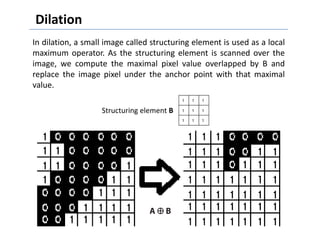
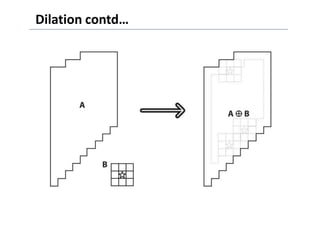
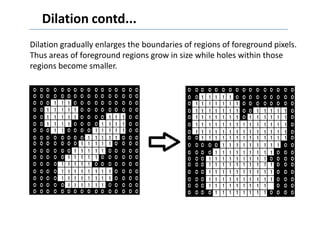
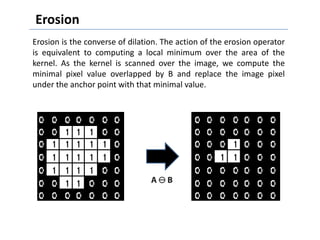
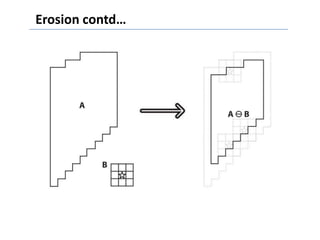
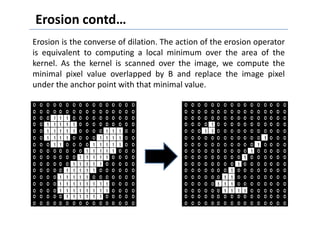
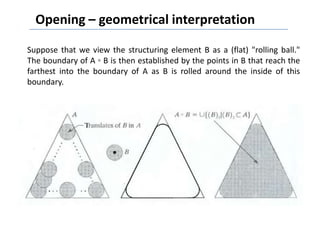
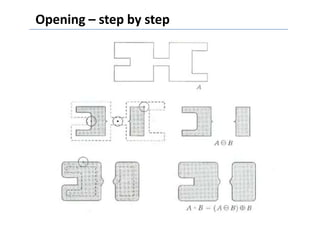
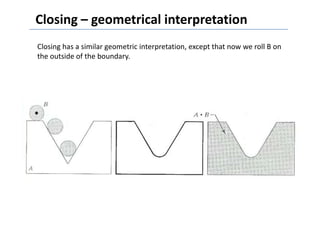
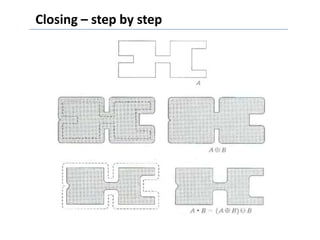
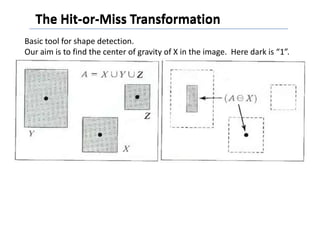
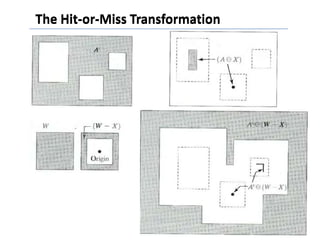
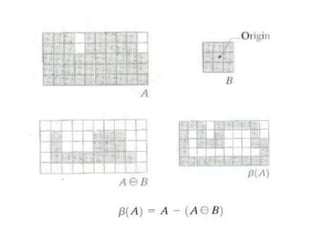
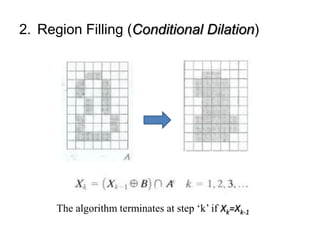
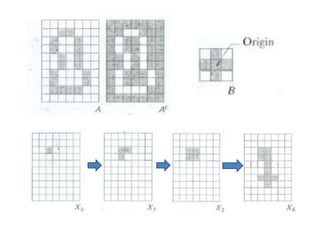
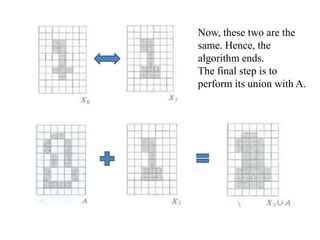
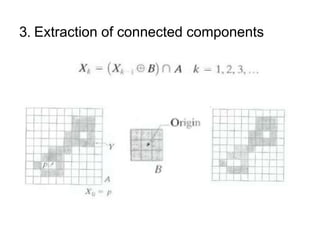
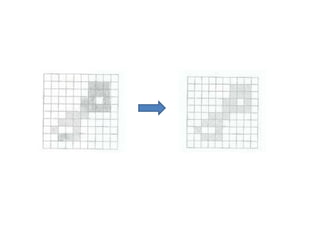
This document discusses morphological image processing techniques. It begins by explaining that morphology uses mathematical morphology operations to extract image components and describe shapes. It then outlines common morphological algorithms like dilation, erosion, opening, closing, and hit-or-miss transformations. Dilation enlarges object boundaries while erosion shrinks them. Opening can smooth contours and closing can fuse breaks or fill gaps. These operations use a structuring element to transform images. The document provides examples of using morphological filters and algorithms for tasks like noise removal, region filling, and connected component extraction.