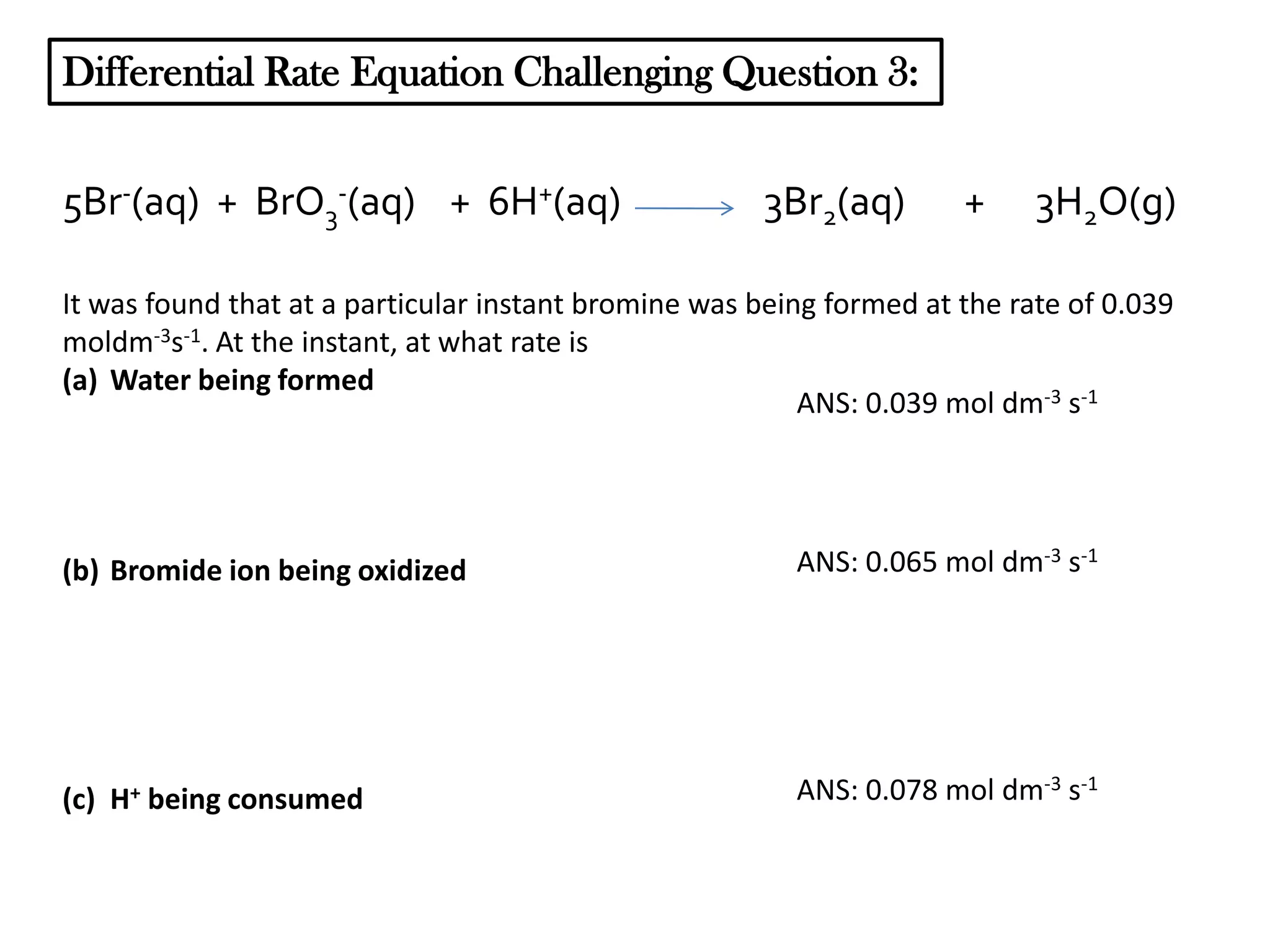
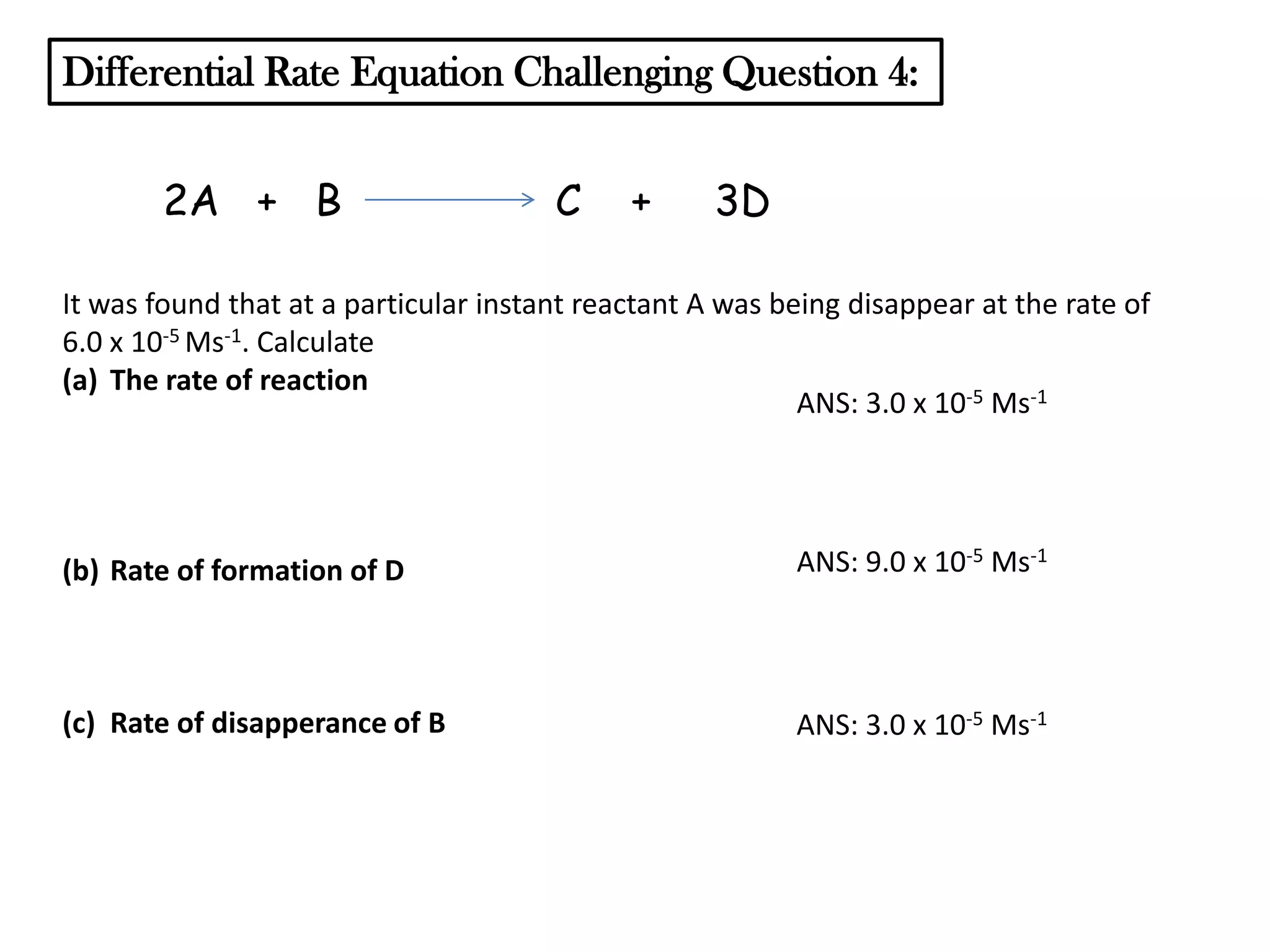
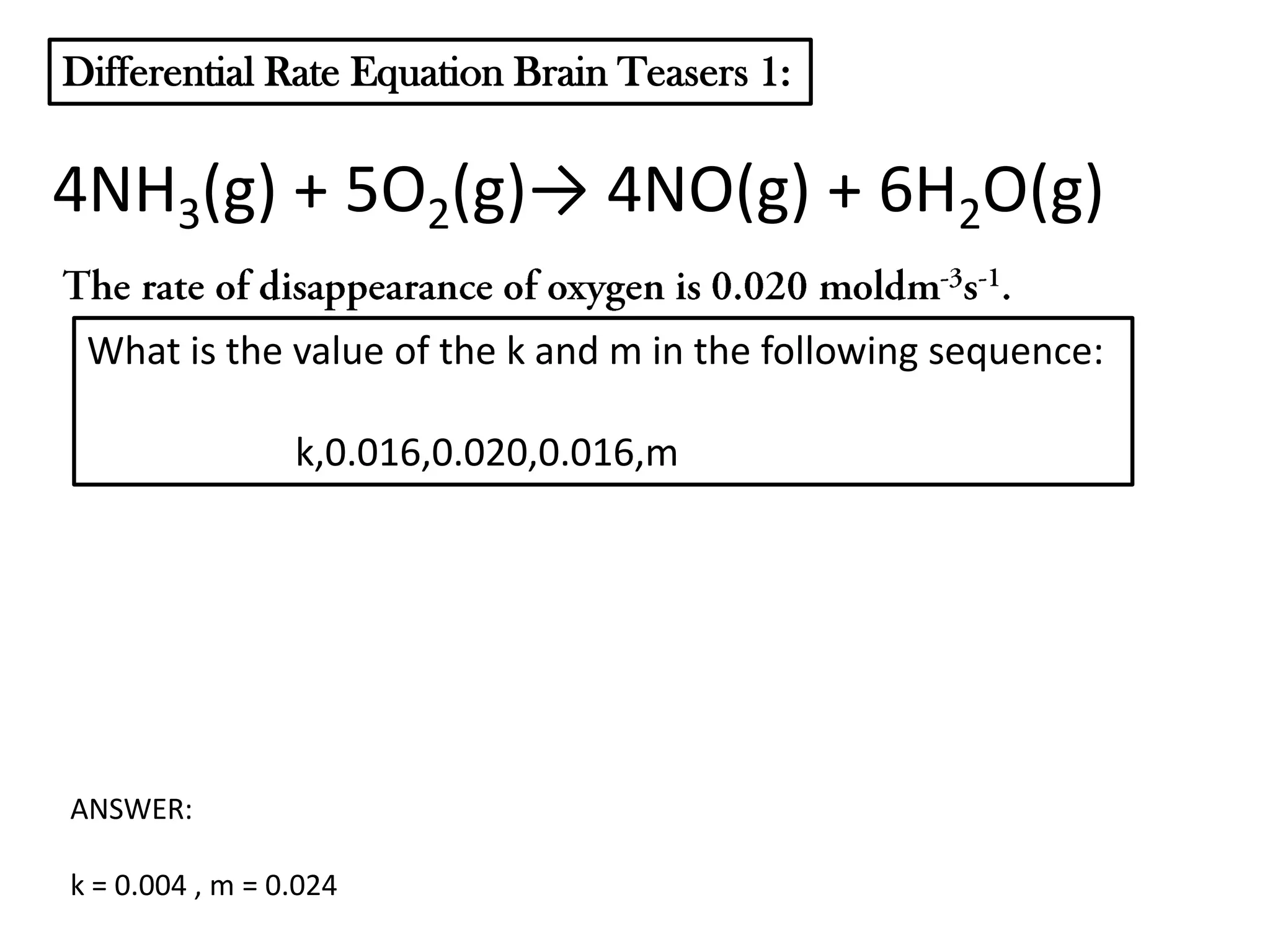
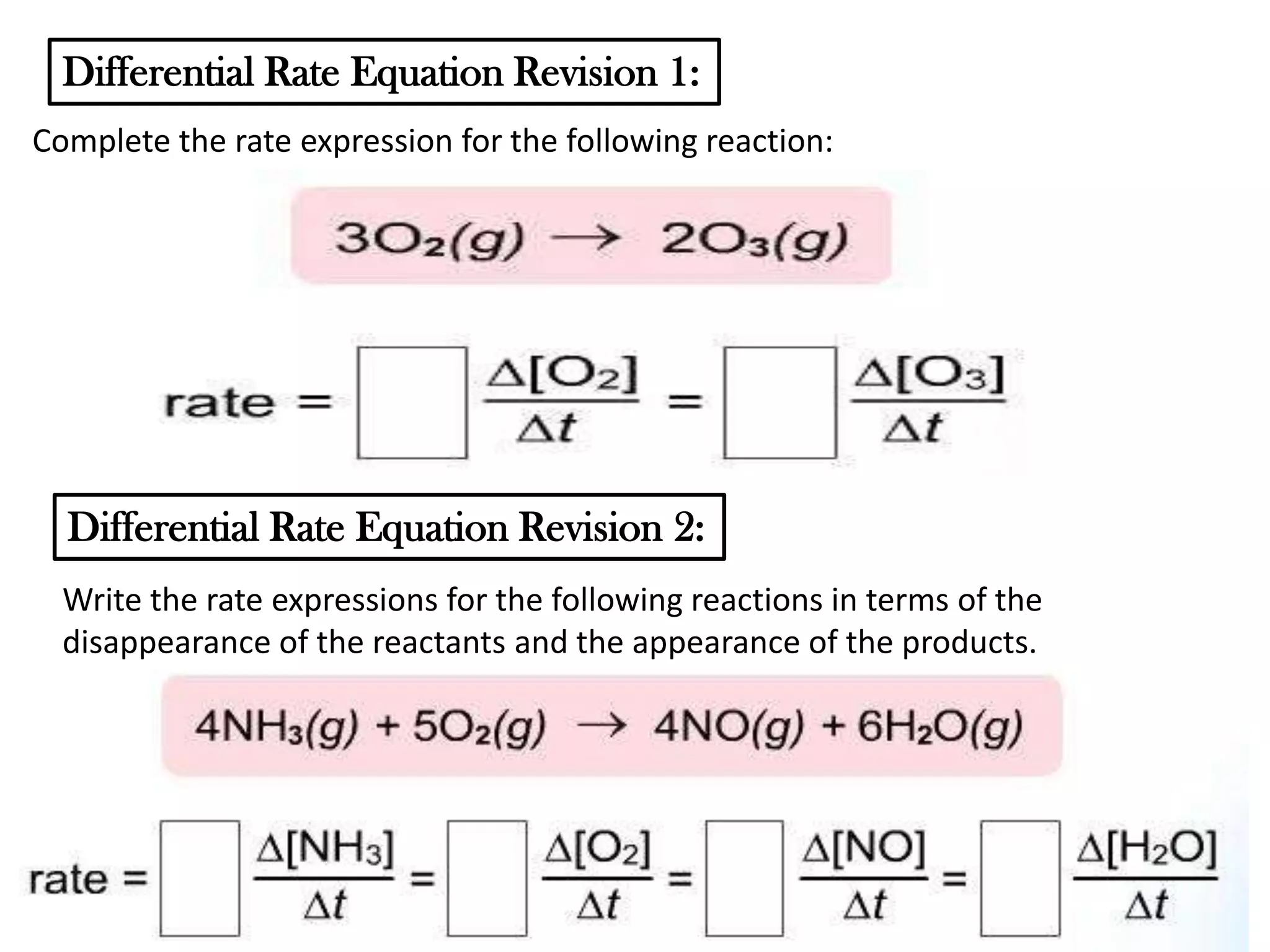
