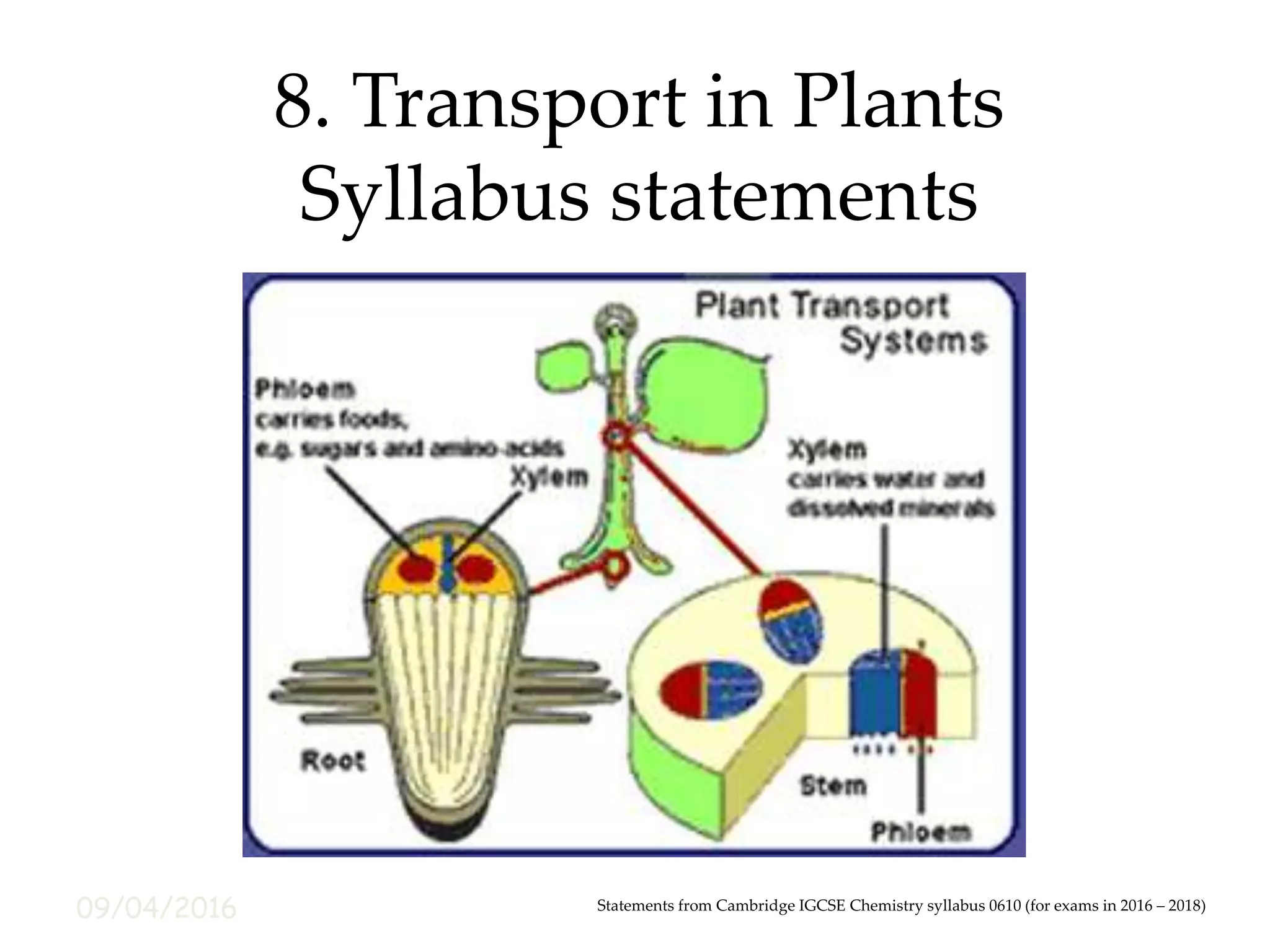
This document outlines the key concepts around transport in plants that are covered in the Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry syllabus. It discusses the functions of xylem and phloem, the pathway of water uptake through root hair cells, root cortex cells, and xylem, and how transpiration is the loss of water vapor from leaves through evaporation and diffusion through stomata. It also covers the mechanism of transpiration pull that moves water upward through the xylem, how wilting occurs, and how temperature and humidity affect transpiration rate. Finally, it defines translocation as the movement of sucrose and amino acids from regions of production to regions of storage or use through the phloem.