Embed presentation


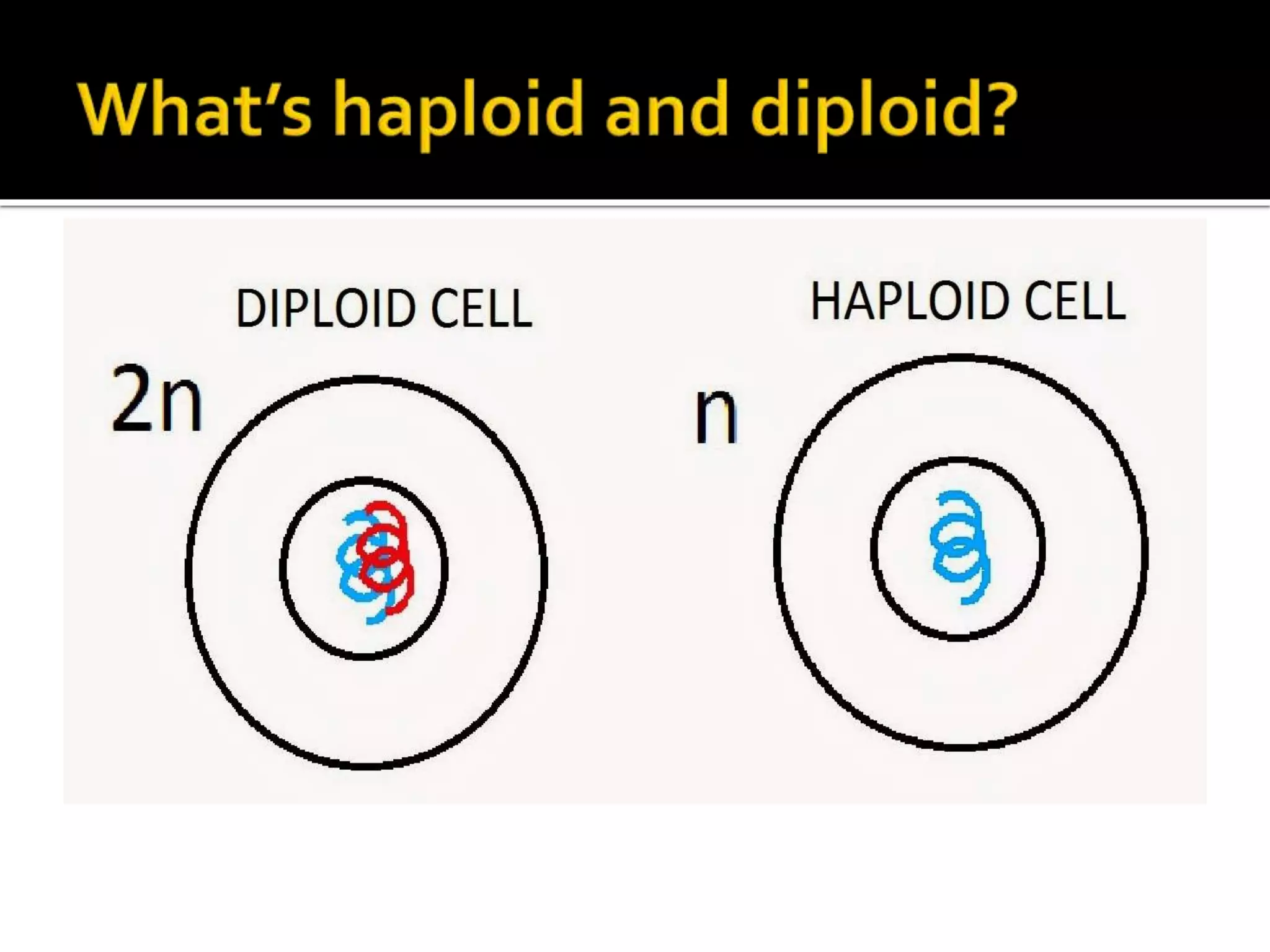








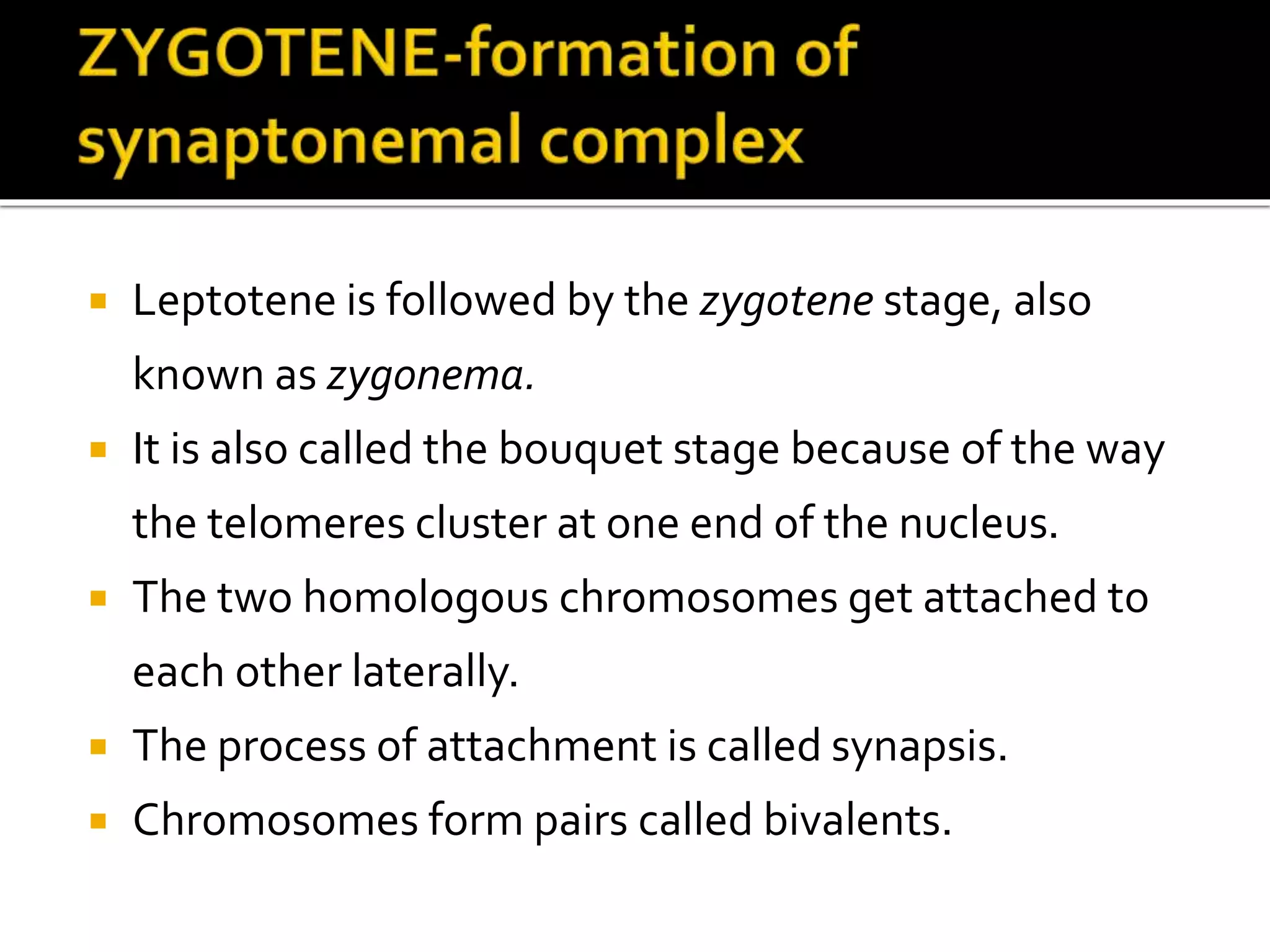


