Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times
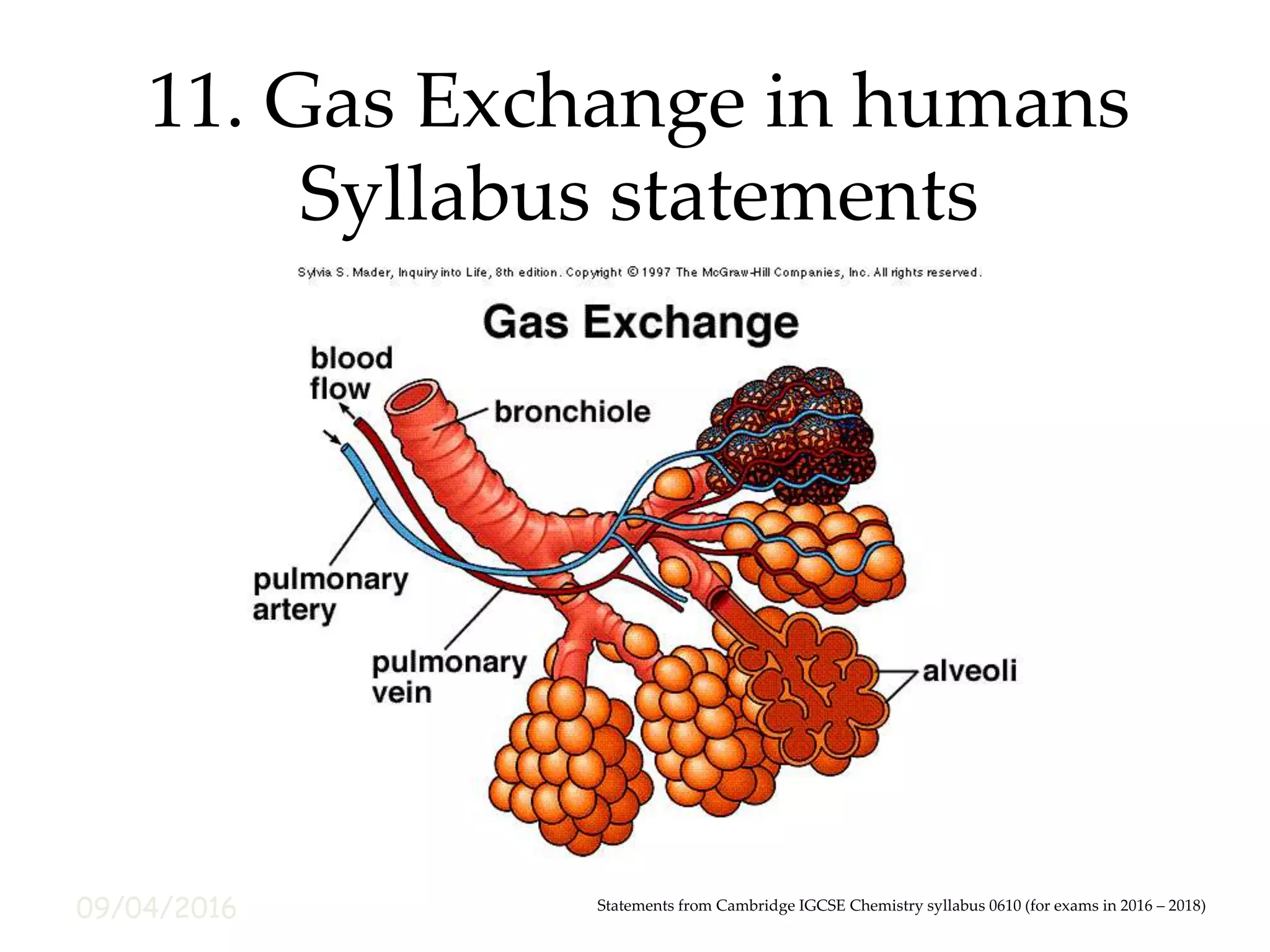



The document summarizes key concepts about gas exchange in humans. It lists the major features of the lungs that enable efficient gas exchange, including large surface area, thin membranes, good blood supply, and effective ventilation. It also names and identifies the major structures involved in breathing, such as the lungs, diaphragm, ribs, and airways. Finally, it outlines several experiments that can be done to investigate the differences in gas composition between inhaled and exhaled air and the effects of physical activity on breathing rate and depth.



