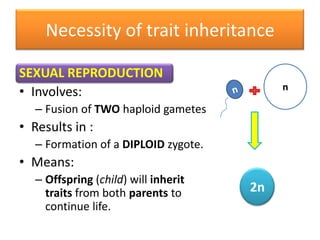
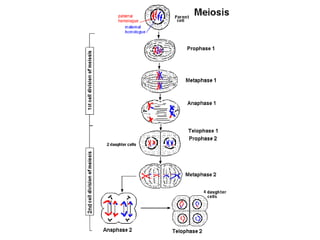
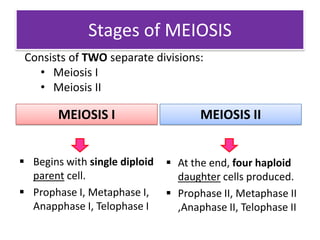
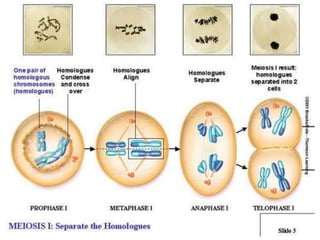
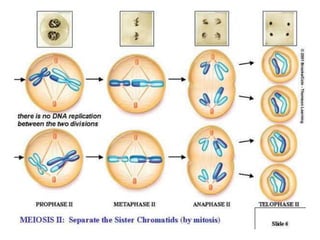
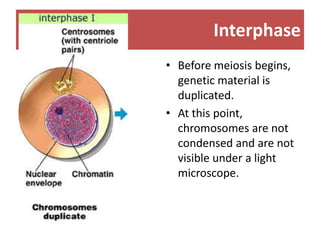
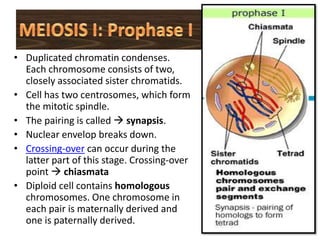
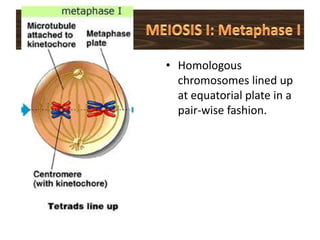
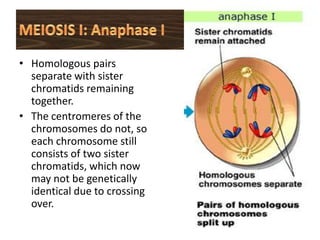
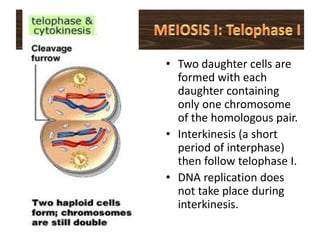
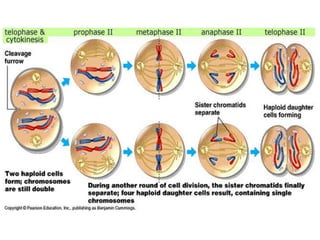
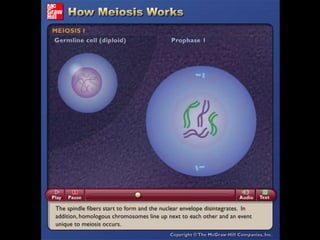
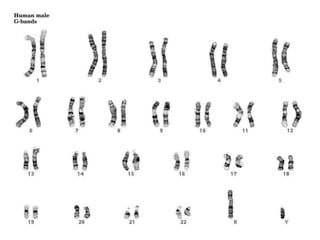
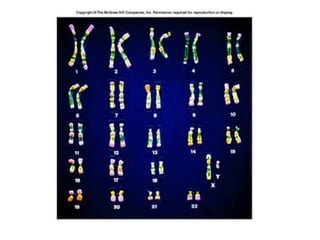
Meiosis is the process of cell division that produces gametes with half the normal number of chromosomes. It involves two rounds of division (Meiosis I and Meiosis II) starting with one diploid cell and resulting in four haploid cells. This ensures offspring inherit a mix of traits from both parents and allows for genetic variation between offspring. Meiosis occurs in the testes and ovaries, where homologous chromosomes separate in Meiosis I and sister chromatids separate in Meiosis II.


![What is meiosis?The process of nuclear division that reduces the number of chromosomes in new cells to half the number of chromosomes in parent cell. 2n (diploid) [parent cell] n (diploid) [new cell]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5-2-110516062455-phpapp02/85/5-2-5-320.jpg)