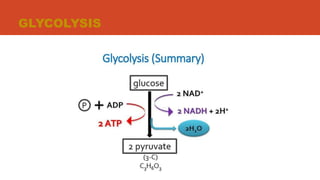
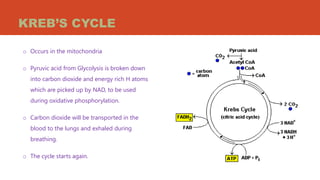
Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms produce energy through the breakdown of glucose and oxygen. It takes place in the mitochondria of cells. The three main stages are glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis breaks down glucose, the Krebs cycle further breaks down these products, and oxidative phosphorylation uses the energy from these processes to produce ATP through electron transport chains. Cellular respiration requires oxygen and glucose and produces carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of ATP. It is essential for energy production in all living organisms.