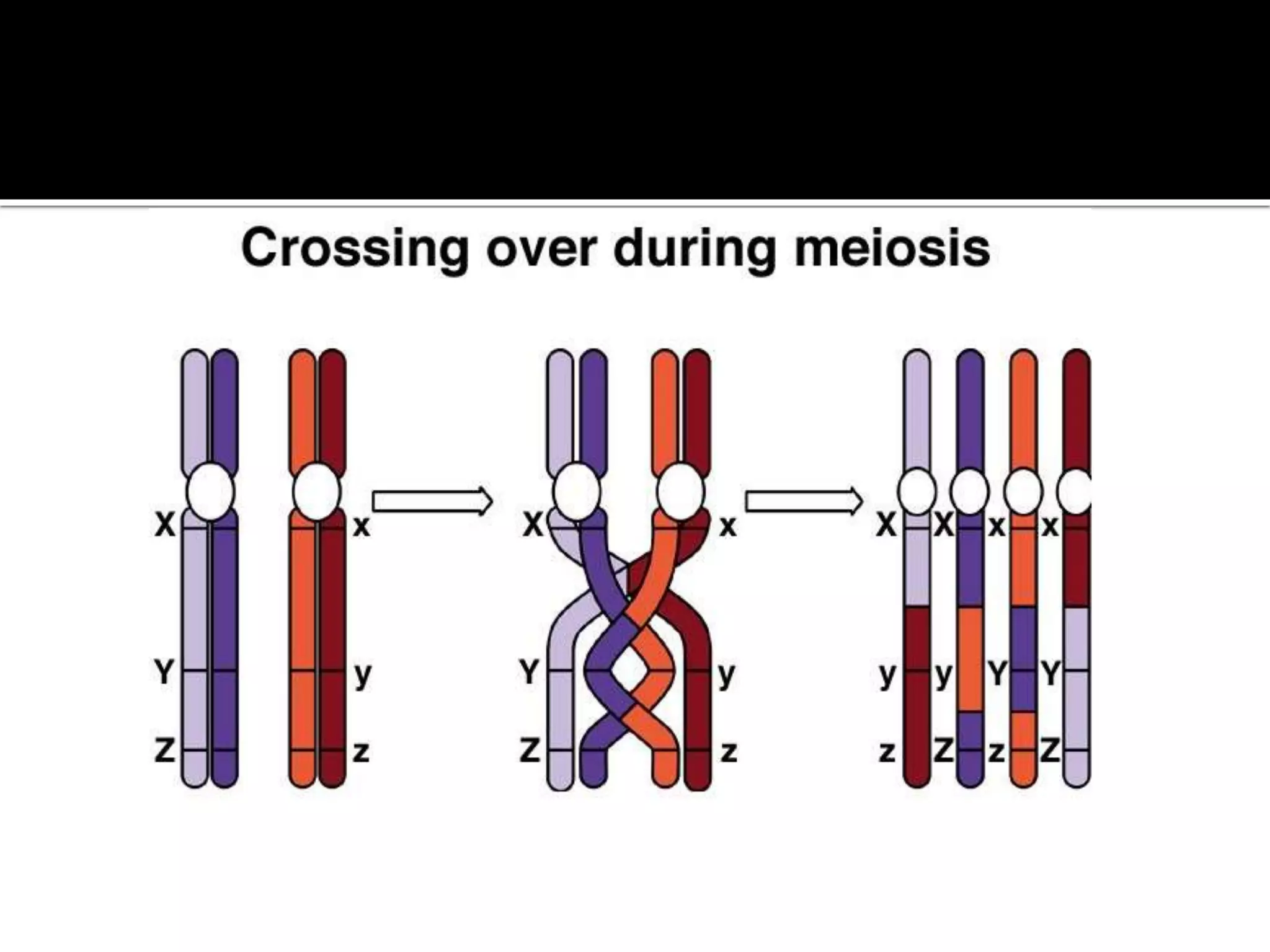
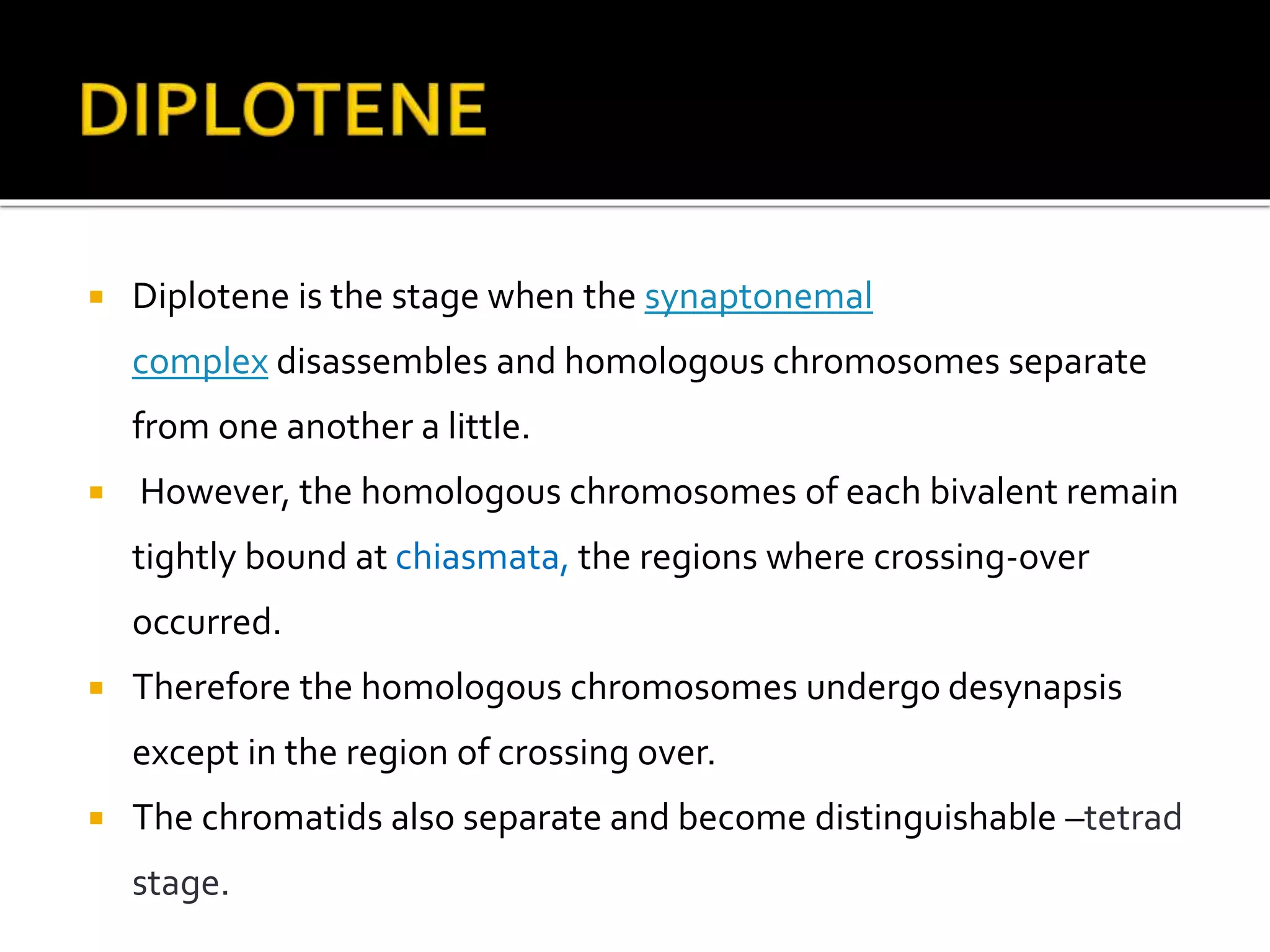
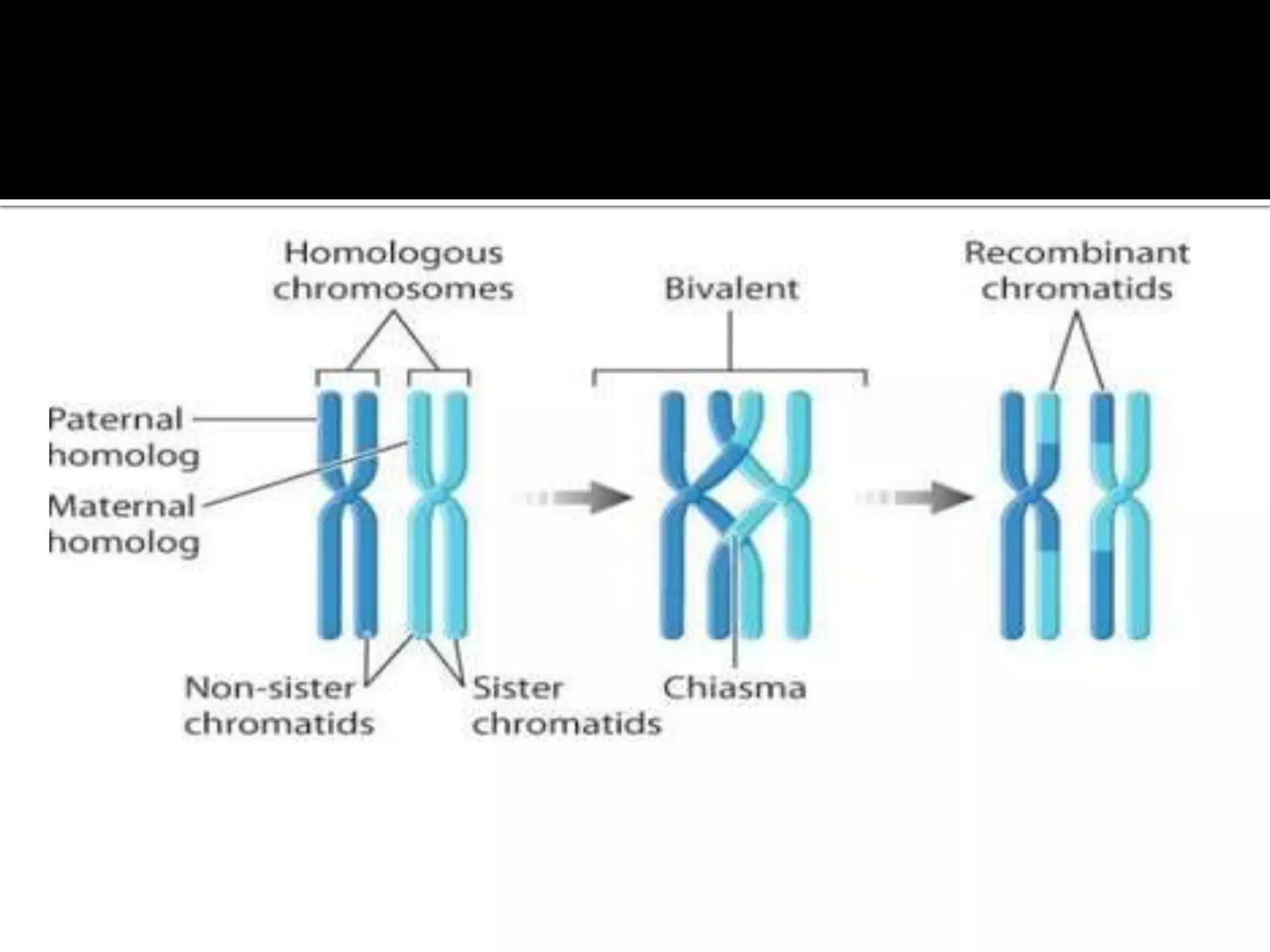



