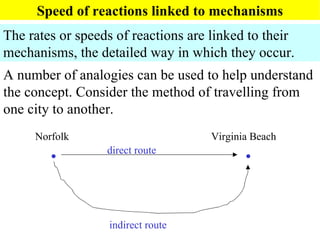
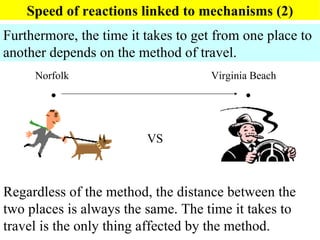
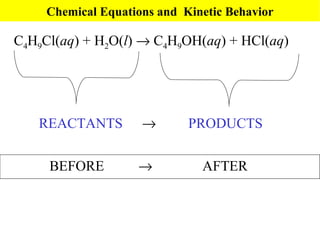
This document discusses kinetics and factors that affect reaction rates. It defines kinetics as how quickly reactions occur and the factors that influence reaction rates, such as temperature, concentration, and the presence of catalysts. Reaction rates are linked to reaction mechanisms - the step-by-step processes by which reactions take place. Increasing temperature leads to more collisions between reactant particles and faster reaction rates, as described by the Arrhenius equation. Catalysts lower the activation energy of reactions, speeding up reaction rates without being consumed.


![Calculation of Average Rate A B Rate of reaction based on: Rate of disappearance of reactant A or Rate of appearance of product B Use [ ] to designate concentration in moles per liter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-10-320.jpg)

![Exponents in Rate Laws and Reaction Orders Rate = k[reactant1] m [reactant2] n ... Exponents m and n are called reaction orders. Exponents can be 0, 1, 2 and (sometimes) fractions. Overall order is the sum of the exponents. What is overall order for above? third Rate = k[NO] 2 [Cl 2 ] First order with respect to Cl 2 Second order with respect to NO](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-15-320.jpg)
![Rate Laws versus Stoichiometry Additional examples of equations and rate laws 2N 2 O 5 ( g ) 4NO 2 ( g ) + O 2 ( g ) Rate = k[N 2 O 5 ] CHCl 3 ( g ) + Cl 2 ( g ) CCl 4 ( g ) + HCl( g ) Rate = k[CHCl 3 ][Cl 2 ] 1/2 H 2 ( g ) + I 2 ( g ) 2HI( g ) Rate = k[H 2 ][I 2 ] Note that the exponents in the rate law do not always match the coefficients in the balanced equation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-16-320.jpg)
![Units of the Rate Constant The units of the rate constant, k, depend upon the overall order of the reaction. All of the units for the factors on the left side of the rate equation need to cancel in such a way that you get molarity per time (e.g. M/s) as the final units. First order process: rate = k[A]; units of k = reciprocal time (s -1 , min -1 , etc.) Second order process: rate = k[A] 2 ; units of k = M -1 s -1 etc. Third order process: rate = k[A] 2 [B]; units of k = M -2 s -1 etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-17-320.jpg)
![Determination of a Rate Law/Constant Using Initial Rates Holding [CH 3 CO 2 CH 3 ] constant while doubling [OH - ], leads to a doubling of the reaction rate. Rate is directly proportional to [OH - ]. Holding [OH - ] constant while doubling [CH 3 CO 2 CH 3 ], leads to a doubling of the reaction rate. Rate is directly proportional to [CH 3 CO 2 CH 3 ] Rate = k[CH 3 CO 2 CH 3 ][OH - ] CH 3 CO 2 CH 3 + OH - products](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-18-320.jpg)
![Determination of a Rate Law/Constant Using Initial Rates Holding [Cl 2 ] constant while doubling [NO], leads to a quadroupling of the reaction rate. Rate is directly proportional to the square of [NO] Holding [NO] constant while doubling [Cl 2 ], leads to a doubling of the reaction rate. Rate is directly proportional to [Cl 2 ] Rate = k[NO] 2 [Cl 2 ] 2NO( g ) + Cl 2 ( g ) 2NOCl(g)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-19-320.jpg)



