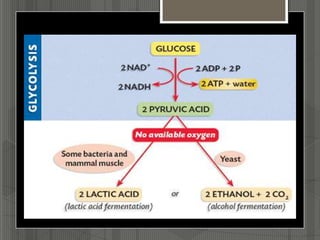
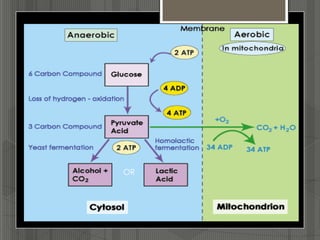
This document summarizes anaerobic respiration. It begins by explaining cellular respiration and how cells break down food to produce ATP energy. It then describes glycolysis, which breaks down glucose to pyruvate. When oxygen is limited, anaerobic respiration occurs through fermentation instead of aerobic respiration. Two types of fermentation are lactic acid fermentation, where pyruvate is converted to lactate, and ethanol fermentation, where pyruvate is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide. The document also notes that humans undergo anaerobic respiration in muscles during intense exercise when oxygen demands outpace supply.