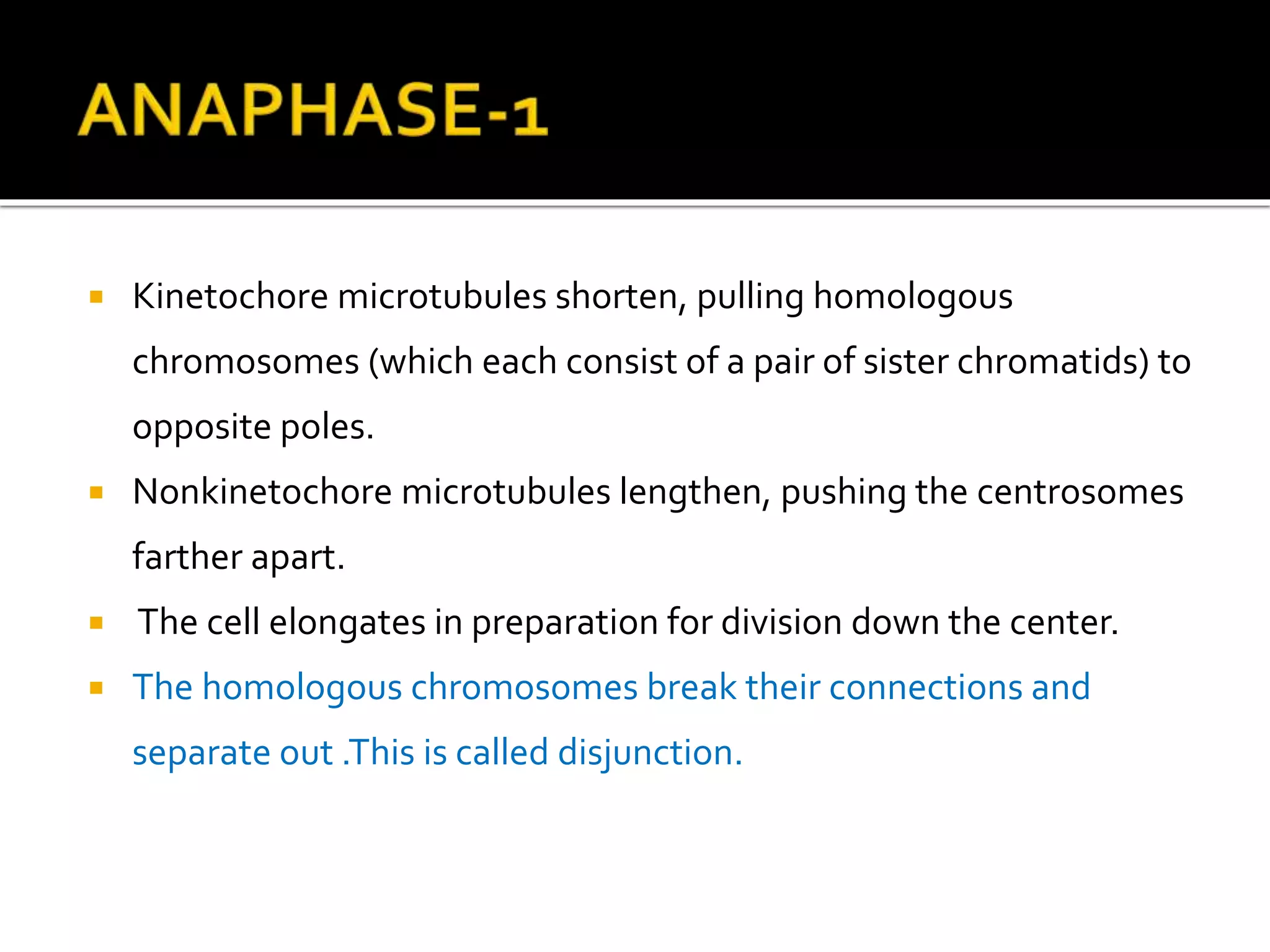
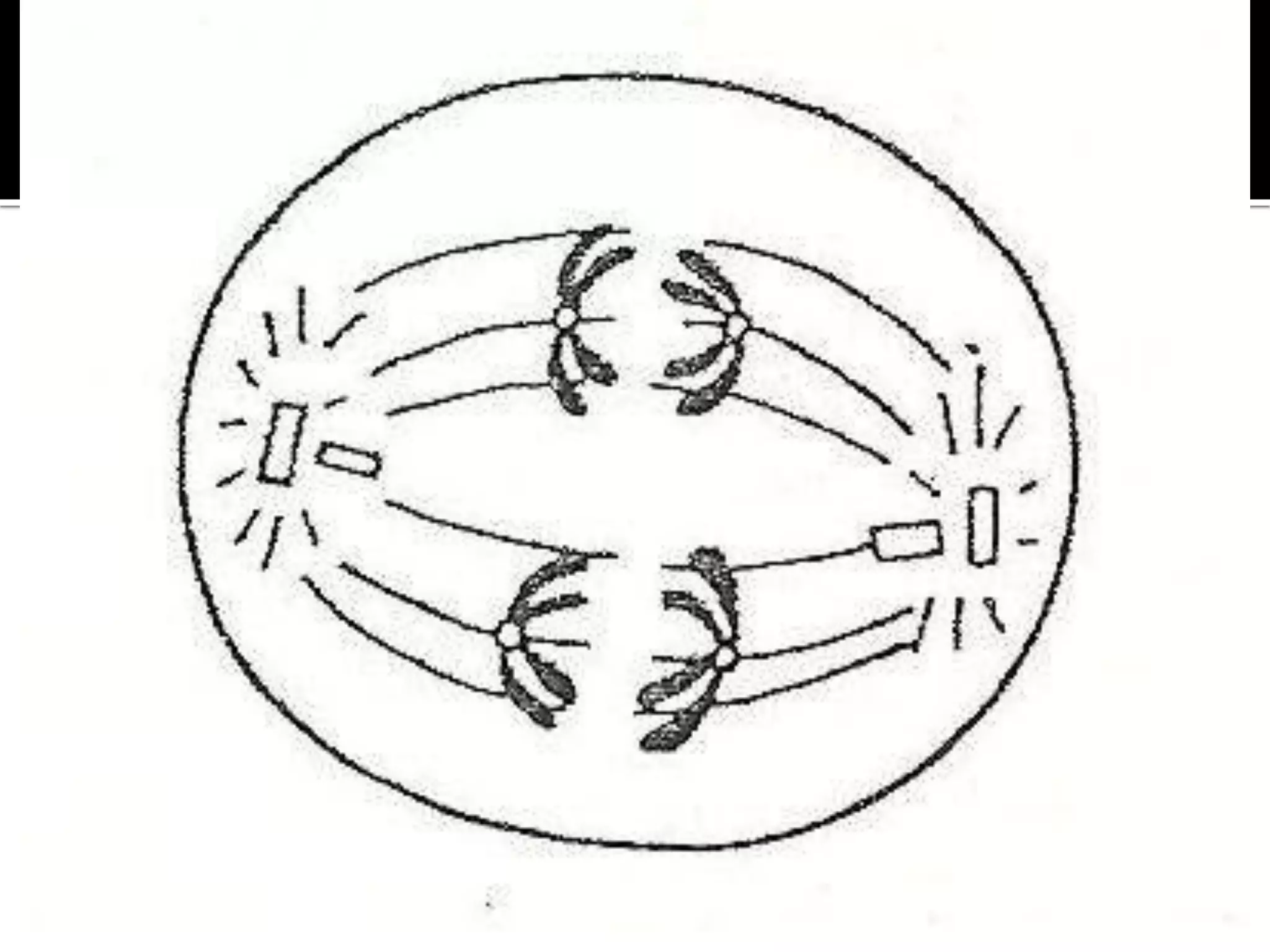

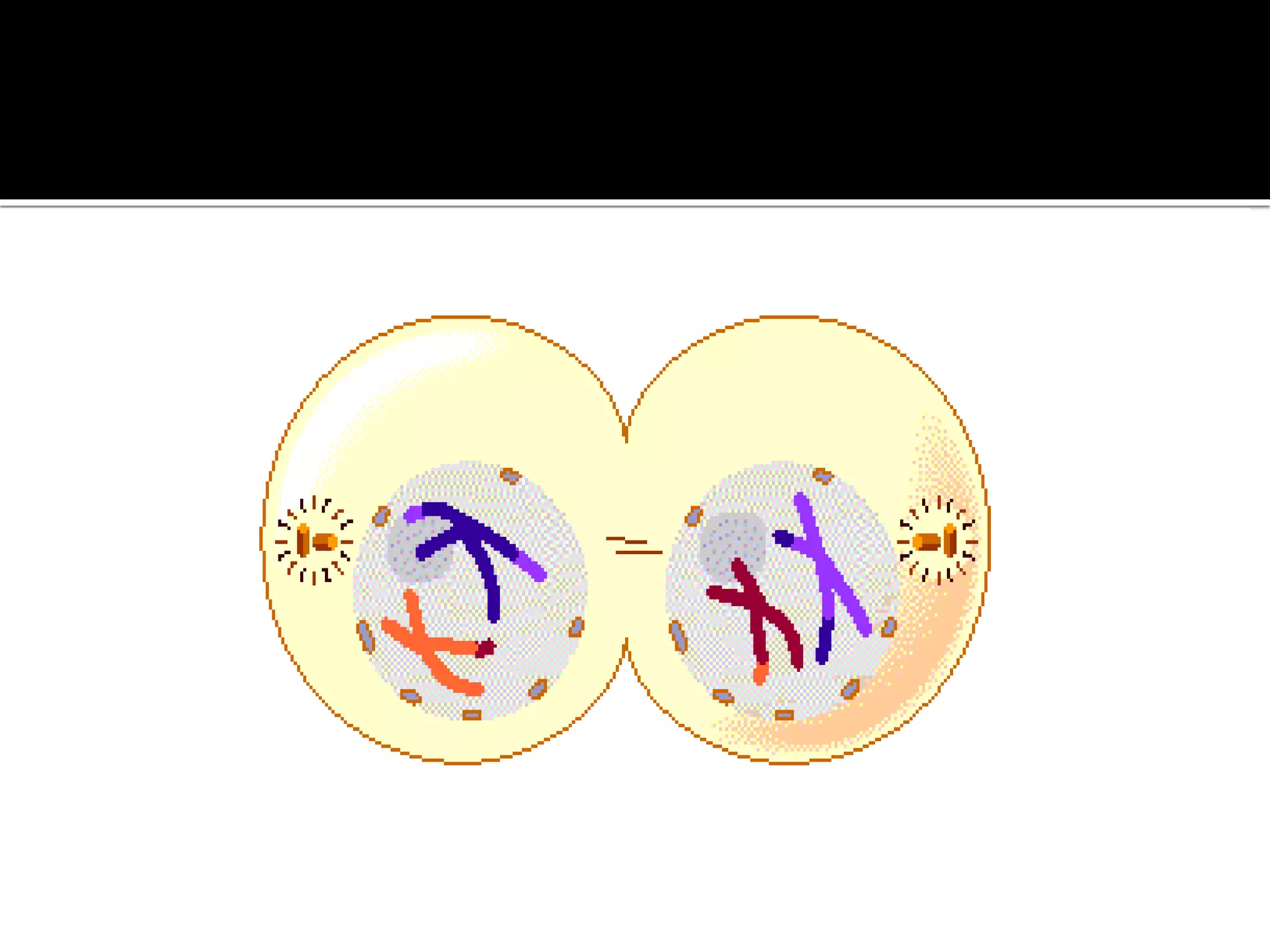


