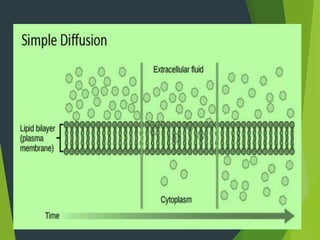
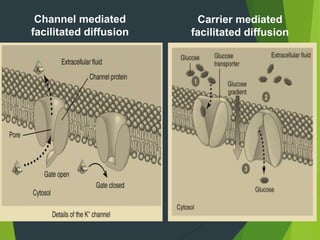
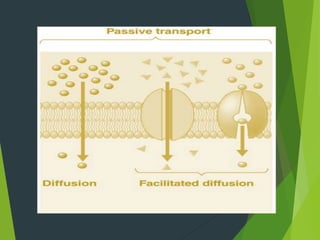
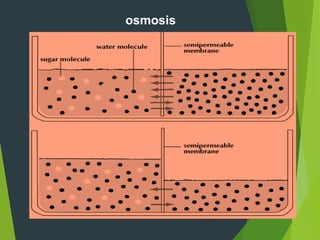
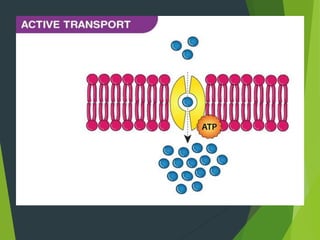
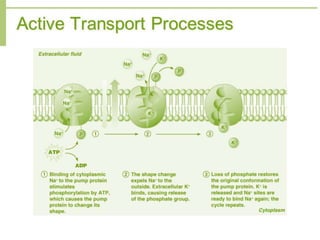
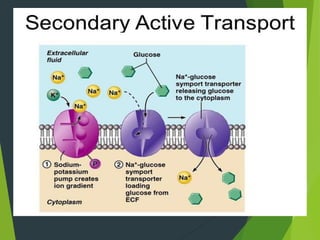
This document discusses transport processes across cell membranes, including passive and active transport. Passive transport includes simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis, and moves substances down concentration gradients without energy input. Active transport moves substances against concentration gradients and requires energy, primarily from ATP. There are two types of active transport: primary active transport uses ATP directly, while secondary active transport couples to the flow of ions down their gradients. Examples like sodium-potassium pumps are given to illustrate these transport concepts.