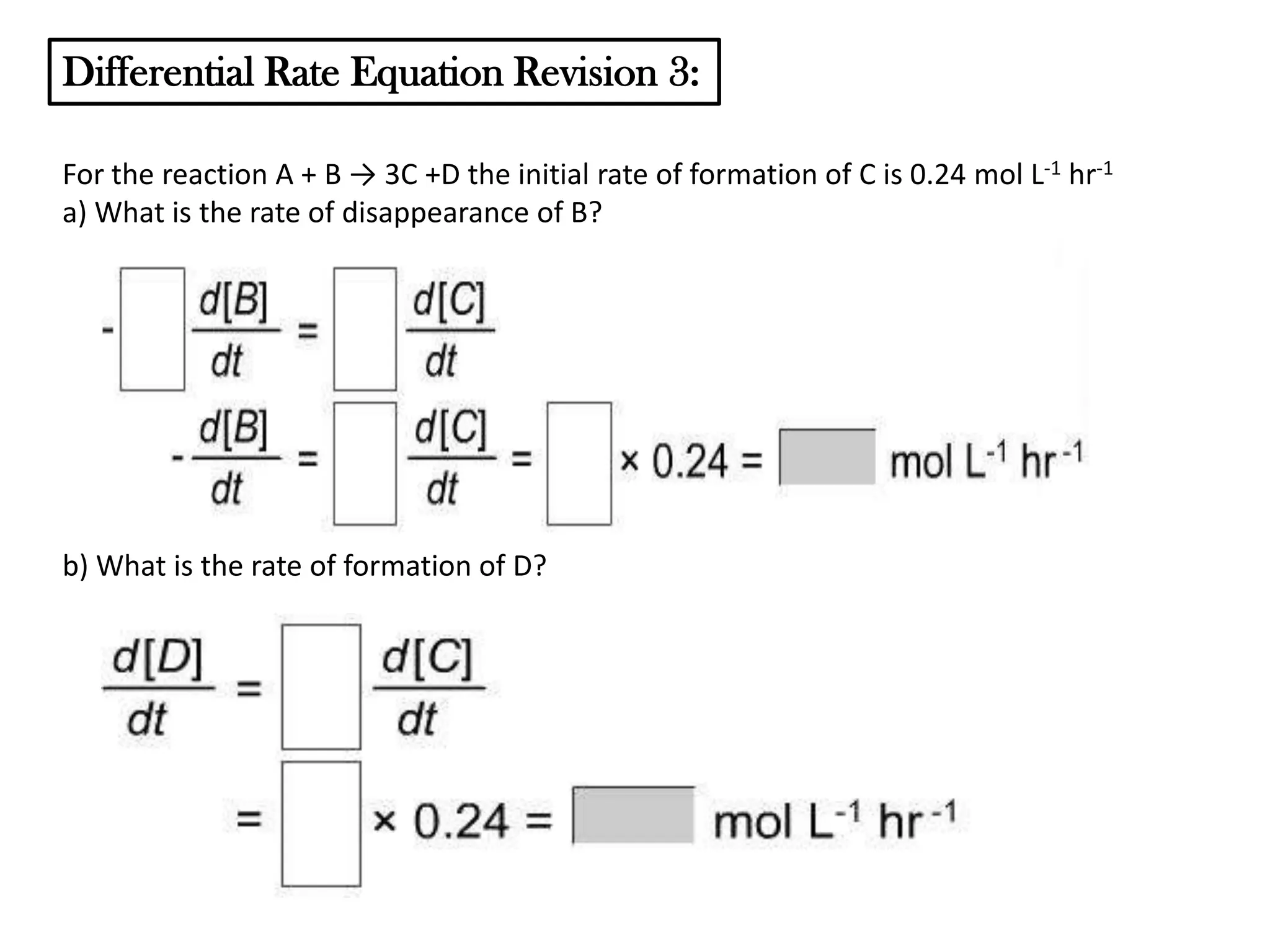
The document discusses reaction kinetics and reaction rates. It defines reaction rate as the change in concentration of a reactant or product with time. Reaction rates can be determined from graphs of concentration versus time or from differential rate equations. Differential rate equations relate the rates of changes of concentrations of reactants and products. Several examples show how to write differential rate equations for reactions and calculate reaction rates from given information. Common student mistakes in working with differential rate equations are also discussed.


![A
B
?
rate = -
?
rate = +
?