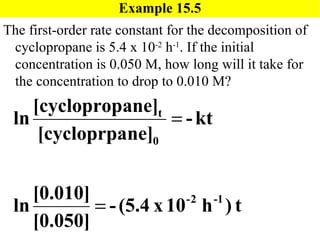

![Exercise 15.5 [Here is a problem similar to 15.5] The first-order rate constant for the decomposition of N 2 O 5 , N 2 O 5 ( g ) 2NO 2 ( g ) + O 2 ( g ) , at 472 C is 6.82 x 10 -3 s -1 . If the initial concentration of N 2 O 5 is 0.0125 M, what is the concentration after 150 seconds? Will use: ln[N 2 O 5 ] t = -kt + ln[N 2 O 5 ] 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-27-320.jpg)
![Exercise 15.5 (cont) [N 2 O 5 ] 150 = e -5.405 = 4.49 x 10 -3 M ln[N 2 O 5 ] 150 = -(6.82 x 10 -3 s -1 )(150 s) + ln(0.0125) = -1.023 + (-4.382) = -5.405 Exercise 15.5 : [sucrose] after 1 hr = 0.0035 M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-28-320.jpg)
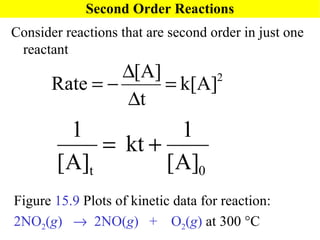
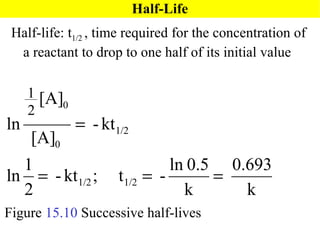
![15.5 Particulate View of Reaction Rates Collision Model: based on the kinetic-molecular theory and accounts for both concentration and temperature effects on rates 1) molecules must collide to react 3) molecules must collide with the appropriate orientation 2) molecules must collide with sufficient energy to react Figure 15.11 NO( g ) + O 3 (g) NO 2 ( g ) + O 2 ( g ) , Rate = k[NO][O 3 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-31-320.jpg)

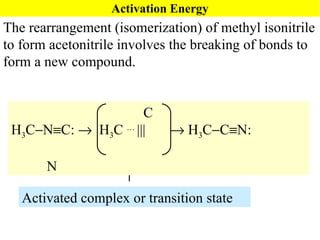
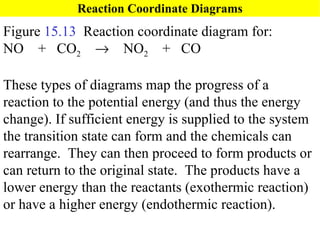
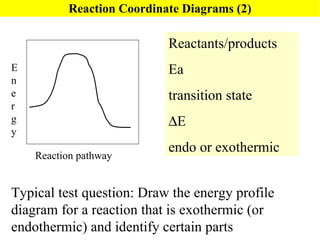


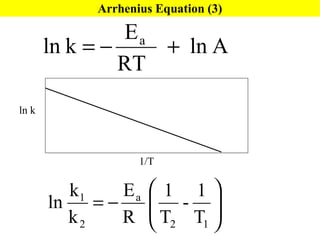

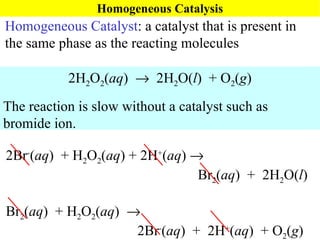

![Rate Equations for Elementary Steps Rate laws are linked to molecularity; If we know a reaction is an elementary step, then we know rate law. A products based on collision theory and statistics: Rate = k[A] A + B products Rate = k[A][B] Table Elementary steps and their rate laws](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-45-320.jpg)
![Example 15.12 If the following reaction occurs in a single elementary step, predict the rate law: H 2 ( g ) + Br 2 ( g ) 2HBr( g ) Rate = k[H 2 ][Br 2 ] Actual (or Experimental) Rate Law: Rate = k[H 2 ][Br 2 ] 1/2 Conclusion? Example 15.12 The self oxidation of ClO to give ClO 3 and Cl ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-46-320.jpg)
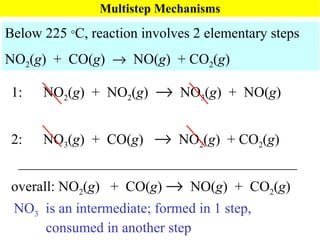
![Rate Laws for Multistep Mechanisms Below 225 C, reaction involves 2 elementary steps Experimental rate law: Rate = k[NO 2 ] 2 Based on molecularity: Rate = k 1 [NO 2 ] 2 1: NO 2 ( g ) + NO 2 ( g ) NO 3 ( g ) + NO( g ) (slow) 2: NO 3 ( g ) + CO( g ) NO 2 ( g ) + CO 2 ( g ) (fast) _______________________________________ overall: NO 2 ( g ) + CO( g ) NO( g ) + CO 2 ( g ) k 1 k 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-47-320.jpg)
![Mechanisms with an Initial Fast Step 2 NO(g) + Br 2 (g) 2NOBr(g) Experimental rate law: Rate = k[NO] 2 [Br 2 ] Rule out termolecular process. Why? k 1 1: NO(g) + Br 2 (g) NOBr 2 (g) (fast) k 2 2: NOBr 2 (g) + NO(g) 2NOBr(g) (slow)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-48-320.jpg)
![Mechanisms with an Initial Fast Step (2) Rate = k 2 [NOBr 2 ][NO] ( based on step 2 ) step 1: NO(g) + Br 2 (g) NOBr 2 (g) reverse rxn: NOBr 2 (g) NO(g) + Br 2 (g) k 1 NO(g) + Br 2 (g) NOBr 2 (g) k -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-49-320.jpg)
![Mechanisms with an Initial Fast Step (2) Equilibrium: rate of forward rxn = rate of reverse rxn k 1 [NO] [Br 2 ] = k -1 [NOBr 2 ] [NOBr 2 ] = (k 1/ k -1 )[NO] [Br 2 ] Rate = k 2 [NOBr 2 ][NO] Rate = k 2 (k 1/ k -1 )[NO] [Br 2 ] [NO] = k[NO] 2 [Br 2 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15web-091110165051-phpapp02/85/Ch-15-Web-50-320.jpg)