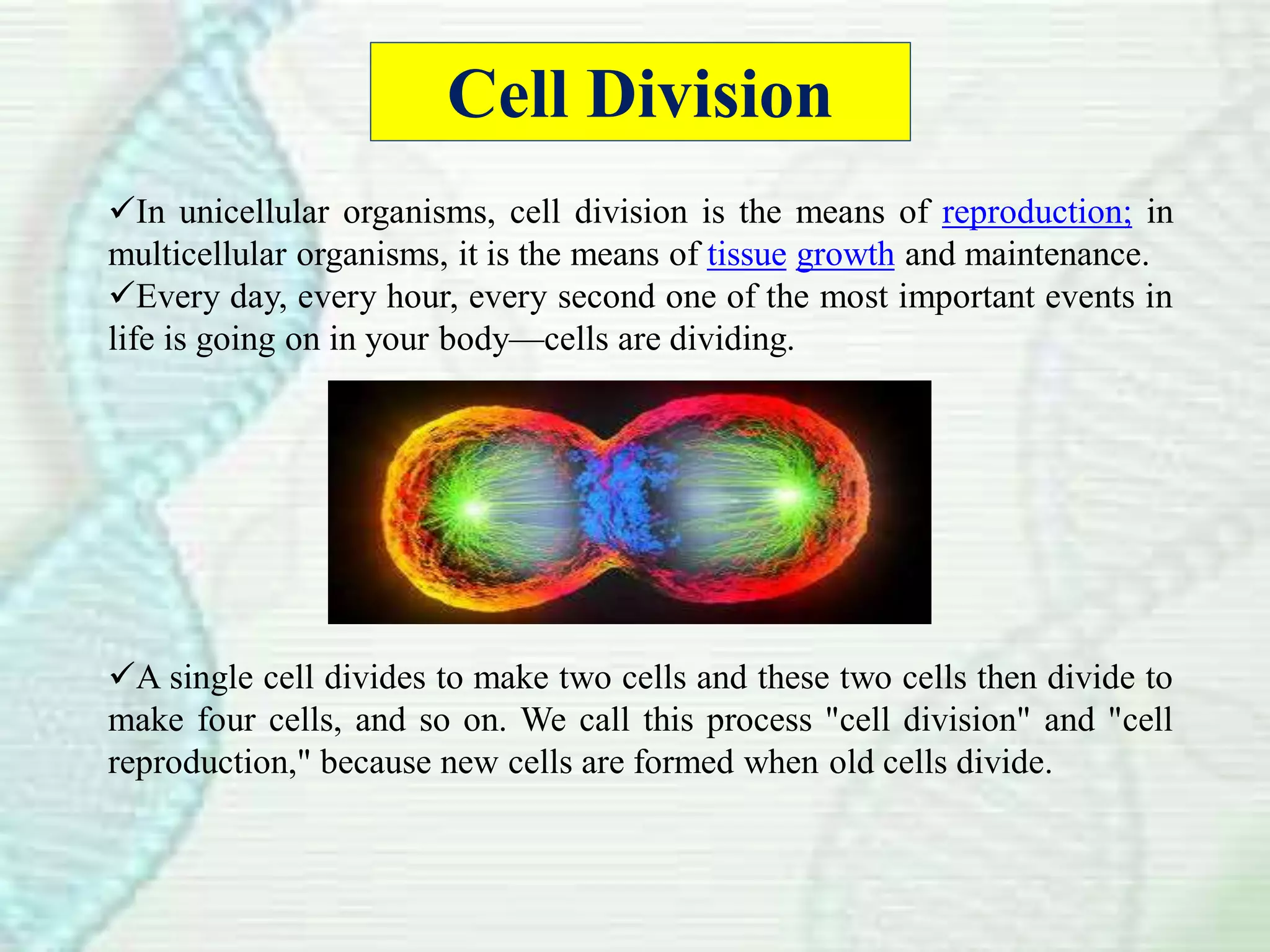
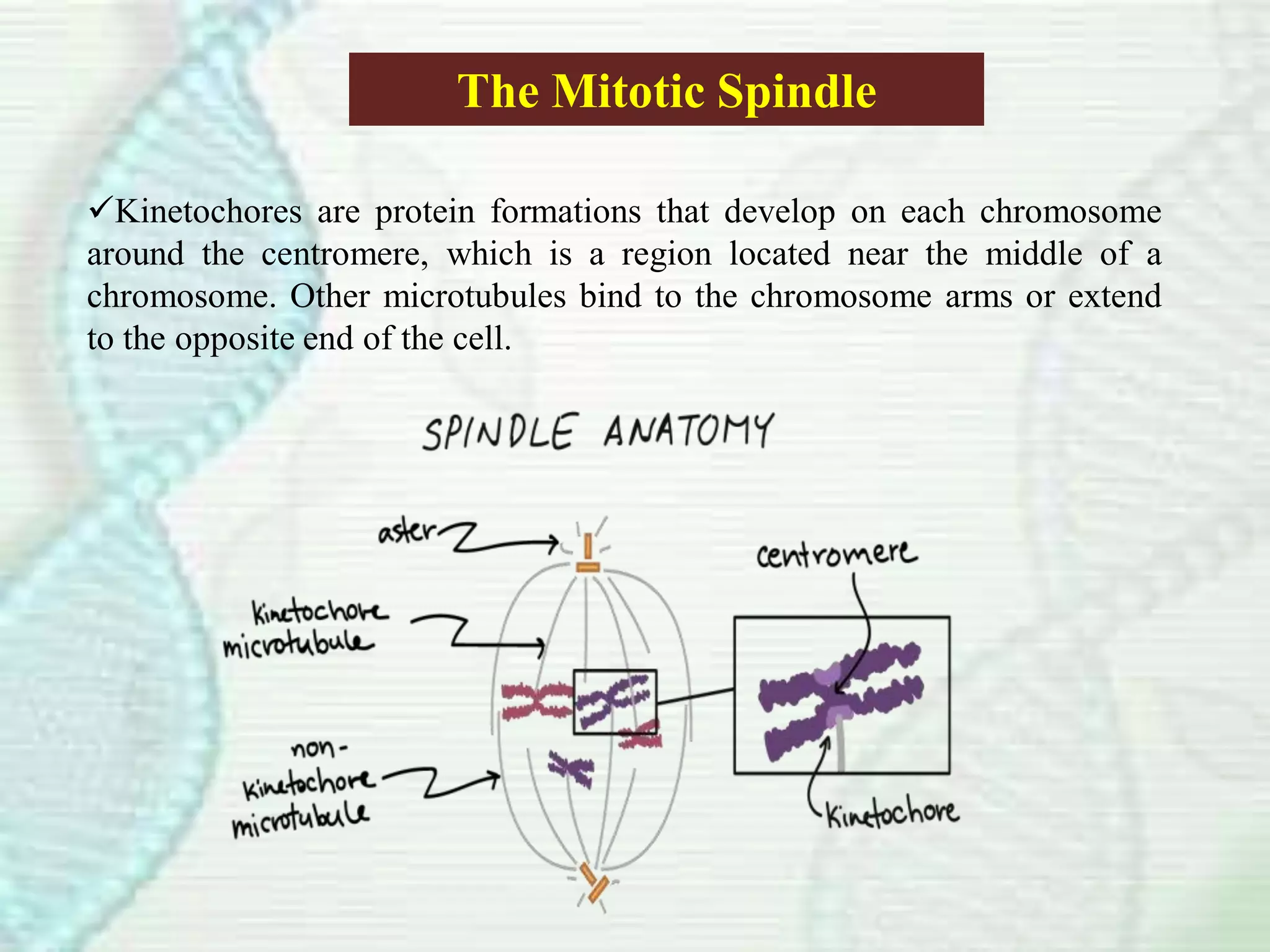
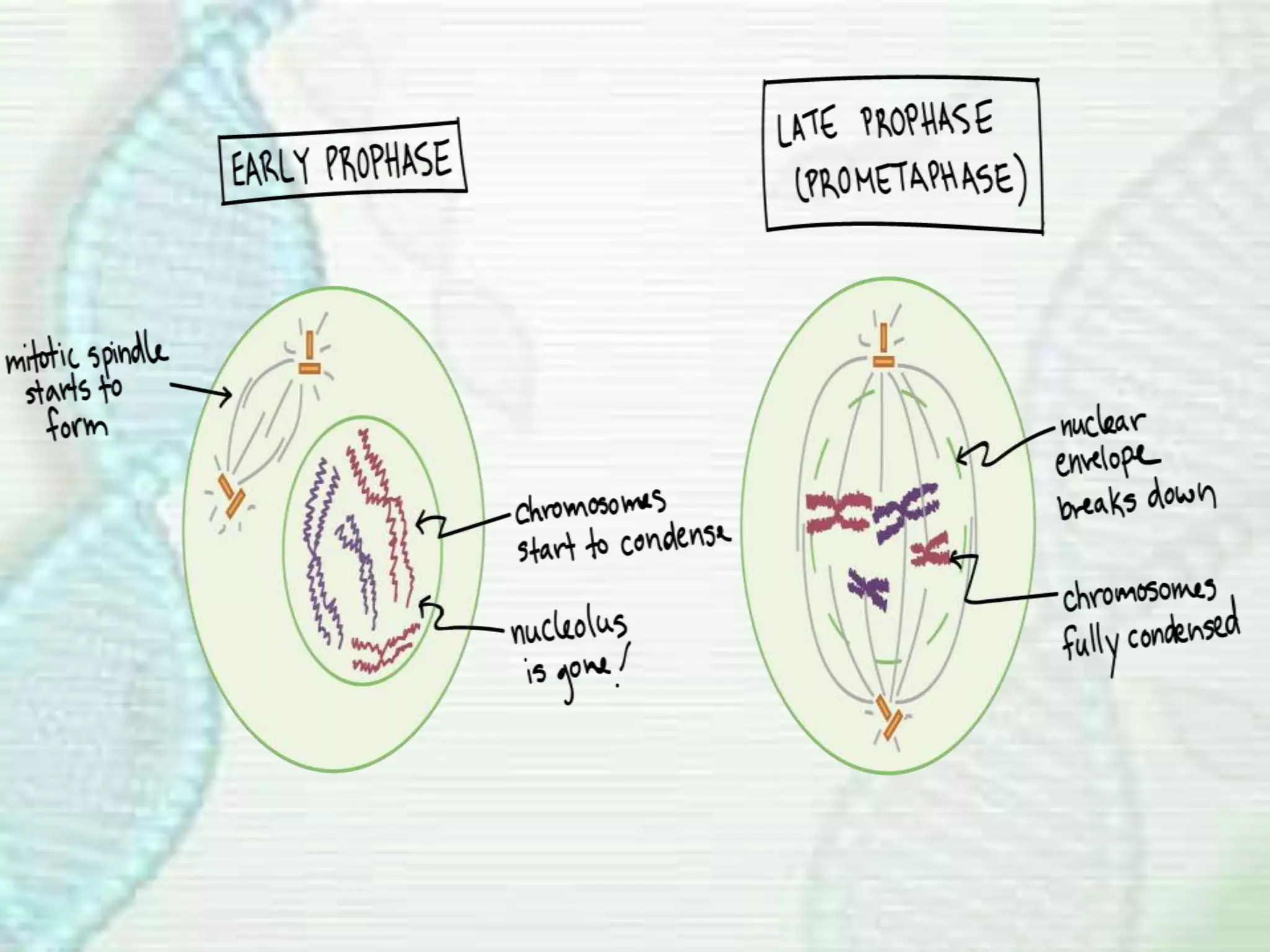