[A]
t
[B]
t
?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-131128092725-phpapp02/75/8-1-reaction-rate-3-2048.jpg)

![Differential rate equation / Rate expressions
aA+bB
rate =
cC+dD
-1 d[A] = -1 d[B] = +1 d[C]
a dt
b dt
c dt
= +1 d[D]
d dt
Differential Rate Equation Example1:
O3(g) + NO(g)
NO2(g) + O2(g)
d O3
d[NO]
d[ NO 2 ]
d[ O 2 ]
rate = ==+
=+
dt
dt
dt
dt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-131128092725-phpapp02/75/8-1-reaction-rate-5-2048.jpg)
![Differential Rate Equation Example2:
2 NOCl (g)
2 NO + Cl2 (g)
1 d NOCl
1 d[NO]
d[Cl2 ]
rate = =
=+
2
dt
2 dt
dt
2 moles of NOCl disappear for every 1 mole Cl2
formed.
Rate of disappearance of NOCl is twice as fast
as the rate of formation of Cl2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-131128092725-phpapp02/75/8-1-reaction-rate-6-2048.jpg)

![Differential Rate Equation Example 3:
C2H6(g) + 7O2(g)
4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
If the ethane, C2H6 is burning at the rate of 0.20 mol dm-3s-1. Calculate the rate of
formation of CO2
STEP 1: Write the differential rate equation for the
substances that related to the question
d [C 2 H 6]
dt
?
1 d [CO 2]
4
dt
STEP 2: Substitute the given information into the
differential equation
d [CO 2]
dt
d [CO 2]
dt
4(0.20moldm 3s 1 )
0.80moldm 3s
1
Rate of formation
of CO2 is
0.80 moldm-3s-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-131128092725-phpapp02/75/8-1-reaction-rate-9-2048.jpg)
![C2H6(g) + 7O2(g)
4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
If the ethane, C2H6 is burning at the rate of 0.20 mol dm-3s-1. Calculate the rate of
formation of CO2
Student common mistakes:
d [C 2 H 6]
dt
1 d [CO 2]
4
dt
d [CO 2]
dt
d [CO 2]
dt
d [CO 2]
dt
1 d [CO 2]
4
dt
d [C 2 H 6]
dt
d [C 2 H 6]
4
dt
4(0.20moldm 3s 1 )
0.80moldm 3s
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-131128092725-phpapp02/75/8-1-reaction-rate-10-2048.jpg)
![Differential Rate Equation Example 4:
C2H6(g) + 7O2(g)
4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
If the ethane, C2H6 is burning at the rate of 0.20 mol dm-3s-1. Calculate the rate of
disappearance of O2
STEP 1: Write the differential rate equation for the
substances that related to the question
d [C 2 H 6]
dt
?
1 d [O 2]
7 dt
STEP 2: Substitute the given information into the
differential equation
d [O 2]
7(0.20moldm 3s 1 )
dt
d [O 2]
1.40moldm 3s 1
dt
Rate of
disappearance of O2
is 1.40 moldm-3s-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-131128092725-phpapp02/75/8-1-reaction-rate-11-2048.jpg)
![C2H6(g) + 7O2(g)
4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
If the ethane, C2H6 is burning at the rate of 0.20 mol dm-3s-1. Calculate the rate of
disappearance of O2
Student common mistakes:
d [C 2 H 6]
1 d [O 2]
dt
7 dt
1 d [O 2]
d [C 2 H 6]
7 dt
dt
d [O 2]
d [C 2 H 6]
7
dt
dt
d [O 2]
7(0.20moldm 3s 1 )
dt
d [O 2]
dt
1.40moldm 3s
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-131128092725-phpapp02/75/8-1-reaction-rate-12-2048.jpg)


![Differential Rate Equation Revision 4:
For the reaction choose the correct phrase:
R
P
(R-reagents, P-products)
The rate of a chemical reaction is the measure of the rate at which
P _________, which is equal to the rate at which the R _________.
The rate of the reaction is the change in concentration over the
change of time and has units of __________. For the reaction,
reactant R gives product P, the rate is ________ divided by Δ of
_________, where Δ means change.The rate is always___________.
Answers:
is formed
is consumed
mol L-1 s-1
-Δ *R]
time
positive.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-131128092725-phpapp02/75/8-1-reaction-rate-21-2048.jpg)