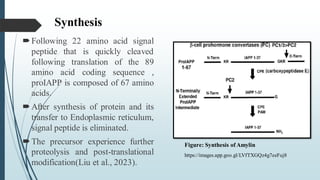
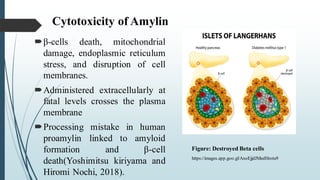
The document discusses the role and significance of amylin, a peptide hormone that regulates glucose metabolism and has implications for obesity and diabetes. It details the synthesis, cytotoxic effects, and its potential link to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's. Additionally, it highlights the pharmacological use of amylin analogs in diabetes management and their side effects based on clinical cases.