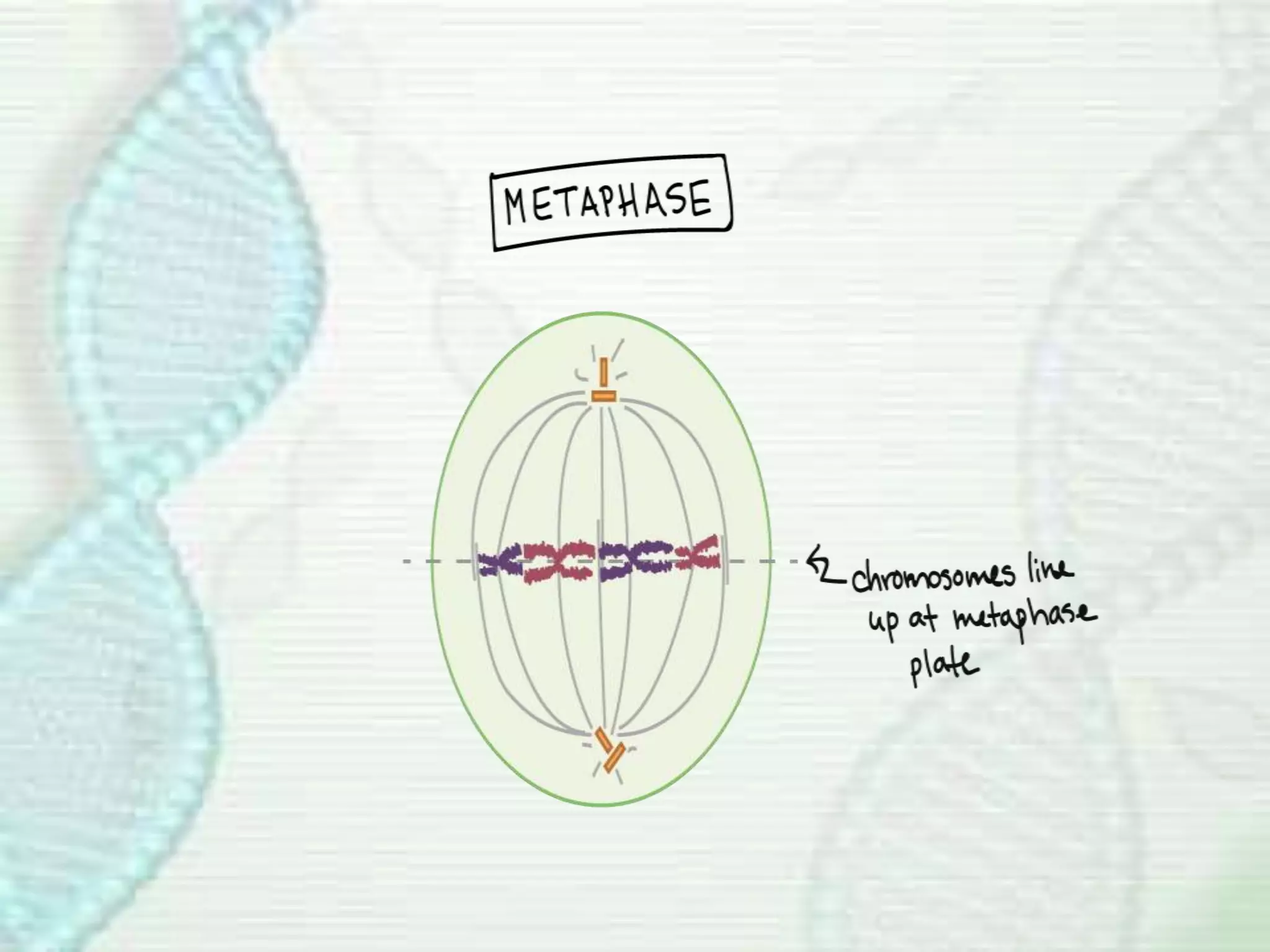
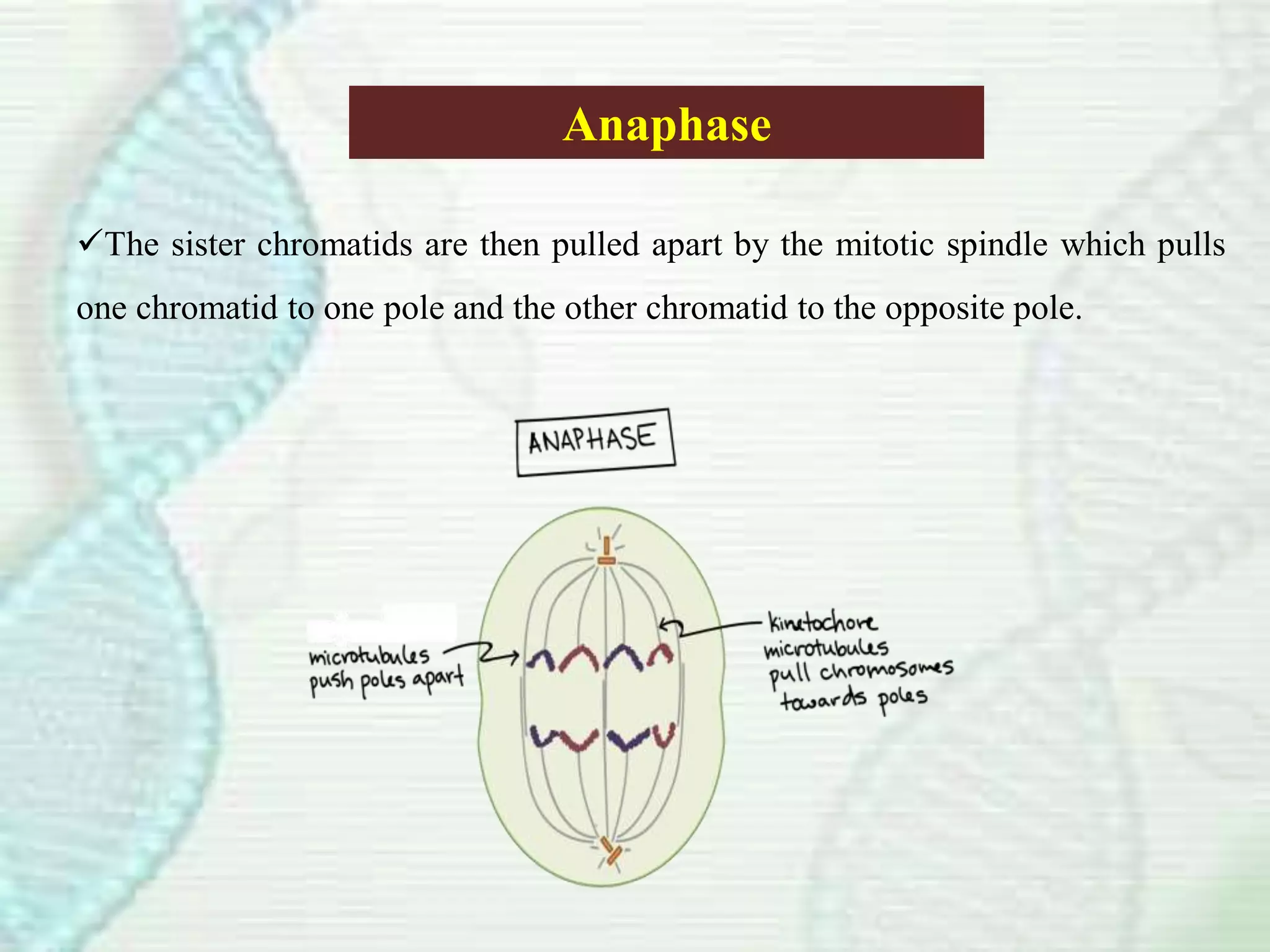
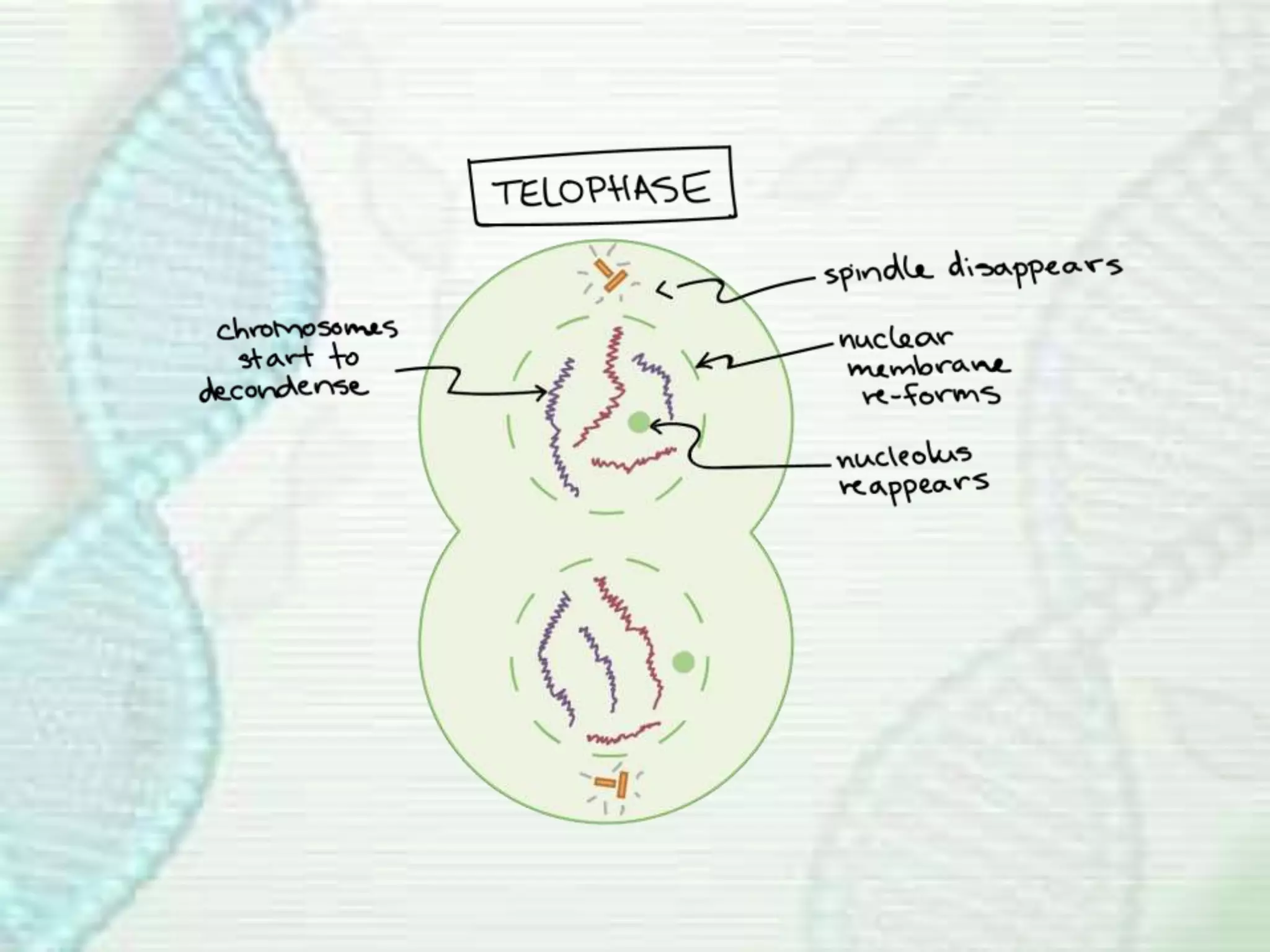
