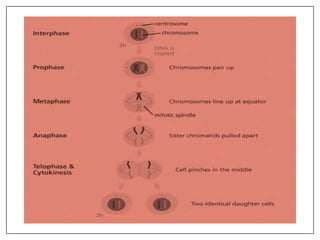
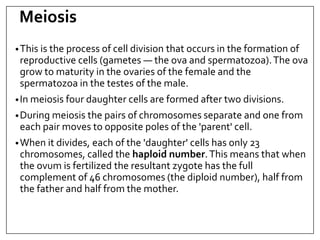
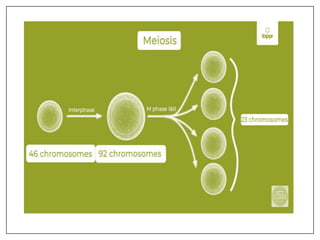
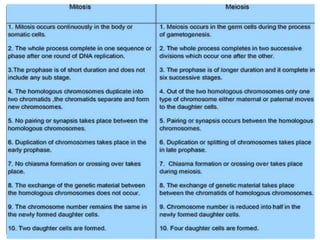
This document provides an overview of cell division, including the two main types - somatic cell division and reproductive cell division. Somatic cell division, via mitosis, produces two identical cells to replace dead or damaged cells. Reproductive cell division, via meiosis, produces gametes and reduces the chromosome number by half. Mitosis and meiosis are then described in more detail, outlining their key phases and processes. The role of cell division in development and growth is also mentioned.