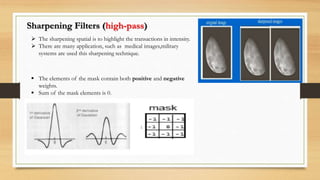
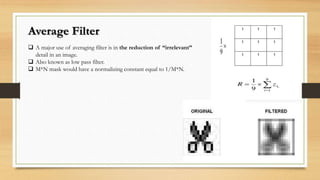
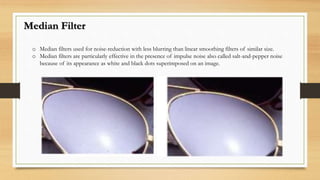
This document discusses different types of spatial filters that can be applied to images, including low-pass, high-pass, average, and median filters. Spatial filters work by applying a filter mask over an image and calculating new pixel values based on the neighborhood defined by the mask. Low-pass filters preserve low frequencies and are used for smoothing and blurring to reduce noise or small details. High-pass filters preserve high frequencies and are used to highlight edges and detail. Average filters reduce irrelevant detail through normalization, while median filters are effective for reducing salt-and-pepper noise with less blurring than linear filters.