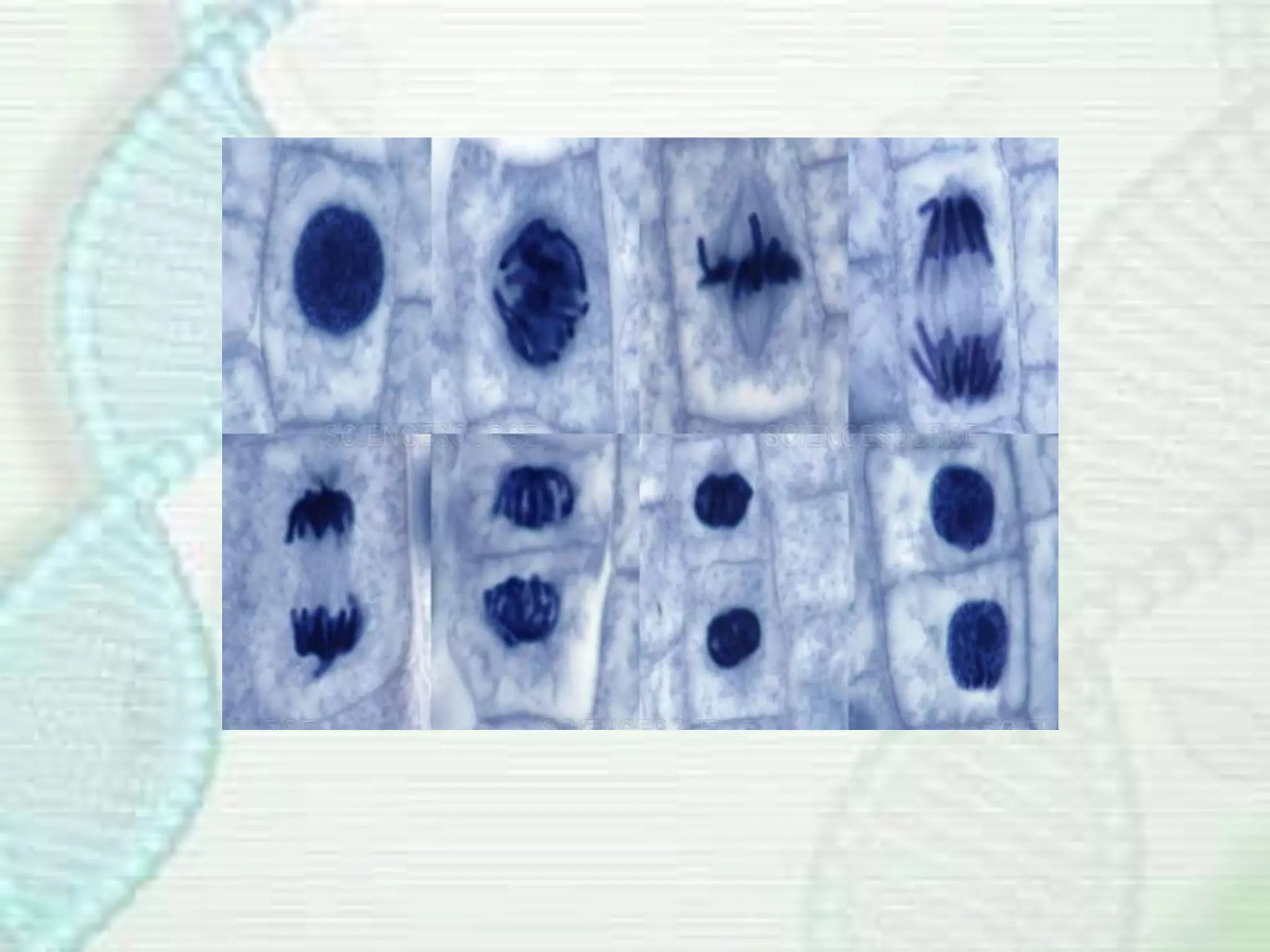
Cell division occurs through mitosis, which produces two identical daughter cells from one parent cell. Mitosis involves several phases - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromosomes condense and the mitotic spindle forms. In metaphase, the chromosomes line up along the center of the cell. Anaphase involves the sister chromatids being pulled apart by the mitotic spindle to opposite poles. Finally, in telophase, a membrane forms around each set of chromosomes, dividing the cell into two identical daughter cells each with their own nucleus.