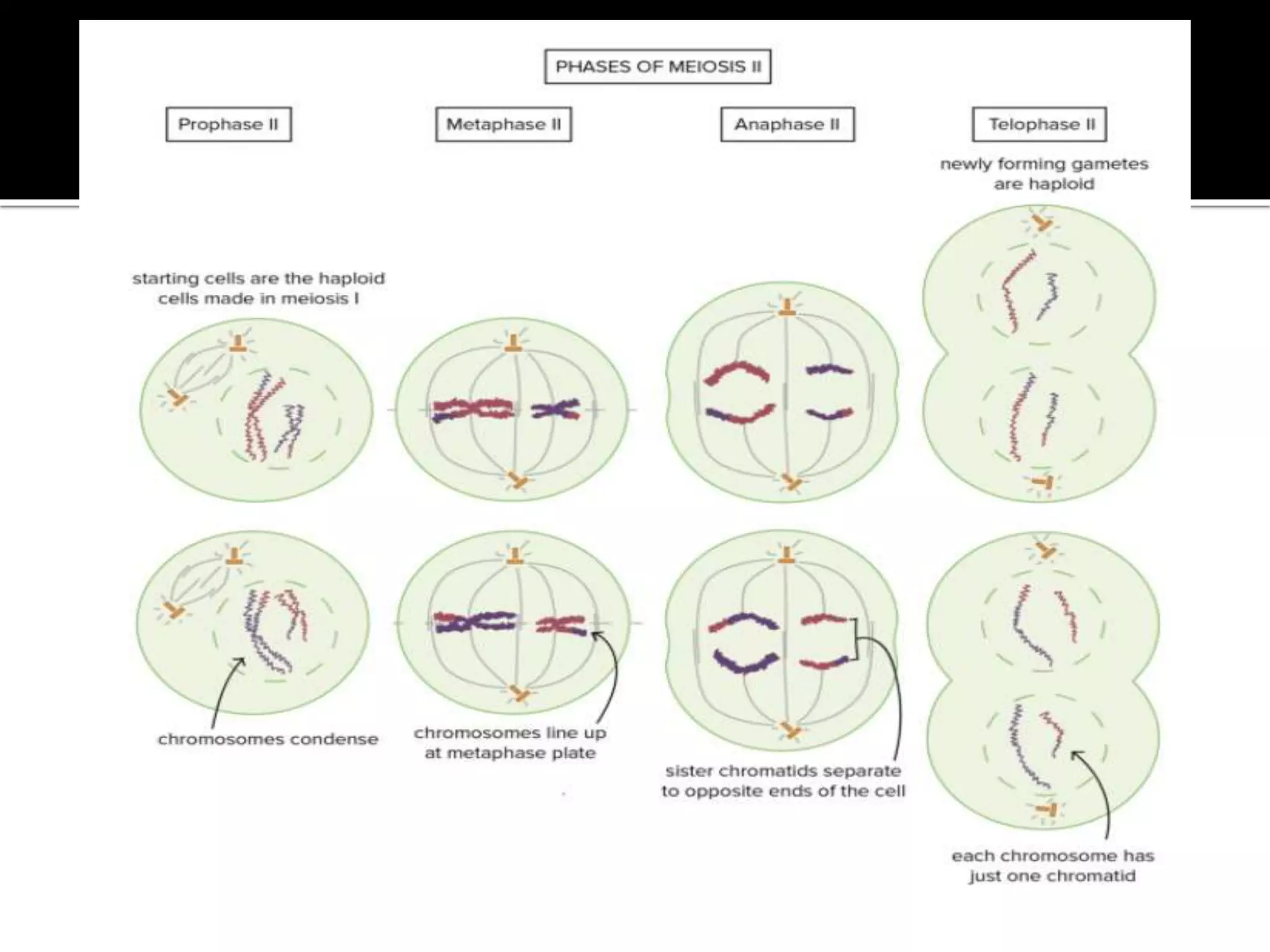



Meiosis is a type of cell division in diploid cells that produces four haploid gametes, crucial for sexual reproduction, where each gamete contains half the chromosomes of the parent cell. The process involves two rounds of division (meiosis I and meiosis II), which include stages such as prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, with crossing over occurring to create genetic diversity. Unlike mitosis, which creates identical daughter cells, meiosis results in genetically diverse cells with unique combinations of chromosomes due to the homologous recombination.





























